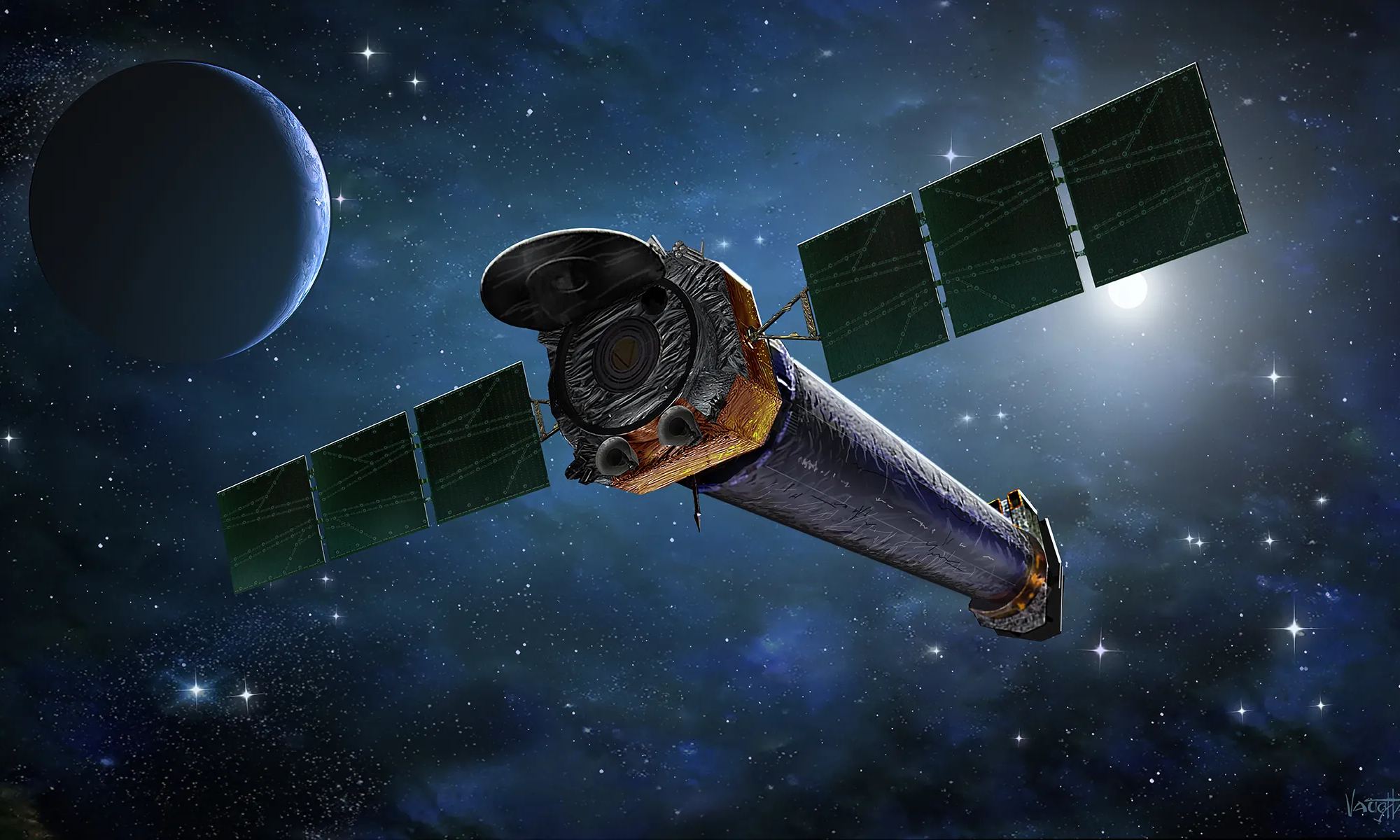
The US Government budget announcement in March left NASA with two billion dollars less than it asked for. The weeks that followed have left NASA with some difficult decisions forcing cuts across the agency. There will be a number of cuts across the agency but one recent decision came as quite a shock to the scientific community. NASA have just announced they are no longer going to support the Chandra X-Ray Observatory which has been operational since 1999 and made countless discoveries.
Continue reading “NASA is Planning to Shut Down One of the Great Observatories to Save Money”Astronomers Find the Most Massive Supercluster to Date
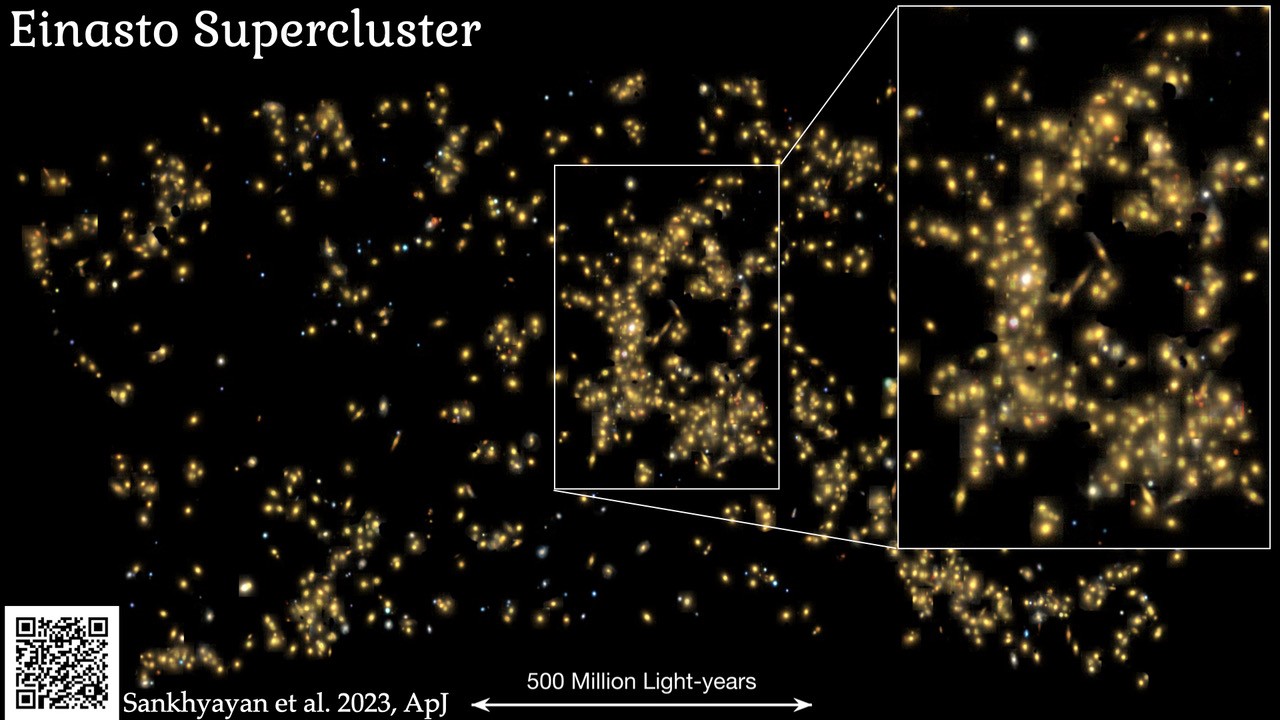
The Earth’s place in space is a fairly familiar one with it orbiting an average star. The star – our Sun – orbits the centre of our Galaxy the Milky Way. From here onwards, the story is less well known. The Milky Way is part of a large structure called the Laniakea Supercluster which is 250 million light years across! That really is a whacking great area of space and it contains at least 100,000 galaxies. There are larger superclusters though like the newly discovered Einasto Supercluster which measures an incredible 360 million light years across and is home to 26 quadrillion stars!
Continue reading “Astronomers Find the Most Massive Supercluster to Date”Gravity From Mars has an Effect on Earth’s Oceans
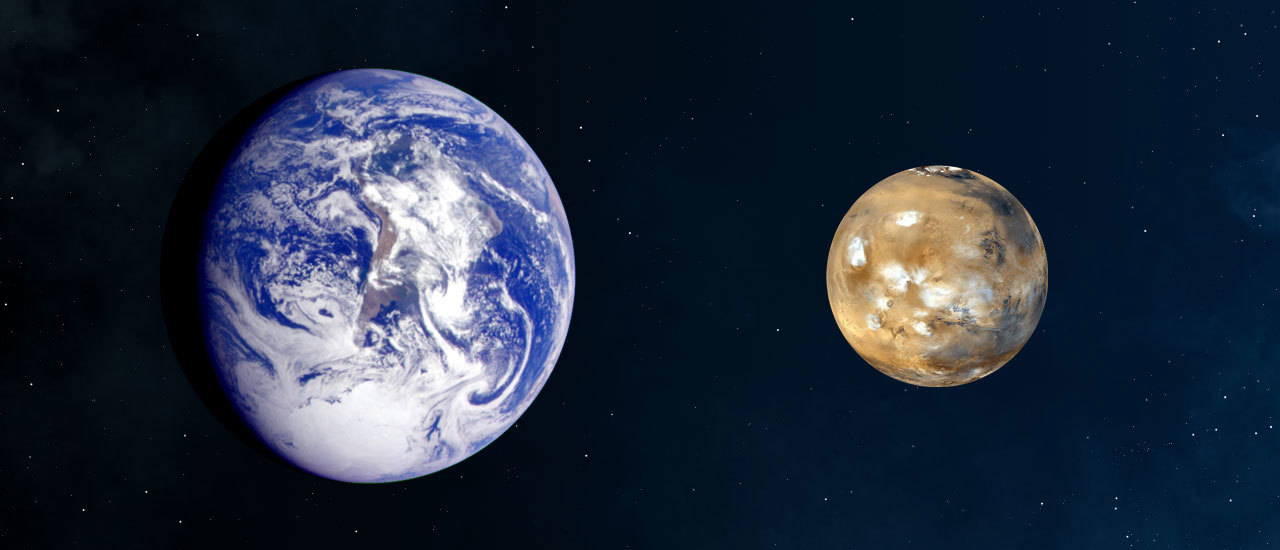
We are all too familiar of the Moon’s effect on our planet. It’s relentless tug causes our tides but even Mars, which is always at least 55 million kilometres away, can have a subtle effect too. A study has revealed a 2.4 million year cycle in the geological records that show the gentle warming and cooling of our oceans. The records match the interactions between the orbits of Earth and Mars over the longest timescales. These are known as the ‘astronomical grand cycles’ but to date, not much evidence has been found.
Continue reading “Gravity From Mars has an Effect on Earth’s Oceans”NASA is Fixing its Link to Voyager 1
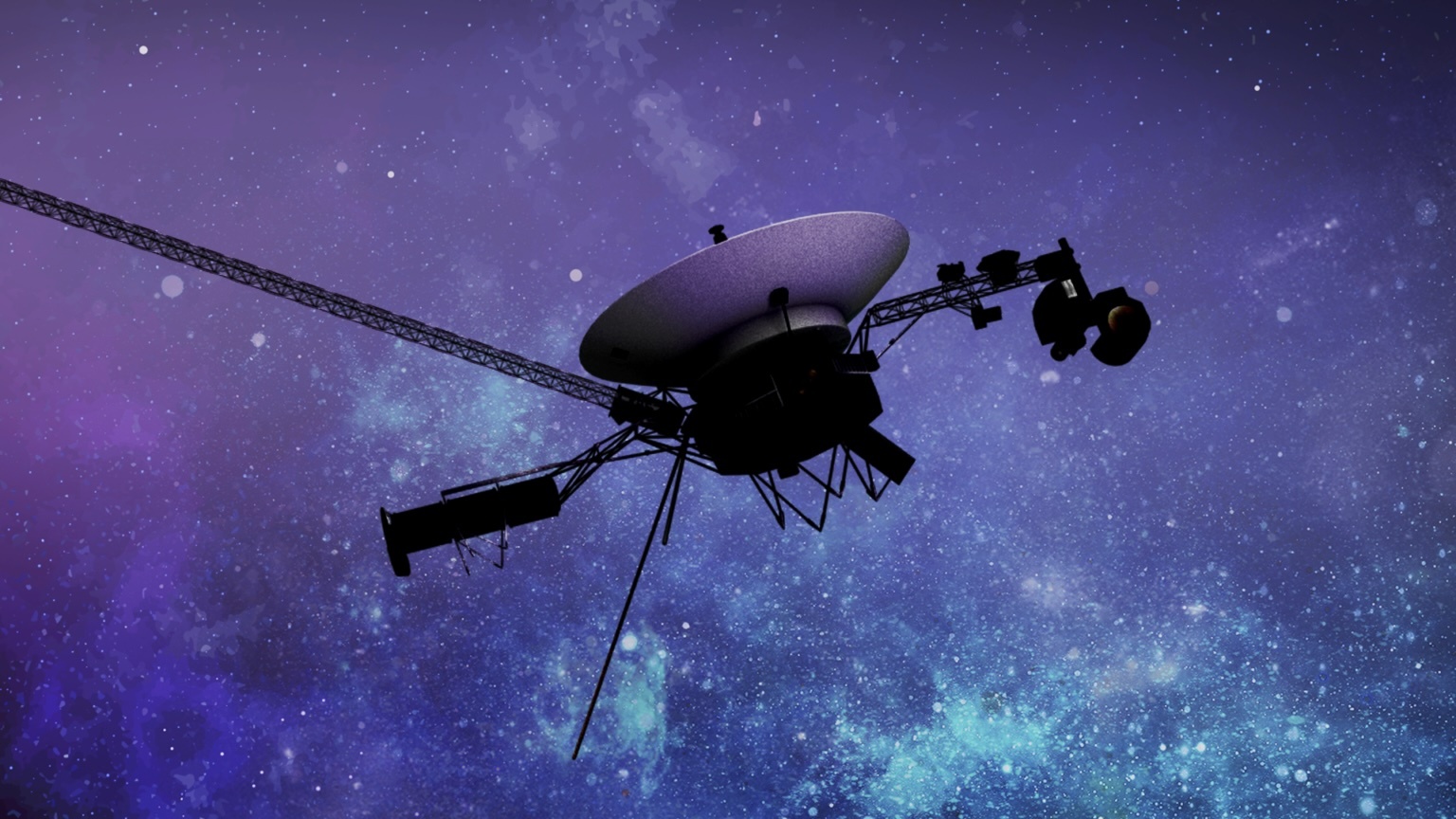
Voyagers 1 and 2 were, to put it simply, incredible. They were true explorers and unveiled many mysteries of the outer Solar System, revealing the outer planets in all their glory. Communication with Voyager 1 has until recently been possible, slow but possible. More recently however, it has been sending home garbled data rendering communication to all intents impossible although messages can still be sent. Engineers at NASA have narrowed the problem down to an onboard computer, the Flight Data System (FDS). A dump of the entire memory of the FDS has now been received so that engineers can attempt to troubleshoot and fix the issue.
Continue reading “NASA is Fixing its Link to Voyager 1”Mars Was Hiding Another Giant Volcano
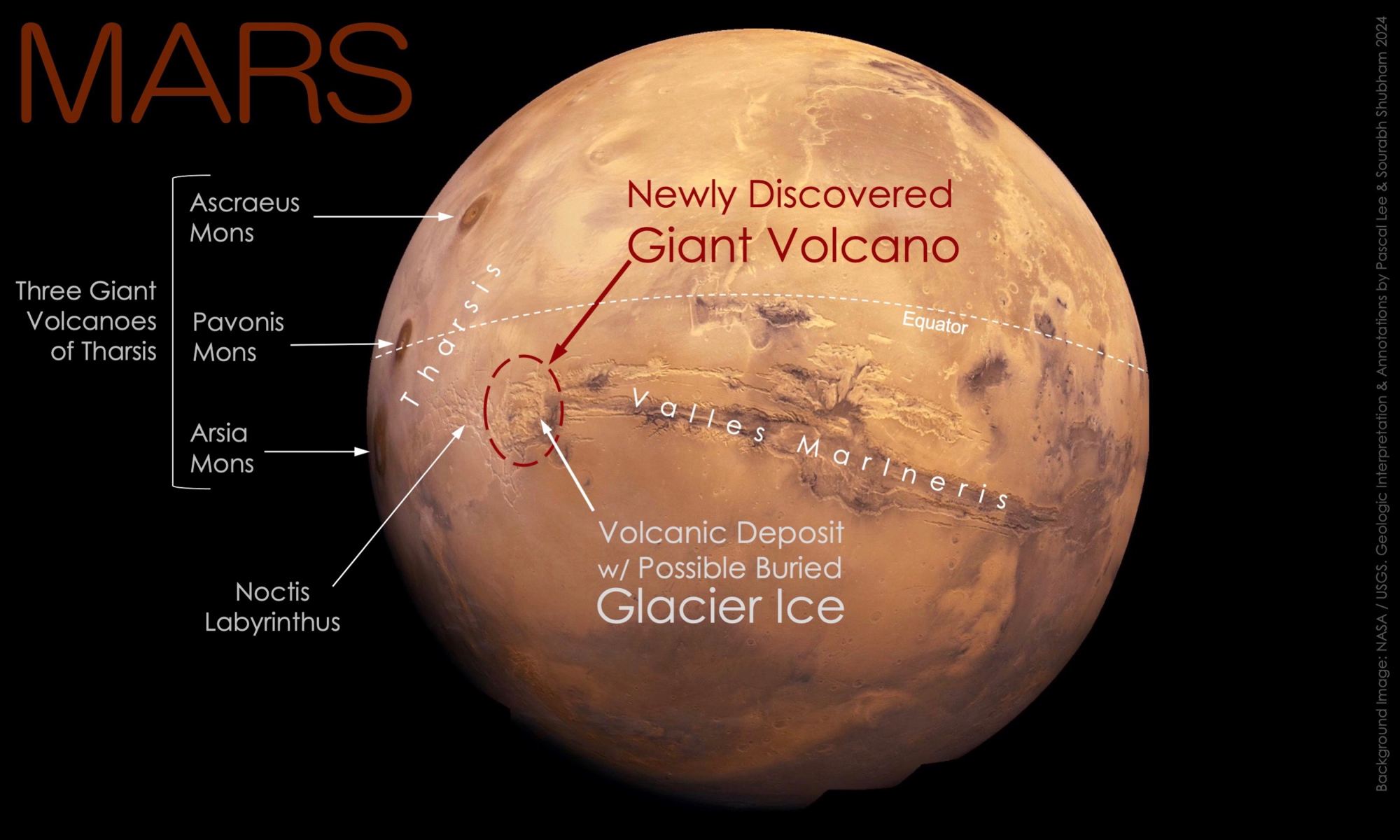
Olympus Mons is well known for being the largest volcano in the Solar System. It’s joined on Mars by three other shield volcanoes; Ascraeus, Pavonis and Arsia but a recent discovery has revealed a fifth. Provisionally called Noctis volcano, this previously unknown Martian feature reaches 9,022 metres high and 450 kilometres across. Its presence has eluded planetary scientists because it has been heavily eroded and is on the boundary of the fractured maze-like terrain of Noctis Labyrinthus.
Continue reading “Mars Was Hiding Another Giant Volcano”This is a 1.3 Gigapixel Image of a Supernova Remnant
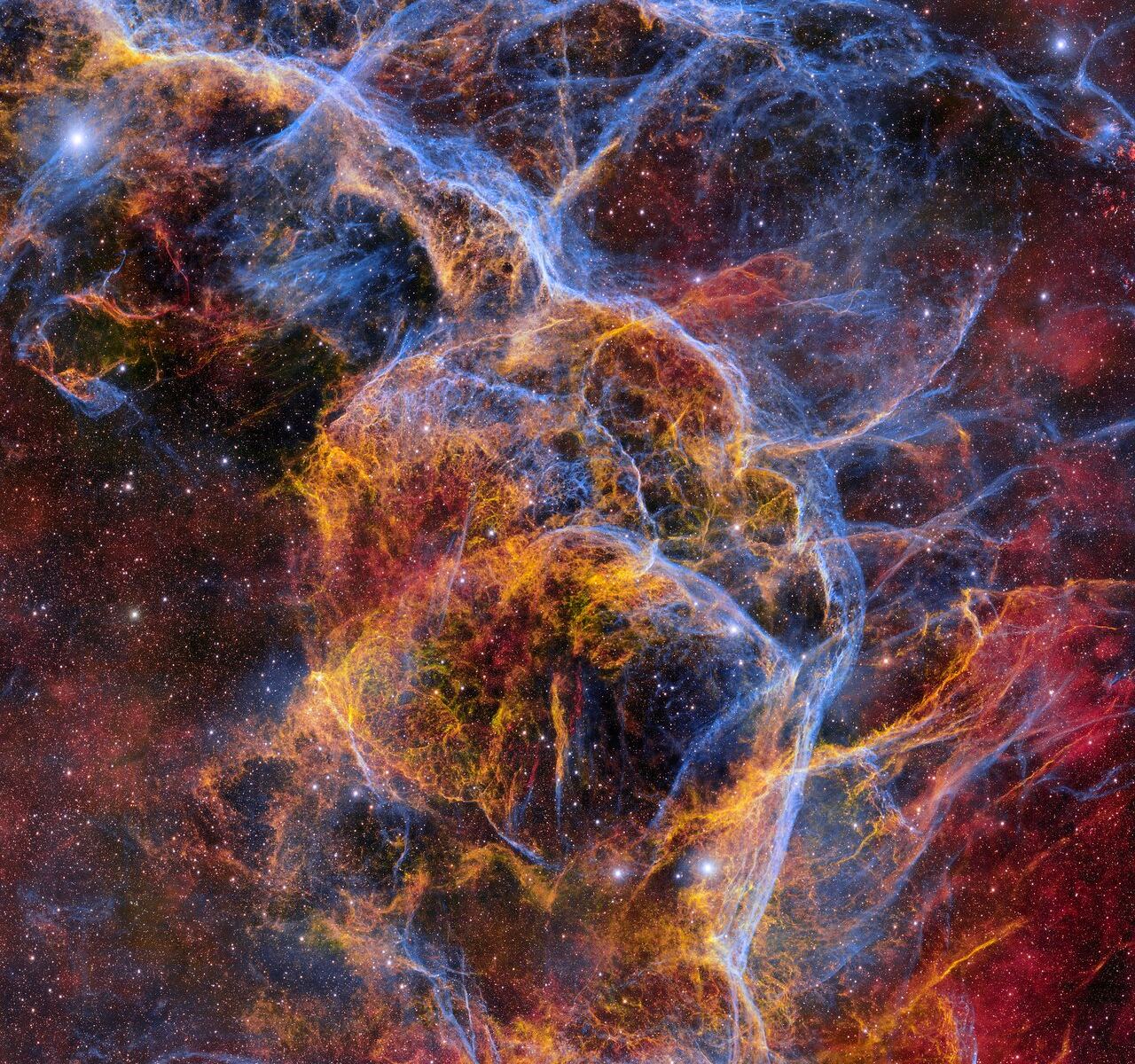

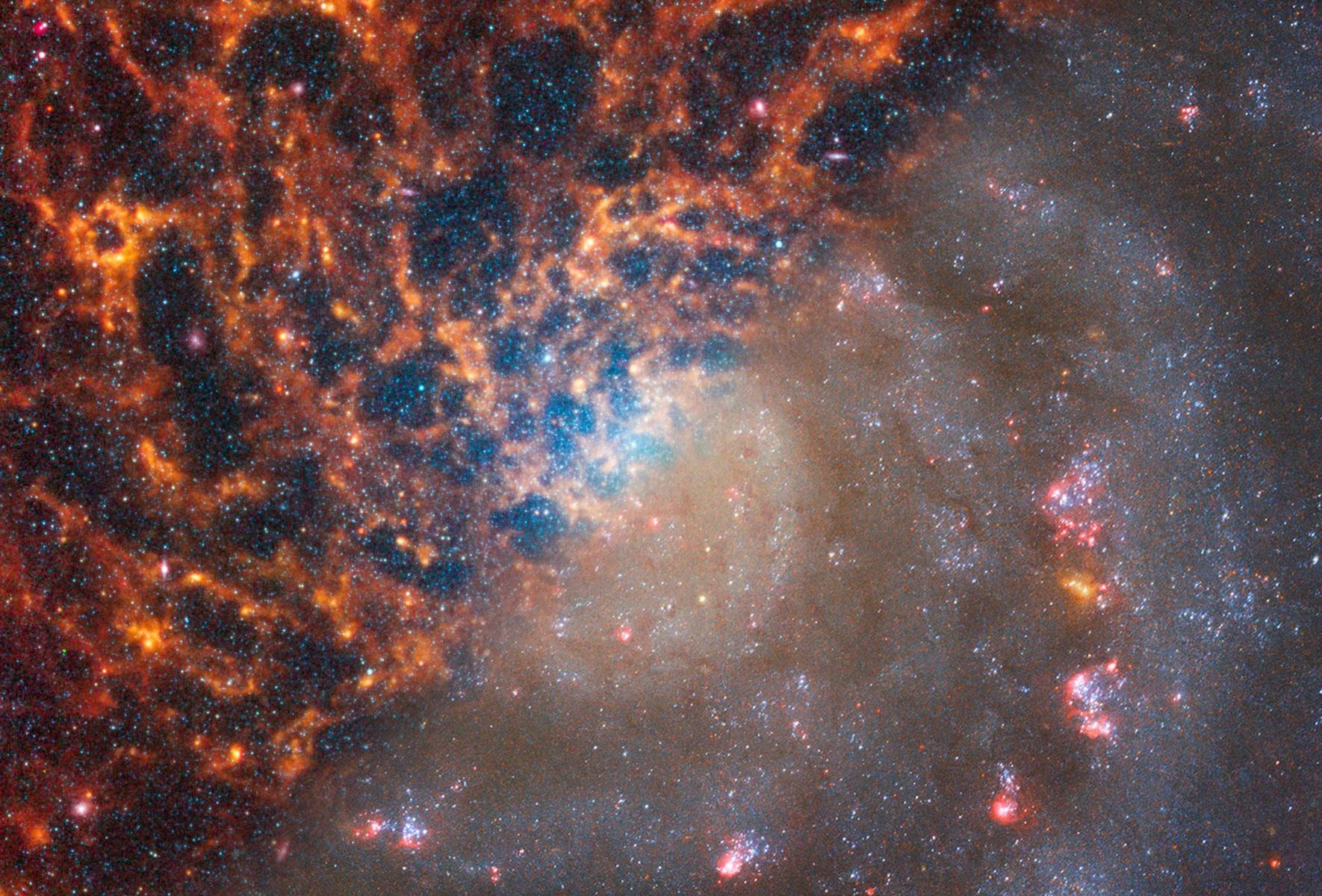
Stars more massive than the Sun blow themselves to pieces at the end of their life. Usually leaving behind either a black hole, neutron star or pulsar they also scatter heavy elements across their host galaxy. One such star went supernova nearly 11,000 years ago creating the Vela Supernova Remnant. The resultant expanding cloud of debris covers almost 100 light years and would be twenty times the diameter of the full Moon. Astronomers have recently imaged the remnant with a 570 megapixel Dark Energy Camera (DECam) creating a stunning 1.3 gigapixel image.
Continue reading “This is a 1.3 Gigapixel Image of a Supernova Remnant”Nancy Grace Roman will Map the Far Side of the Milky Way
The Galaxy is a collection of stars, planets, gas clouds and to the dismay of astronomers, dust clouds. The dust blocks starlight from penetrating so it’s very difficult to learn about the far side of the Galaxy. Thankfully the upcoming Nancy Grace Roman telescope has infrared capability so it can see through the dust. A systematic survey of the far side of the Milky Way is planned to see what’s there and could discover billions of objects in just a month.
Continue reading “Nancy Grace Roman will Map the Far Side of the Milky Way”NASA Announces its 2025 Budget. Lean Times Ahead.
Space flight is an expensive business and that money has to come from somewhere. The White House has just released their budget for fiscal year 2025. What does that mean for NASA?, they will get $25.4 billion, the same as it received last year but $2 billion less than it requested. NASA Administrator Bill Nelson said the constraints come from a debt ceiling agreement that limits non-defence spending. Alas the $2 billion deficit means NASA will need to cut costs from various missions.
Continue reading “NASA Announces its 2025 Budget. Lean Times Ahead.”Ultrablack Coating Could Be Ideal for Telescopes
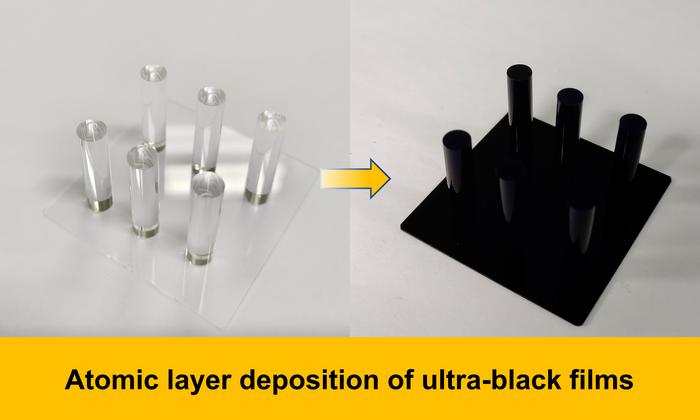
If you, like me, have dabbled with telescope making you will know what a fickle friend light can be. On one hand you want to capture as much as you can (but only from the object, not from nearby lights) and want to reflect or refract it to the point of observation or study. What you most certainly don’t want is stray light to be bounced around inside the telescope so components (except the mirror!) are sprayed as black as possible. Unfortunately black paints tend to be quite susceptible to damage and struggle to cope with the harsh conditions and cold temperatures telescopes are subjected to. A team has recently developed a new atomic-layer deposition method which absorbs 99.3% of light and is durable too.
Continue reading “Ultrablack Coating Could Be Ideal for Telescopes”Are Andromeda and the Milky Way Already Exchanging Stars?
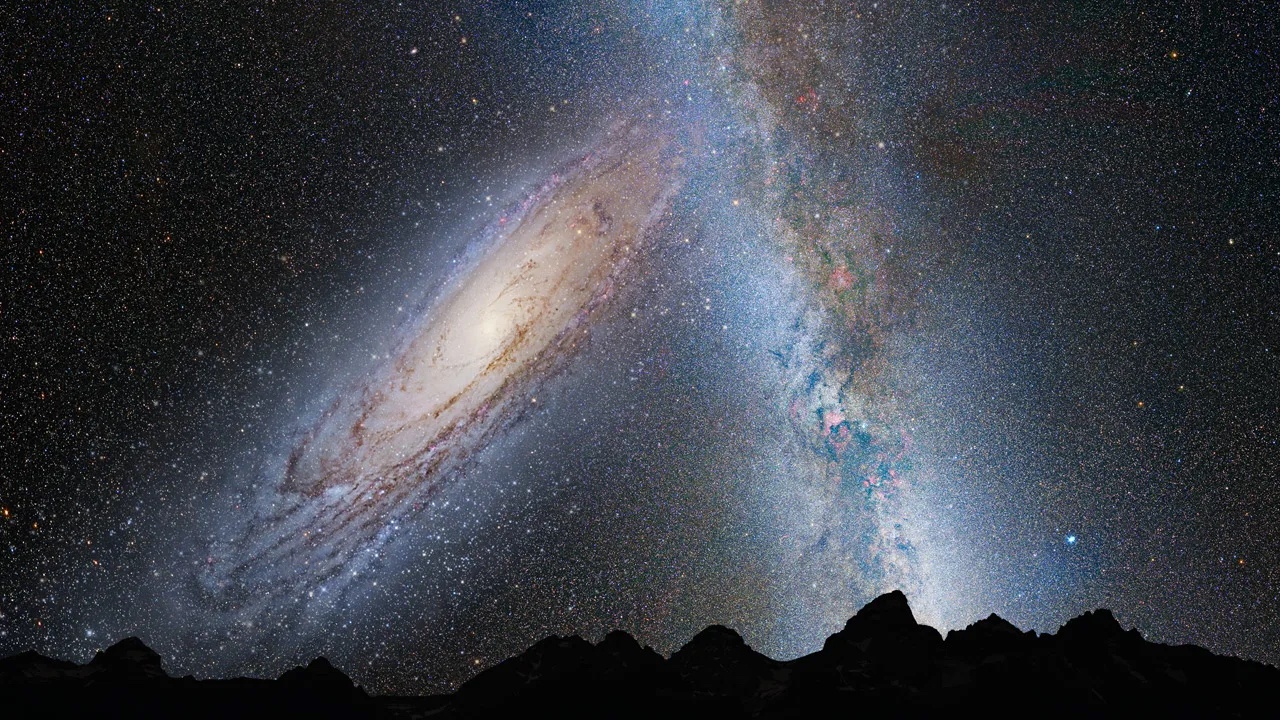

I often drag out the amazing fact that the Andromeda Galaxy, that faint fuzzy blob just off the corner of the Square of Pegasus, is heading straight for us! Of course I continue to tell people it won’t happen for a few billion years yet but a recent study suggests that we are already seeing hypervelocity stars that have been ejected from Andromeda already. It is just possible that the two galaxies have already started to exchange stars long before they are expected to merge.
Continue reading “Are Andromeda and the Milky Way Already Exchanging Stars?”