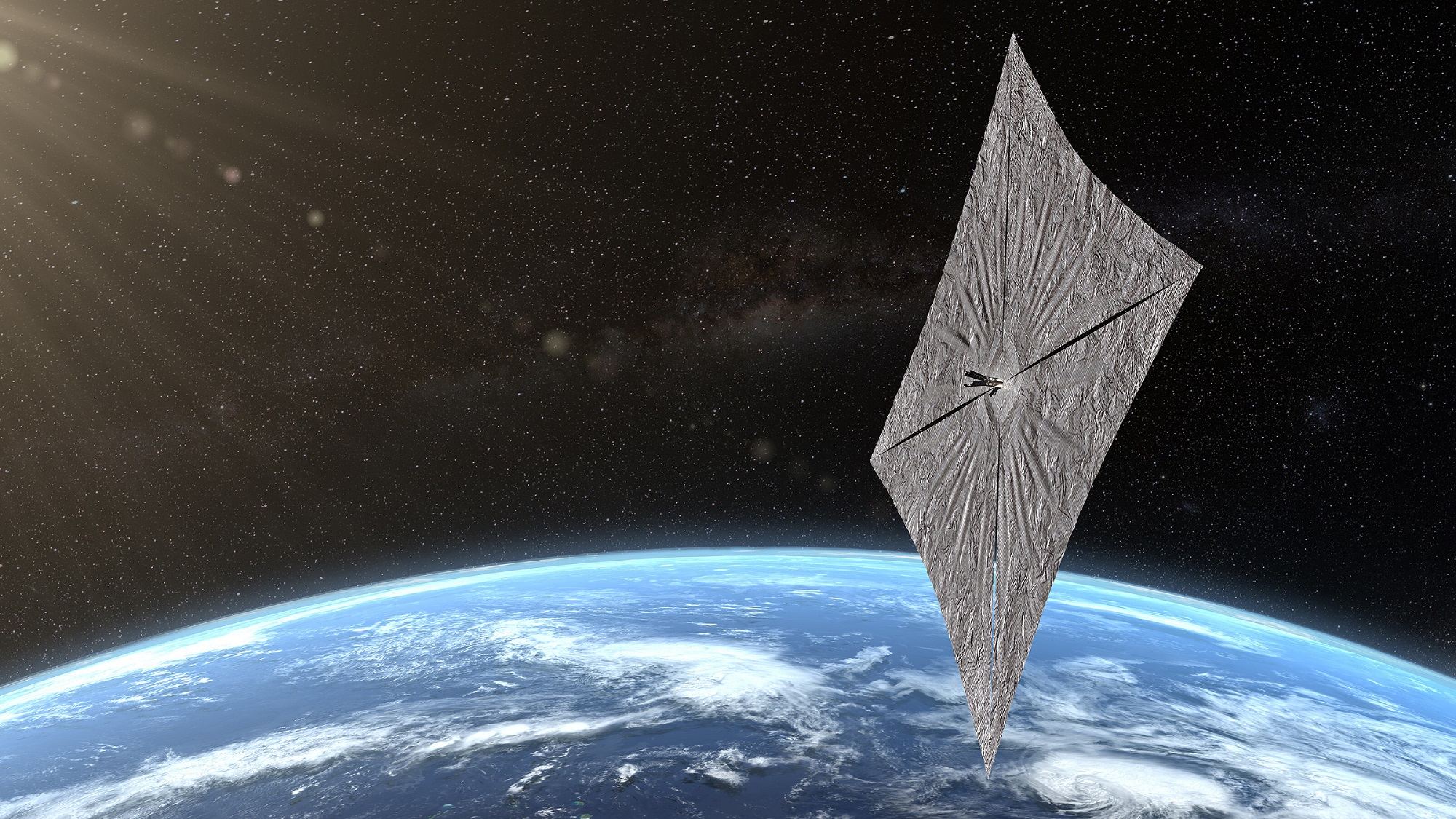
On June 25th, 2019, The Planetary Society‘s
Since reaching orbit, the LightSail 2 has been indicated that it is in good working order, as indicated by the Mission Control Dashboard recently introduced by The Planetary Society. In addition to establishing two-way communications with mission controllers and passing a battery of checkouts, the spacecraft also took its first pictures of Earth (and some selfies for good measure).
Continue reading “LightSail 2 Mission is Going Strong and Sending Mission Info Home!”