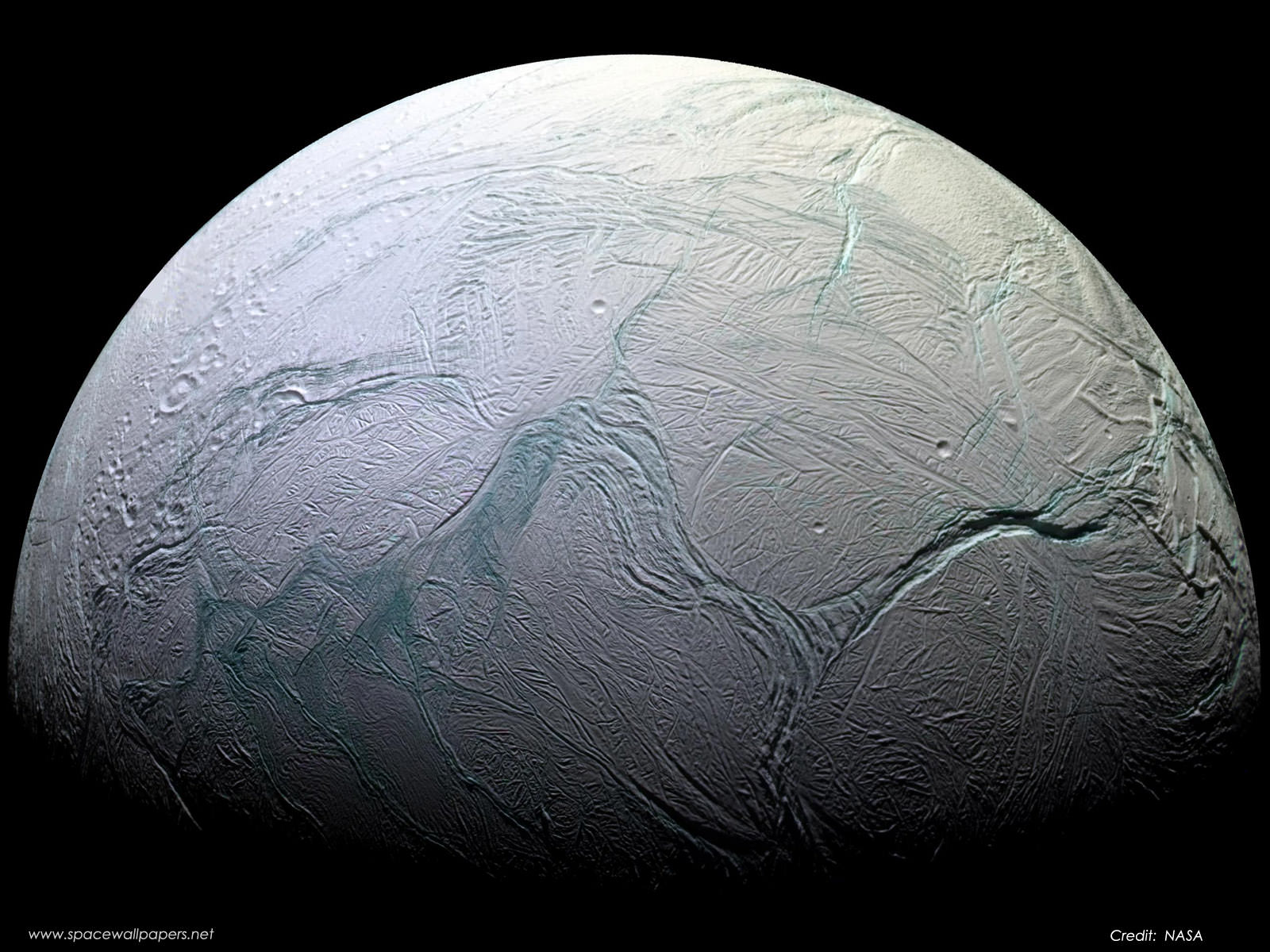
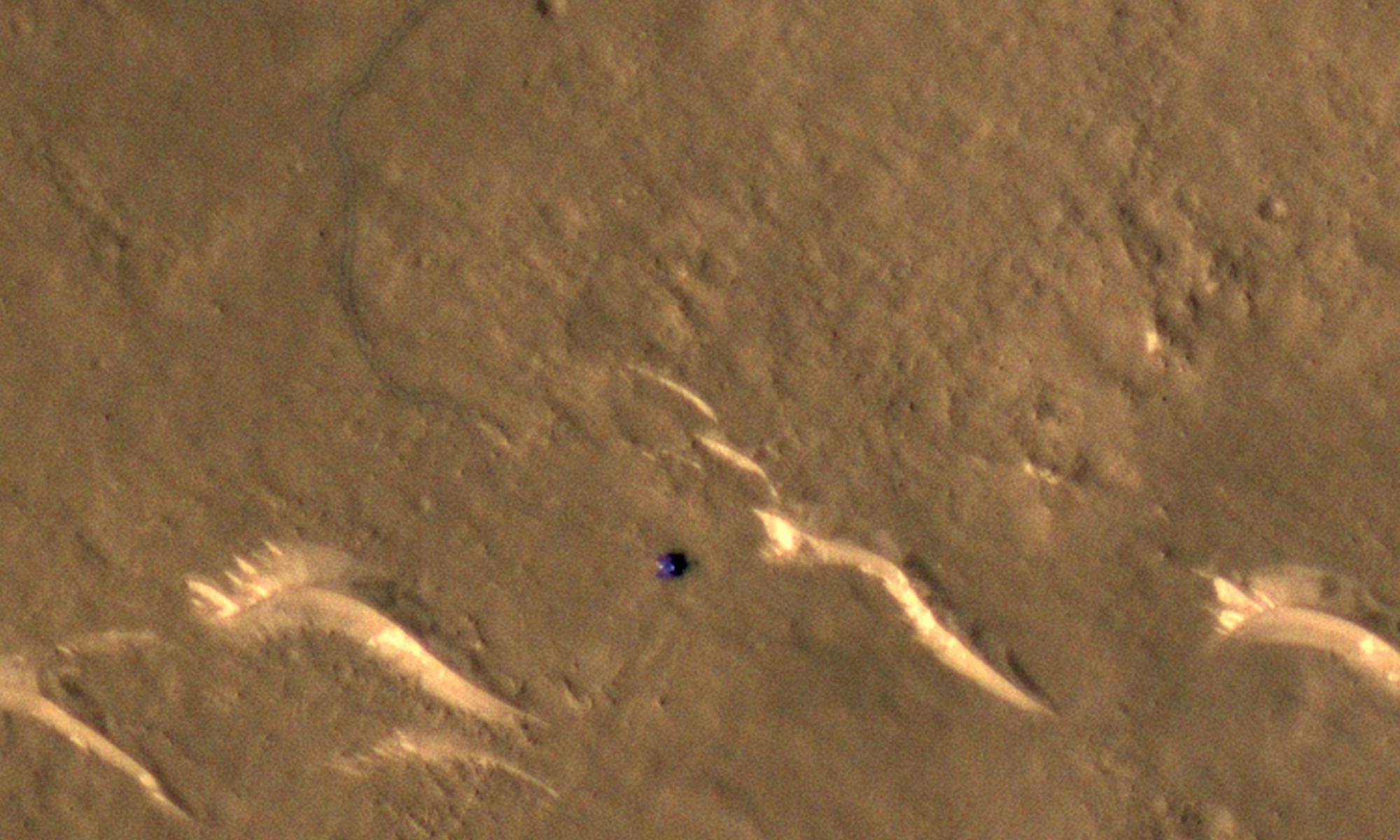
One of the biggest surprises of the 13-year Cassini mission came in Enceladus, a tiny moon with active geysers at its south pole. At only about 504 kilometers (313 miles) in diameter, the bright and ice-covered Enceladus should be too small and too far from the Sun to be active. Instead, this little moon is one of the most geologically dynamic objects in the Solar System.
A new study has modeled how this activity could be taking place, and what mechanism might power the geysers spewing from ‘tiger stripe’ fissures. While previous studies have indicated some type of unknown internal heat source on Enceladus, the new study infers no heat source would be necessary.
Continue reading “We Now Understand Why Enceladus has ‘Tiger Stripe’ Cracks at its Southern Pole”