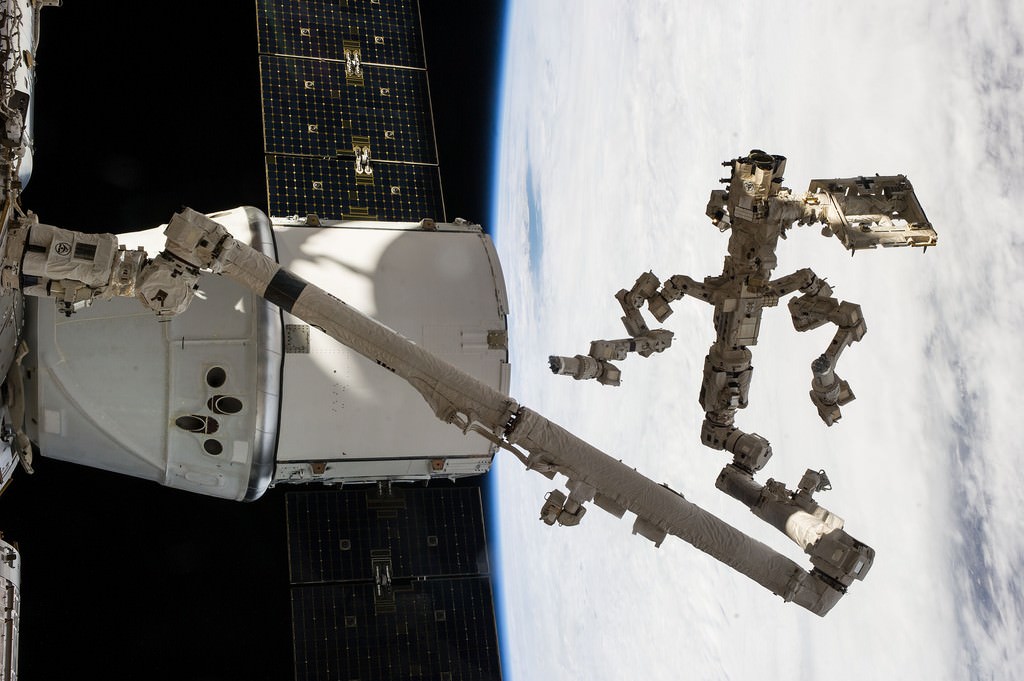
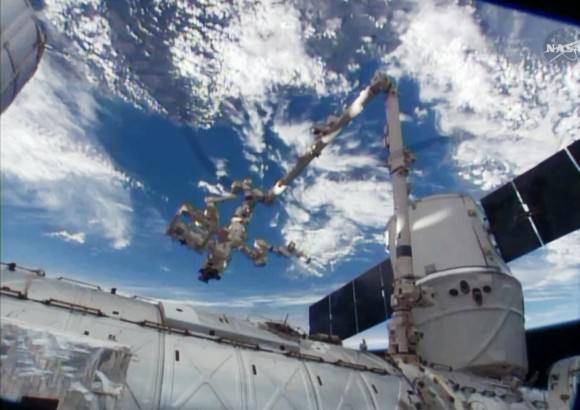
SpaceX-3 Dragon commercial cargo freighter was detached from the ISS at 8 AM EDT on May 18, 2014 and released by station crew at 9:26 AM for splashdown in the Pacific Ocean with science samples and cargo. Credit: NASA
Story updated[/caption]
The 30 day flight of the SpaceX-3 Dragon commercial cargo freighter loaded with a huge cache of precious NASA science experiments including a freezer packed with research samples ended today with a spectacular departure from the orbiting lab complex soaring some 266 miles (428 km) above Earth.
Update 3:05 PM EDT May 18: SpaceX confirms successful splashdown at 3:05 p.m. EDT today.
“Splashdown is confirmed!! Welcome home, Dragon!”
Robotics officers at Mission Control at NASA’s Johnson Space Center detached Dragon from the Earth-facing port of the Harmony module at 8 a.m. EDT (1300 GMT) this morning, Sunday, May 18, 2014 using the stations Canadian-built robotic arm.
Engineers had earlier unbolted all 16 hooks and latches firmly connecting the vehicle to the station in preparation.
NASA astronaut Steve Swanson then commanded the gum dropped shaped Dragon capsule’s release from Canadarm2 as planned at 9:26 a.m. EDT (1326 GMT) while the pair were flying majestically over southern Australia.
The undocking operation was shown live on NASA TV.
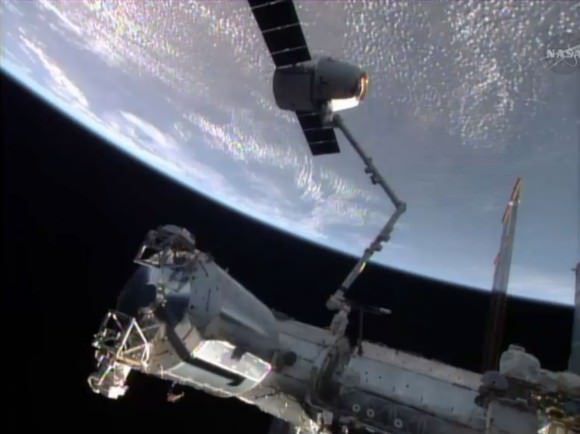

Swanson was assisted by Russian cosmonaut Alexander Skvortsov as the US- Russian team were working together inside the domed Cupola module.
Following the cargo ships release by the 57 foot long arms grappling snares, Swanson carefully maneuvered the arm back and away from Dragon as it moved ever so slowly in free drift mode.
It was already four feet distant within three minutes of release.
Three departure burns by the Dragon’s Draco maneuvering thrusters followed quickly in succession and occurred precisely on time at 9:29, 9:30 and 9:38 a.m. EST.
Dragon exited the 200 meter wide keep out zone – an imaginary bubble around the station with highly restricted access – at the conclusion of the 3rd departure burn.
“The Dragon mission went very well. It was very nice to have a vehicle take science equipment to the station, and maybe some day even humans,” Swanson radioed after the safe and successful departure was completed.
“Thanks to everyone who worked on the Dragon mission.”
The private SpaceX Dragon spent a total of 28 days attached to the ISS.
The six person international crew from Russia, the US and Japan on Expeditions 39 and 40 unloaded some 2.5 tons of supplies aboard and then repacked it for the voyage home.
The SpaceX resupply capsule is carrying back about 3500 pounds of spacewalk equipment, vehicle hardware, science samples from human research, biology and biotechnology studies, physical science investigations and education activities, as well as no longer needed trash.
“The space station is our springboard to deep space and the science samples returned to Earth are critical to improving our knowledge of how space affects humans who live and work there for long durations,” said William Gerstenmaier, associate administrator for human exploration and operations.
“Now that Dragon has returned, scientists can complete their analyses, so we can see how results may impact future human space exploration or provide direct benefits to people on Earth.”
Among the research investigations conducted that returned samples in the cargo hold were an examination of the decreased effectives of antibiotics in space, better growth of plants in space, T-Cell activation in aging and causes of human immune system depression in the microgravity environment.
The 10 minute long deorbit burn took place as scheduled at 2:10 p.m. EDT (1810 GMT) today.
Dragon returned to Earth for a triple parachute assisted splash down today at around 3:02 p.m. EDT (19:02 GMT) in the Pacific Ocean – some 300 miles west of Baja California.

It will be retrieved by recovery boats commissioned by SpaceX. The science cargo will be extracted and then delivered to NASA’s Johnson Space Center within 48 hours.
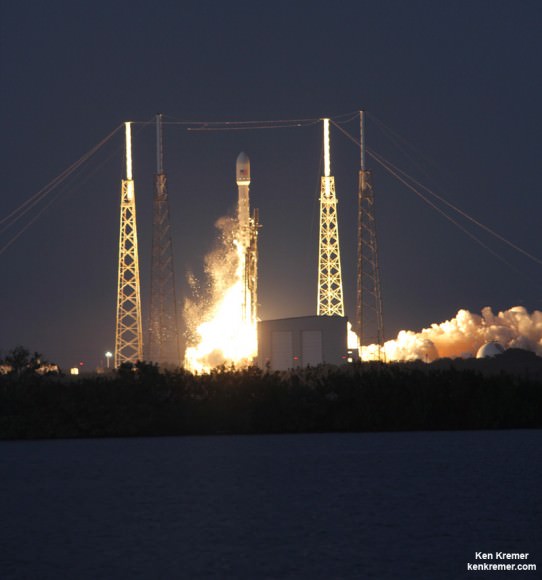
Dragon thundered to orbit atop SpaceX’s powerful new Falcon 9 v1.1 rocket on April 18, from Cape Canaveral, Fla.
This unmanned Dragon delivered about 4600 pounds of cargo to the ISS including over 150 science experiments, a pair of hi tech legs for Robonaut 2, a high definition Earth observing imaging camera suite (HDEV), the laser optical communications experiment (OPALS), the VEGGIE lettuce growing experiment as well as essential gear, spare parts, crew provisions, food, clothing and supplies to the six person crews living and working aboard in low Earth orbit.

It reached the ISS on April 20 for berthing.
Dragon is the only unmanned resupply vessel supply that also returns cargo back to Earth.
The SpaceX-3 mission marks the company’s third resupply mission to the ISS under the $1.6 Billion Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract with NASA to deliver 20,000 kg (44,000 pounds) of cargo to the ISS during a dozen Dragon cargo spacecraft flights through 2016.
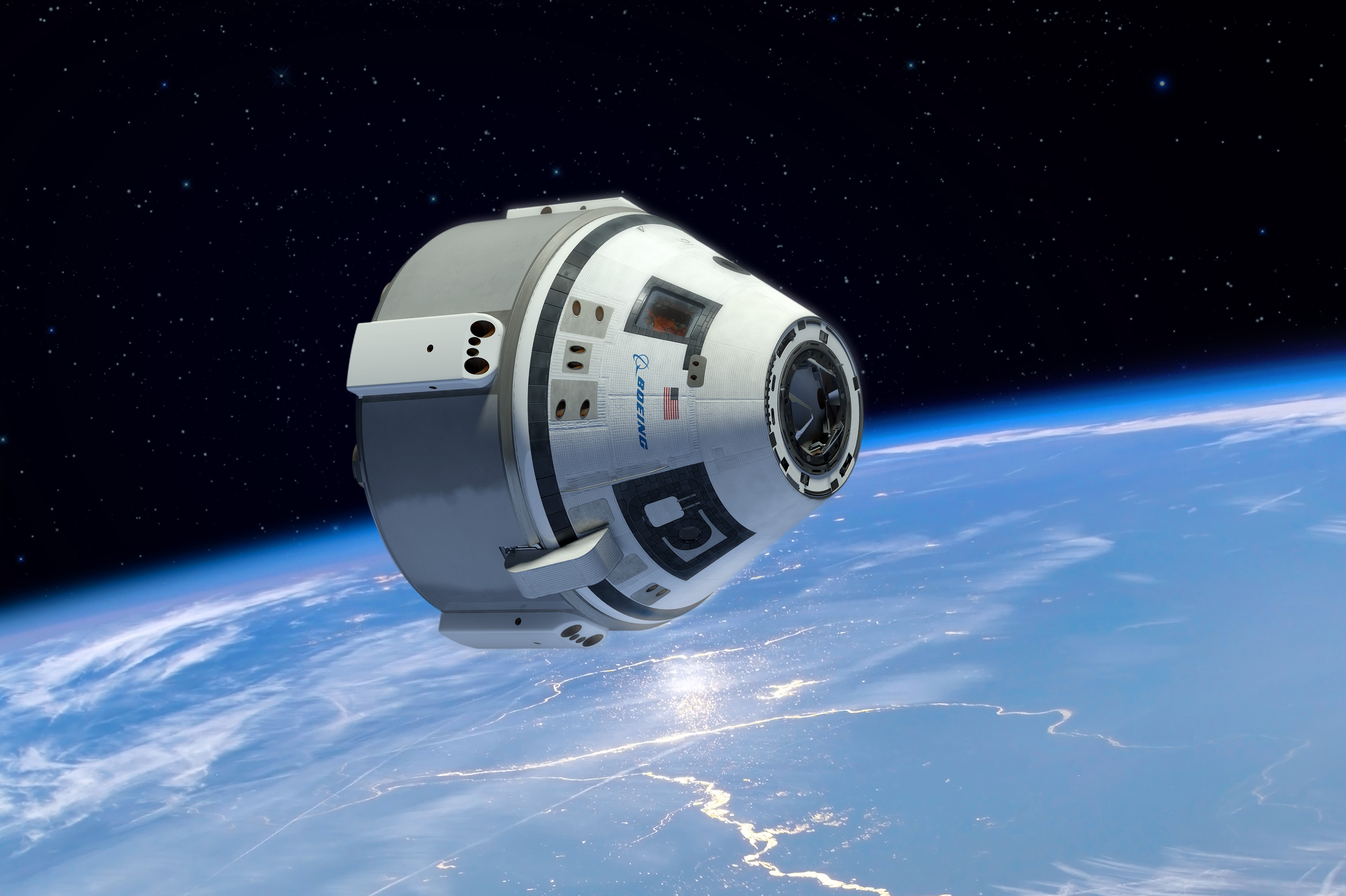
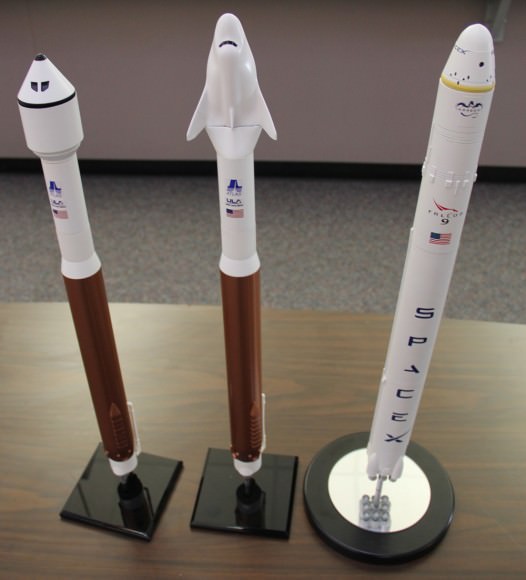
The SpaceX Dragon is among a trio of American vehicles, including the Boeing CST-100 and Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser vying to restore America’s capability to fly humans to Earth orbit and the space station by late 2017, using seed money from NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP) in a public/private partnership. The next round of contracts will be awarded by NASA about late summer 2014.
Another significant milestone was the apparently successful attempt by SpaceX to accomplish a controlled soft landing of the Falcon 9 boosters first stage in the Atlantic Ocean for eventual recovery and reuse. It was a first step in a guided 1st stage soft landing back at the Cape.
The next unmanned US cargo mission to the ISS is set for early morning on June 10 with the launch of the Orbital Sciences Cygnus freighter atop an Antares booster from a launch pad at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility on the eastern shore of Virginia.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing SpaceX, Orbital Sciences, Boeing, commercial space, Orion, Chang’e-3, LADEE, Curiosity, Mars rover, MAVEN, MOM and more planetary and human spaceflight news.
………
Ken’s upcoming presentation: Mercy College, NY, May 19: “Curiosity and the Search for Life on Mars” and “NASA’s Future Crewed Spaceships.”