Multisol composite photo mosaic shows deployment of Curiosity rovers robotic arm and APXS X-ray spectrometer onto the ‘Winjana’ rock target at Mount Remarkable for evaluation as missions third drill target inside Gale Crater on Mars. The navcam raw images were stitched together from several Martian days up to Sol 612, April 26, 2014 and colorized. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ken Kremer – kenkremer.com/Marco Di Lorenzo
See more Curiosity photo mosaics below[/caption]
To Drill or not to Drill?
That’s the momentous question posed by the international team of scientists and engineers who commanded NASA’s SUV sized Curiosity rover to reach out with her high tech robotic arm this weekend (Apr 25-27) and gather critical science measurements for high powered scrutiny of an outcrop on a Martian butte named Mount Remarkable.
See our multisol, composite photo mosaic – above – illustrating Curiosity’s arm in action pressing down her X-ray spectrometer on Saturday, April 26, Sol 612, at an alien rock on Mount Remarkable at the current stopping point at “The Kimberley Waypoint” along the epic trek to towering Mount Sharp.
Via a combination of laser shots, images, brushings and spectrometry the team is pondering new data streaming back daily across hundreds of millions of kilometers of interplanetary space to Earth to determine whether to bore into a sandstone slab being evaluated as the target for the missions third drilling campaign.
The team deployed the arm this weekend onto a rock target called “Windjana,” after a gorge in Western Australia.

After confirming that the 1 ton robot was in a stable position, the team commanded study observations on Saturday, Sol 612, using the APXS spectrometer and MAHLI camera on the terminus of the arm’s turret.
“The observation will document its chemical composition and morphology before drilling,” says science team member Ken Herkenoff in a mission update.
She also brushed off the potential ‘Windjana’ drill target with the wire-bristle Dust Removal Tool (DRT) to clear away obscuring Red Planet dirt and dust hindering the data collections.
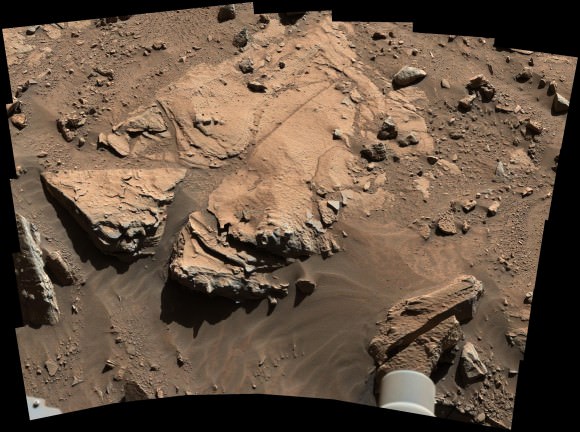

The rover is also conducting continuing remote sensing observations with the ChemCam, Mastcam and Navcam cameras mounted on the Mast.
Today, April 27, Sol 613, “MAHLI will take another selfie of the rover” according to Herkenhoff.
In early April, the six wheeled rover pulled into a scientifically enticing science destination known as “The Kimberley Waypoint” in hopes of carrying out the next drilling operation into alien Martian terrain in search of further clues about ancient Martian environments that may have been favorable for life.
“We are officially in ‘The Kimberley’ now,” Curiosity Principal Investigator John Grotzinger, of the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, told me at that time.
Since arriving in the Kimberley region, Curiosity’s earth bound handlers have been maneuvering the 1 ton robot around to thoroughly survey destination “Kimberley” in choosing the best drill site.
Why was Kimberley chosen as a science destination ?
“The Kimberley” has interesting, complex stratigraphy,” Grotzinger told me.
If Windjana meets the required criteria, Curiosity will bore into the sandstone rock, and then pulverize and filter it prior to delivery to the two onboard miniaturized chemistry labs – SAM and CheMin.
Windjana would be the first sandstone drill target, if selected. The first two drill locations at ‘John Klein’ and ‘Cumberland’ inside Yellowknife Bay were mudstone.

Curiosity departed the ancient lakebed at the Yellowknife Bay region in July 2013 where she discovered a habitable zone with the key chemical elements and a chemical energy source that could have supported microbial life billions of years ago – and thereby accomplished the primary goal of the mission.
“We want to learn more about the wet process that turned sand deposits into sandstone here,” said Grotzinger, in a NASA statement.
“What was the composition of the fluids that bound the grains together? That aqueous chemistry is part of the habitability story we’re investigating.”
“Understanding why some sandstones in the area are harder than others also could help explain major shapes of the landscape where Curiosity is working inside Gale Crater. Erosion-resistant sandstone forms a capping layer of mesas and buttes. It could even hold hints about why Gale Crater has a large layered mountain, Mount Sharp, at its center,” NASA elaborated in the statement.
To date, Curiosity’s odometer totals 3.8 miles (6.1 kilometers) since landing inside Gale Crater on Mars in August 2012. She has taken over 143,000 images.
The sedimentary foothills of Mount Sharp, which reaches 3.4 miles (5.5 km) into the Martian sky, is the 1 ton robots ultimate destination inside Gale Crater because it holds caches of water altered minerals. Such minerals could possibly indicate locations that sustained potential Martian life forms, past or present, if they ever existed.
Curiosity has some 4 kilometers to go to reach the base of Mount Sharp sometime later this year.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Curiosity, Opportunity, Chang’e-3, SpaceX, Orbital Sciences, LADEE, MAVEN, MOM, Mars and more planetary and human spaceflight news.