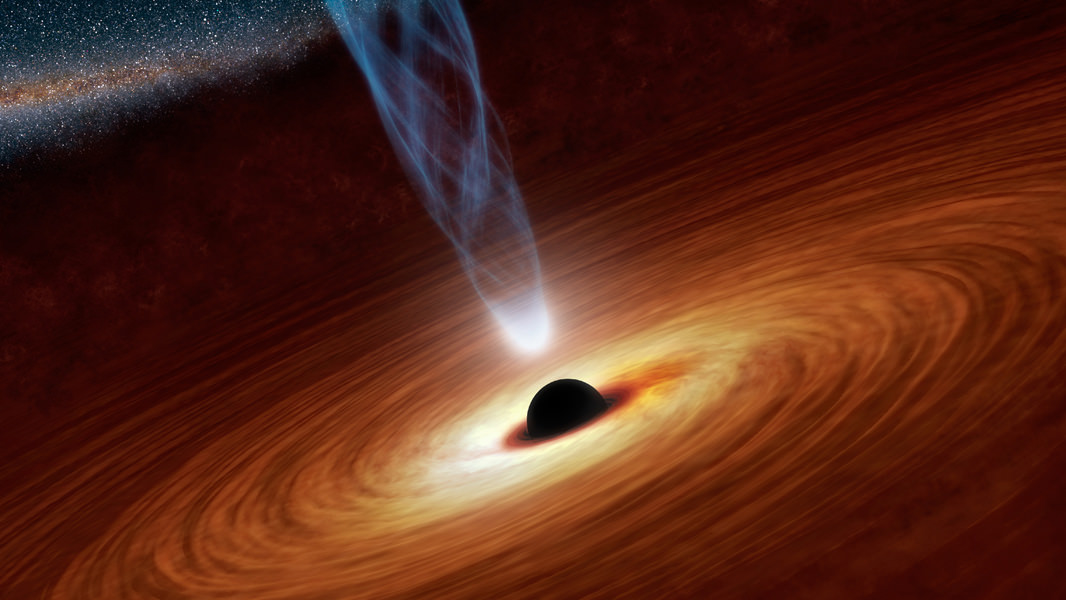
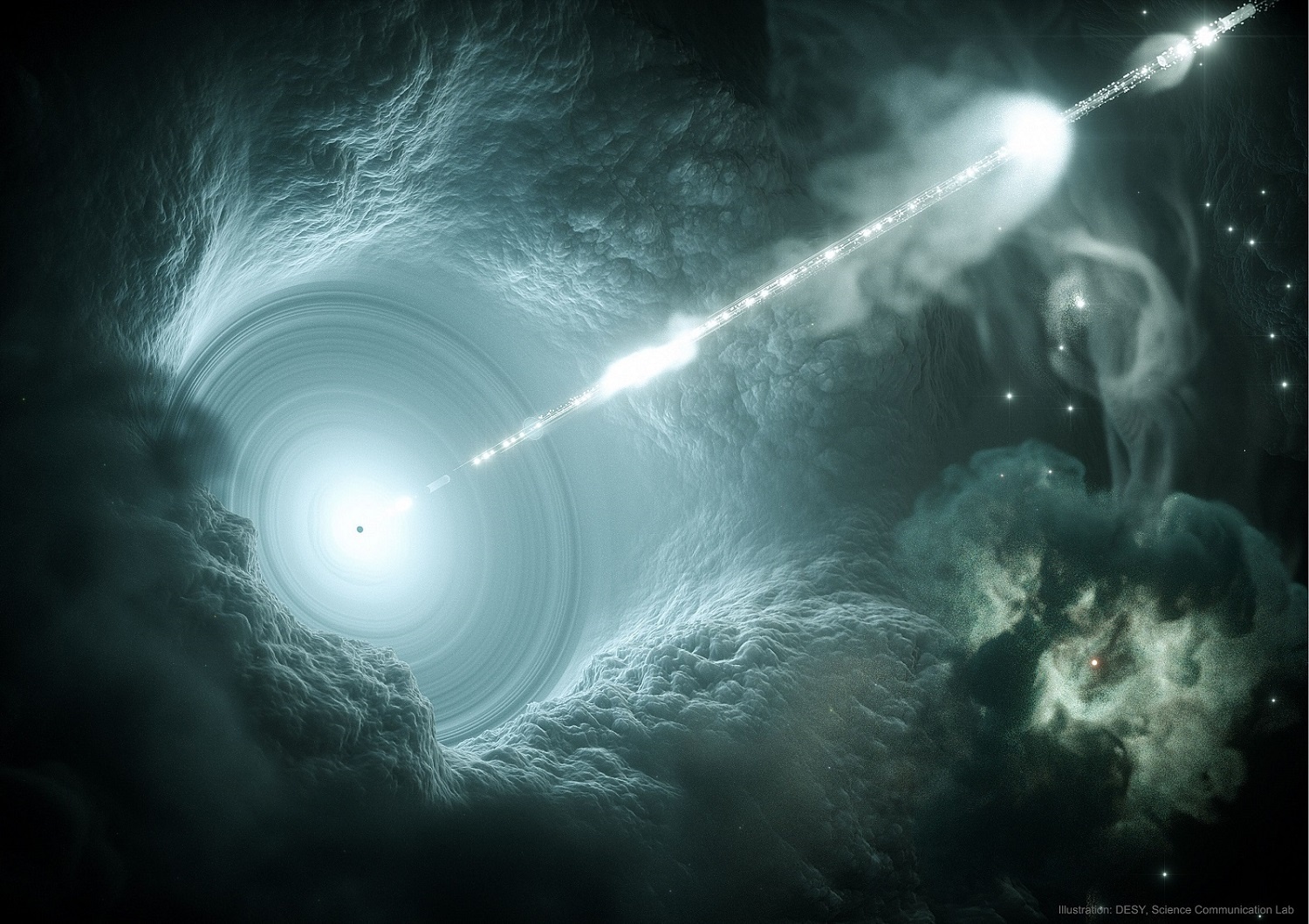
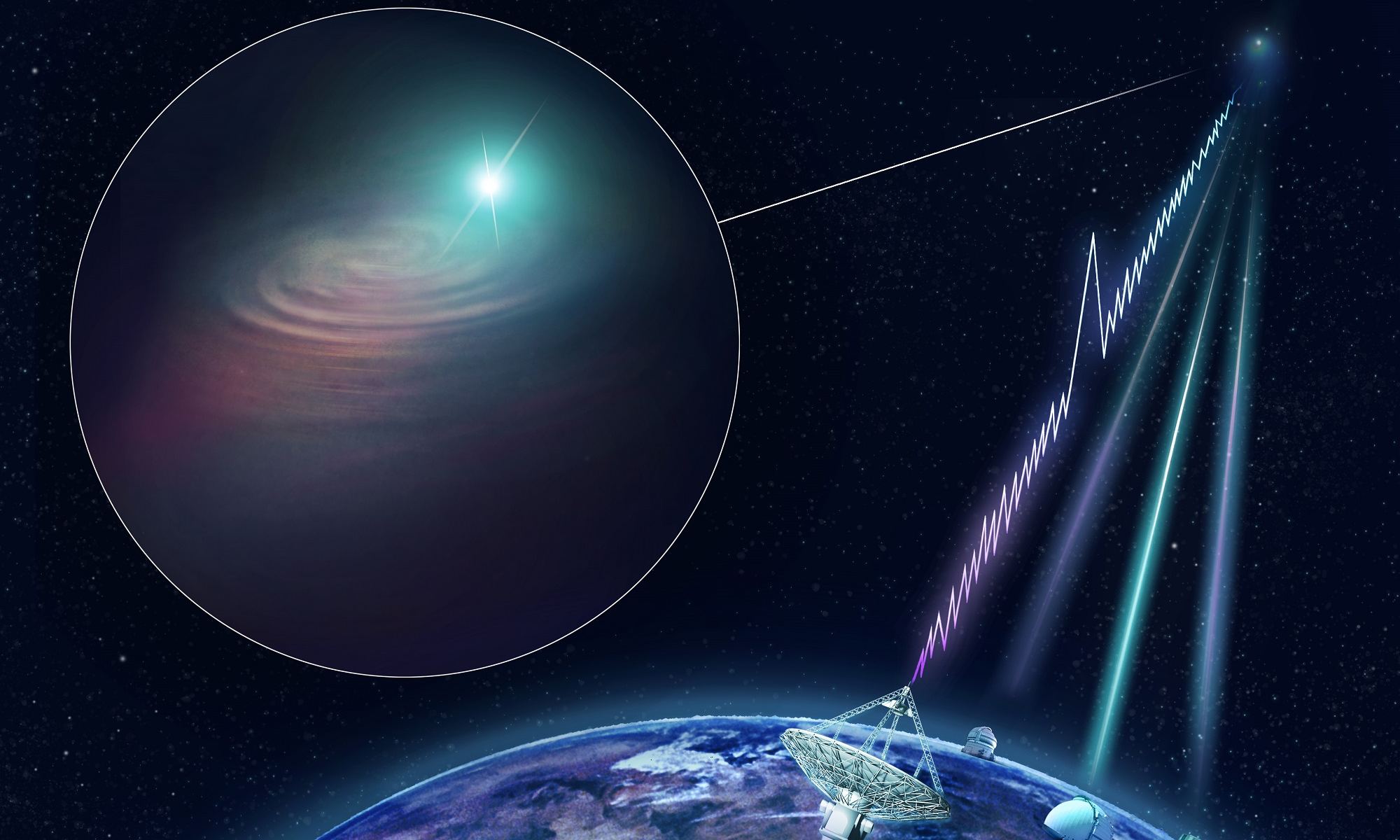
In the past few decades, astronomers have been able to look farther into the Universe (and also back in time), almost to the very beginnings of the Universe. In so doing, they’ve learned a great deal about some of the earliest galaxies in the Universe and their subsequent evolution. However, there are still some things that are still off-limits, like when galaxies with supermassive black holes (SMBHs) and massive jets first appeared.
According to recent studies from the International School for Advanced Studies (SISSA) and a team of astronomers from Japan and Taiwan provide new insight on how supermassive black holes began forming just 800 million years after the Big Bang, and relativistic jets less than 2 billion years after. These results are part of a growing case that shows how massive objects in our Universe formed sooner than we thought.
Continue reading “How were Supermassive Black Holes Already Forming and Releasing Powerful Jets Shortly After the Big Bang?”