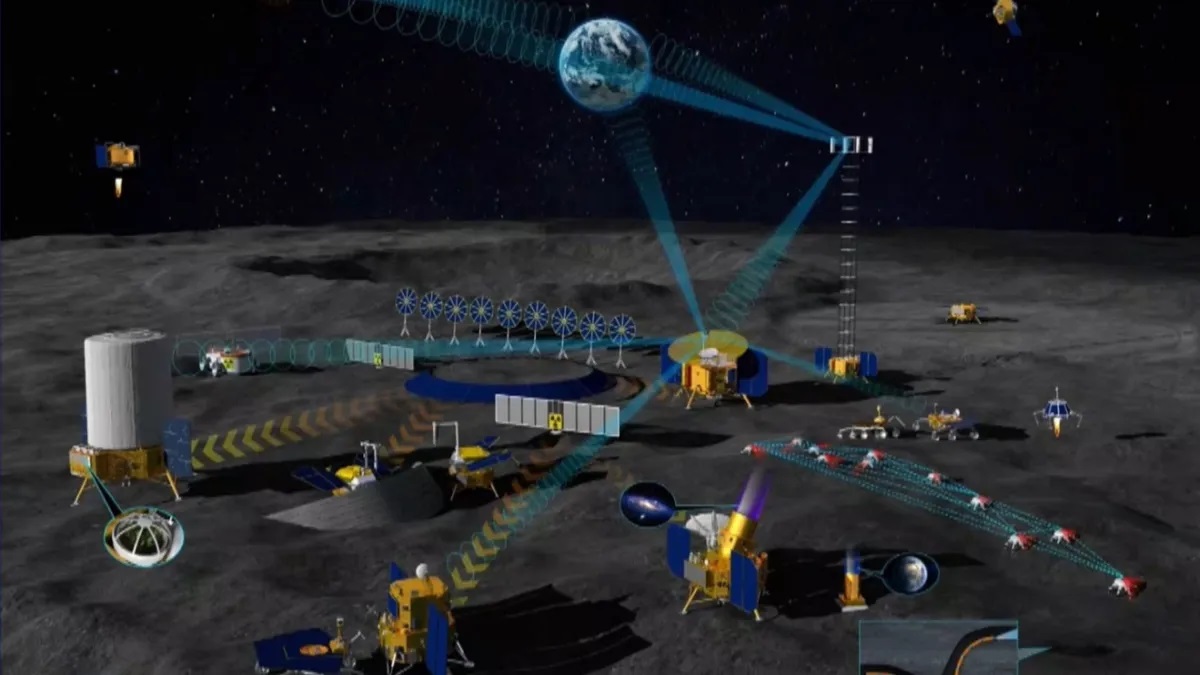
Between now and the mid-2030s, multiple space agencies hope to send crewed missions to the Moon. of These plans all involve establishing bases around the Moon’s southern polar region, including the Artemis Base Camp and the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS). These facilities will enable a “sustained program of lunar exploration and development,” according to the NASA Artemis Program mission statement. In all cases, plans for building facilities on the surface call for a process known as In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU), where local resources are used as building materials.
This presents a bit of a problem since not all lunar soil (regolith) is well-suited for construction. Much like engineering and construction projects here on Earth, builders need to know what type of soil they are building on and if it can be used to make concrete. In a recent study, planetary scientist Kevin M. Cannon proposed a lunar soil classification scheme for space resource utilization. This could have significant implications for future missions to the Moon, where it would help inform the construction of bases, habitats, and other facilities based on soil type and location.
Continue reading “Some Lunar Regolith is Better for Living Off the Land on the Moon”