Humans have long dreamed of setting foot on Mars or beyond, and the advances by companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin means perhaps the dream could be closer than ever to becoming reality. But as it stands now, sending astronauts on long-duration missions to other worlds would be impossible because of the hazardous radiation levels in space, outside of Earth’s protective magnetic field.
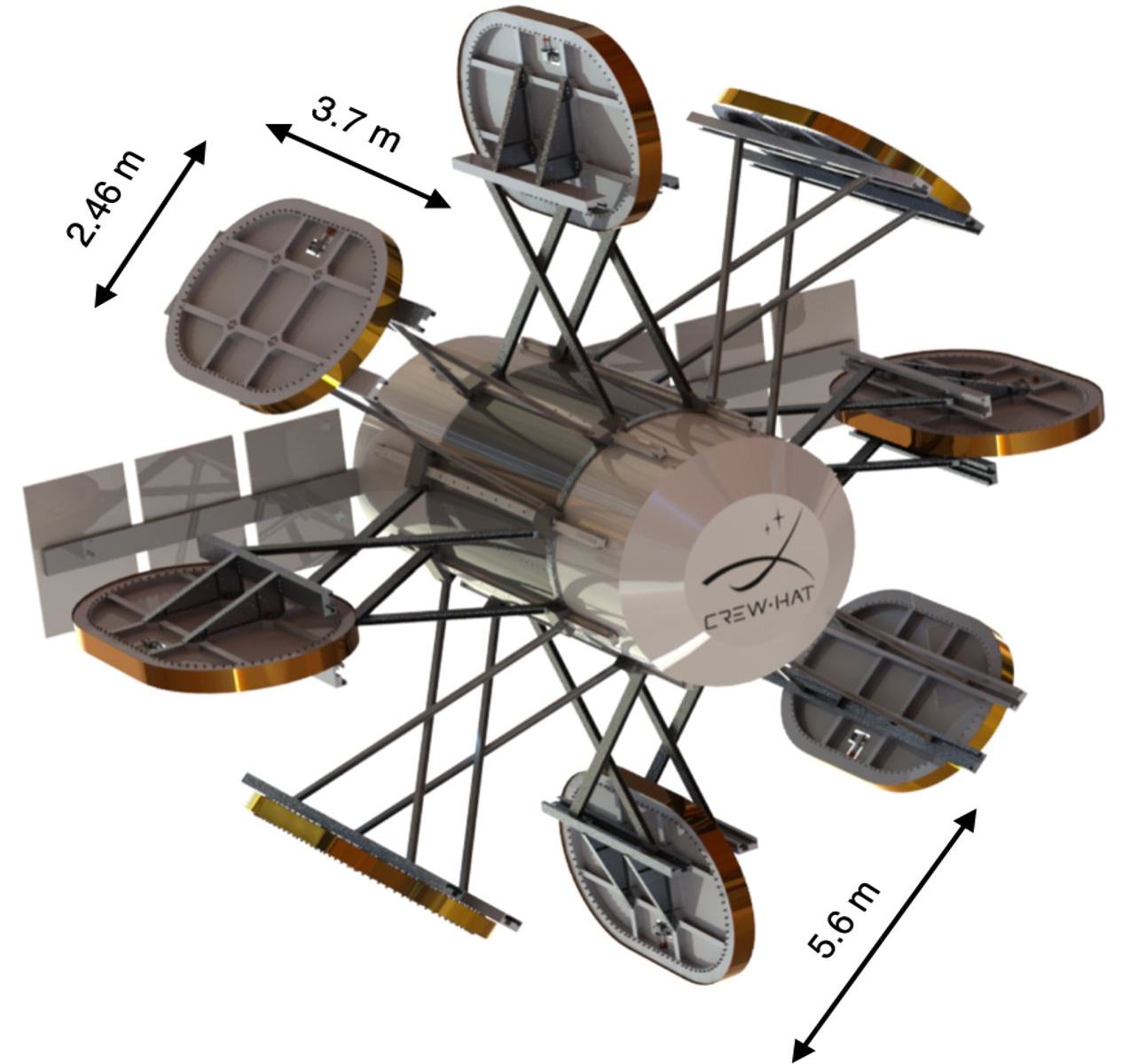
However, a new concept offers hope on the horizon, and the researchers behind it have received funding from the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program to build a prototype. Called CREW HaT, the proposal takes advantage of the latest advances in superconducting magnet technology to effectively shield spacecraft – and the astronauts inside — from harmful space radiation.
Continue reading “A Magnetic Bubble Could Protect Astronauts From Dangerous Space Radiation”