Universe Today has explored the importance of studying impact craters and planetary surfaces and what these scientific disciplines can teach us about finding life beyond Earth. We learned that impact craters are caused by massive rocks that can either create or destroy life, and planetary surfaces can help us better understand the geologic processes on other worlds, including the conditions necessary for life. Here, we will venture far beyond the confines of our solar system to the many stars that populate our Milky Way Galaxy and the worlds they orbit them, also known as exoplanets. We will discuss why astronomers study exoplanets, challenges of studying exoplanets, what exoplanets can teach us about finding life beyond Earth, and how upcoming students can pursue studying exoplanets, as well. So, why is it so important to study exoplanets?
Continue reading “Exoplanets: Why study them? What are the challenges? What can they teach us about finding life beyond Earth?”Venus’ Clouds Contain Sulfuric Acid. That’s Not a Problem for Life.
A recent study published in Astrobiology investigates the potential habitability in the clouds of Venus, specifically how amino acids, which are the building blocks of life, could survive in the sulfuric acid-rich upper atmosphere of Venus. This comes as the potential for life in Venus’ clouds has become a focal point of contention within the astrobiology community in the last few years. On Earth, concentrated sulfuric acid is known for its corrosivity towards metals and rocks and for absorbing water vapor. In Venus’ upper atmosphere, it forms from solar radiation interacting with sulfur dioxide, water vapor, and carbon dioxide.
Continue reading “Venus’ Clouds Contain Sulfuric Acid. That’s Not a Problem for Life.”Planetary Surfaces: Why study them? Can they help us find life elsewhere?
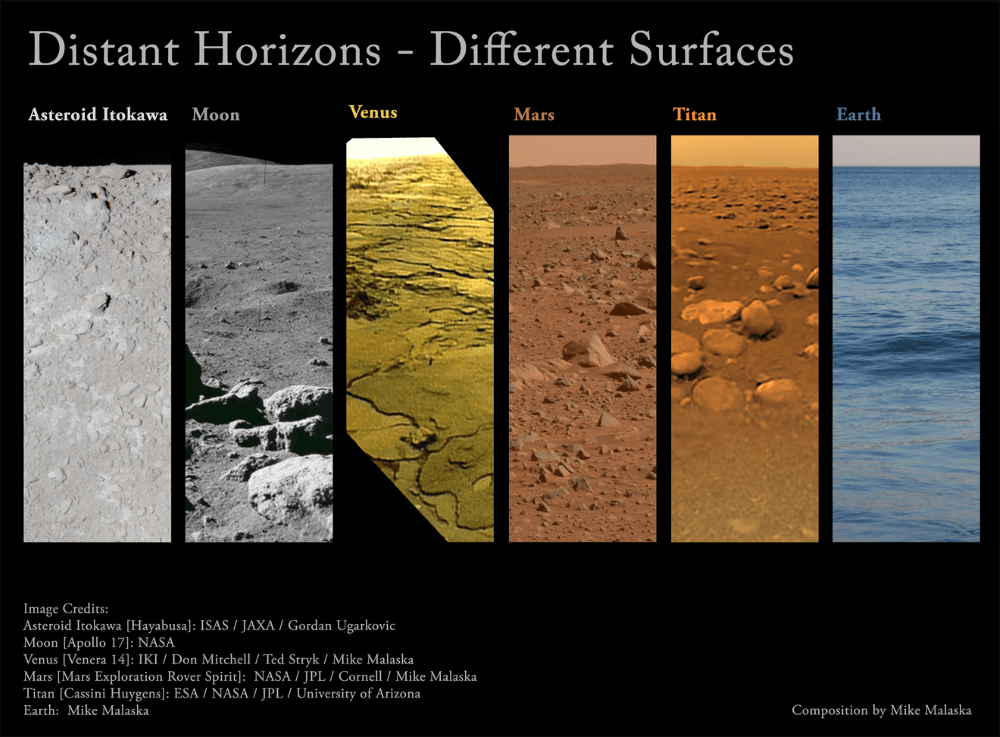
Universe Today recently explored the importance of studying impact craters and what they can teach us about finding life beyond Earth. Impact craters are considered one of the many surface processes—others include volcanism, weathering, erosion, and plate tectonics—that shape surfaces on numerous planetary bodies, with all of them simultaneously occurring on Earth. Here, we will explore how and why planetary scientists study planetary surfaces, the challenges faced when studying other planetary surfaces, what planetary surfaces can teach us about finding life, and how upcoming students can pursue studying planetary surfaces, as well. So, why is it so important to study planetary surfaces throughout the solar system?
Continue reading “Planetary Surfaces: Why study them? Can they help us find life elsewhere?”Big Planets Don’t Necessarily Mean Big Moons
Does the size of an exomoon help determine if life could form on an exoplanet it’s orbiting? This is something a February 2022 study published in Nature Communications hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated the potential for large exomoons to form around large exoplanets (Earth-sized and larger) like how our Moon was formed around the Earth. Despite this study being published almost two years ago, its findings still hold strong regarding the search for exomoons, as astronomers have yet to confirm the existence of any exomoons anywhere in the cosmos. But why is it so important to better understand the potential for large exomoons orbiting large exoplanets?
Continue reading “Big Planets Don’t Necessarily Mean Big Moons”Impact Craters: Why study them and can they help us find life elsewhere?
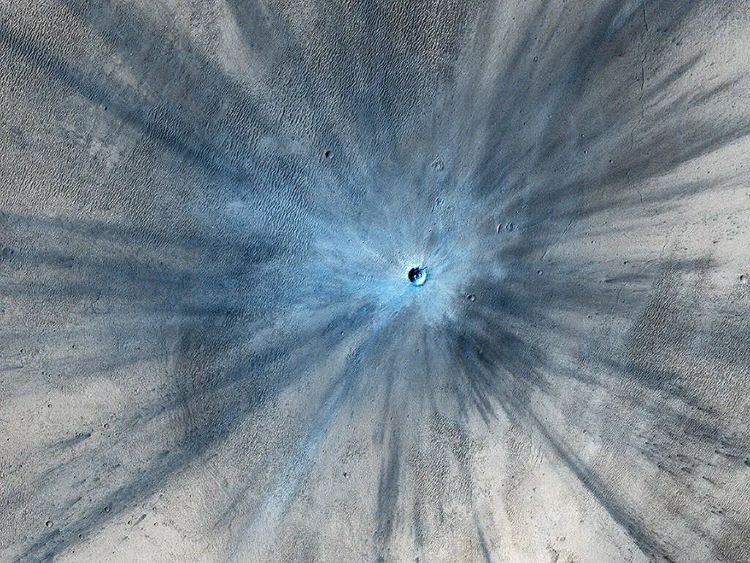

When we look at the Moon, either through a pair of binoculars, a telescope, or past footage from the Apollo missions, we see a landscape that’s riddled with what appear to be massive sinkholes. But these “sinkholes” aren’t just on the Moon, as they are evident on nearly every planetary body throughout the solar system, from planets, to other moons, to asteroids. They are called impact craters and can range in size from cities to small countries.
Continue reading “Impact Craters: Why study them and can they help us find life elsewhere?”Should We Send Humans to Pluto?
Universe Today has examined the potential for sending humans to Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa, the planet Venus, and Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, all despite their respective harsh environments and vast distances. These conversations with planetary science experts determined that humans traveling to these worlds in the foreseeable future could be possible, despite the harsh conditions and travel time, specifically to Titan.
Continue reading “Should We Send Humans to Pluto?”How Many Planets Could Be in the Kuiper Belt?
A recent study published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters investigates the potential existence of Mars-sized free-floating planets (FFPs)—also known as rogue planets, starless planets, and wandering planets—that could have been captured by our Sun’s gravity long ago and orbit in the outer solar system approximately 1,400 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun. For context, the farthest known planetary body in the solar system is Pluto, which orbits approximately 39 AU from the Sun, and is also part of the Kuiper Belt, which scientists estimate extends as far out as 1,000 AU from the Sun.
Continue reading “How Many Planets Could Be in the Kuiper Belt?”TRAPPIST-1c Isn’t the Exo-Venus We Were Hoping For. But Don’t Blame the Star
A recent study accepted to The Astrophysical Journal uses computer models to investigate why the exoplanet, TRAPPIST-1c, could not possess a thick carbon dioxide (CO2) atmosphere despite it receiving the same amount of solar radiation from its parent star as the planet Venus receives from our Sun, with the latter having a very thick carbon dioxide atmosphere. This study comes after a June 2023 study published in Nature used data from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to ascertain that TRAPPIST-1c does not possess a carbon dioxide atmosphere. Both studies come as the TRAPPIST-1 system, which is located approximately 41 light-years from Earth and orbits its star in just 2.4 days, has received a lot of attention from the scientific community in the last few years due to the number of confirmed exoplanets within the system and their potential for astrobiology purposes.
Continue reading “TRAPPIST-1c Isn’t the Exo-Venus We Were Hoping For. But Don’t Blame the Star”NASA Astronauts are Trying Out the Starship Lunar Elevator
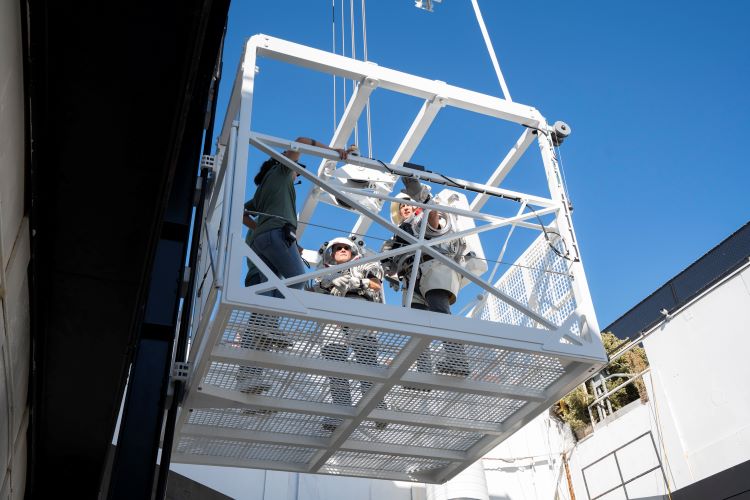

As NASA continues to ramp up efforts for its Artemis program, which has the goal of landing the first woman and person of color on the lunar surface, two NASA astronauts recently conducted training with a replica of SpaceX’s Starship human landing system (HLS), albeit on a much smaller scale. Given that Starship is 50 meters (160 feet) tall, and the crew quarters are located near the top of Starship, the HLS will need an elevator with a basket to transport crew and supplies from the crew quarters down to the surface. The purpose of this training is to familiarize astronauts with all aspects of this system, including elevator and gate controls and latches, along with how the astronauts perform these tasks in their bulky astronaut suits, which both astronauts wore during the training.
Continue reading “NASA Astronauts are Trying Out the Starship Lunar Elevator”Should We Send Humans to Titan?
Universe Today recently examined the potential for sending humans to Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa, and the planet Venus, both despite their respective harsh surface environments. While human missions to these exceptional worlds could be possible in the future, what about farther out in the solar system to a world with much less harsh surface conditions, although still inhospitable for human life? Here, we will investigate whether Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, could be a feasible location for sending humans sometime in the future. Titan lacks the searing temperatures and crushing pressures of Venus along with the harsh radiation experienced on Europa. So, should we send humans to Titan?
Continue reading “Should We Send Humans to Titan?”