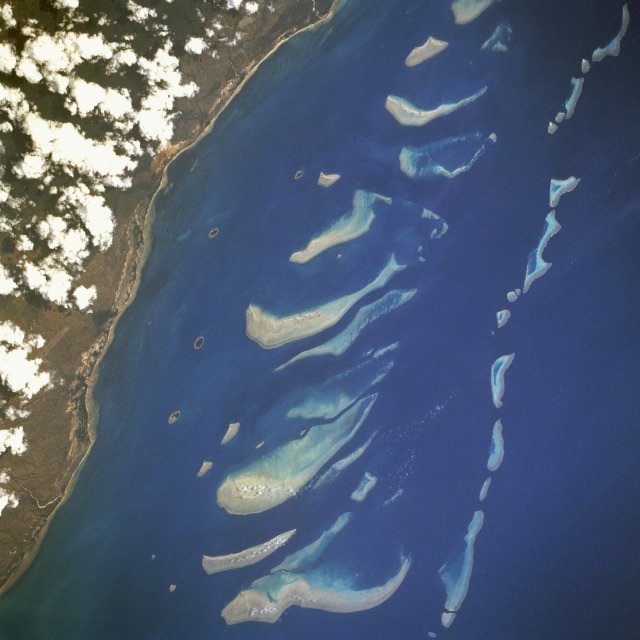
A new study found that warmer ocean temperatures driven by climate change have caused Australia’s Great Barrier Reef to lose more than half of its corals since 1995. The researchers say virtually all coral populations along the Great Barrier Reef have declined due to repeated “bleaching events” in the past 25 years. They said the devastation of the coral will continue unless action is taken to mitigate the causes of a warming climate.
Continue reading “Great Barrier Reef Has Lost Half of its Coral Over the Last 25 Years”Summer is Dust Devil Time on Mars
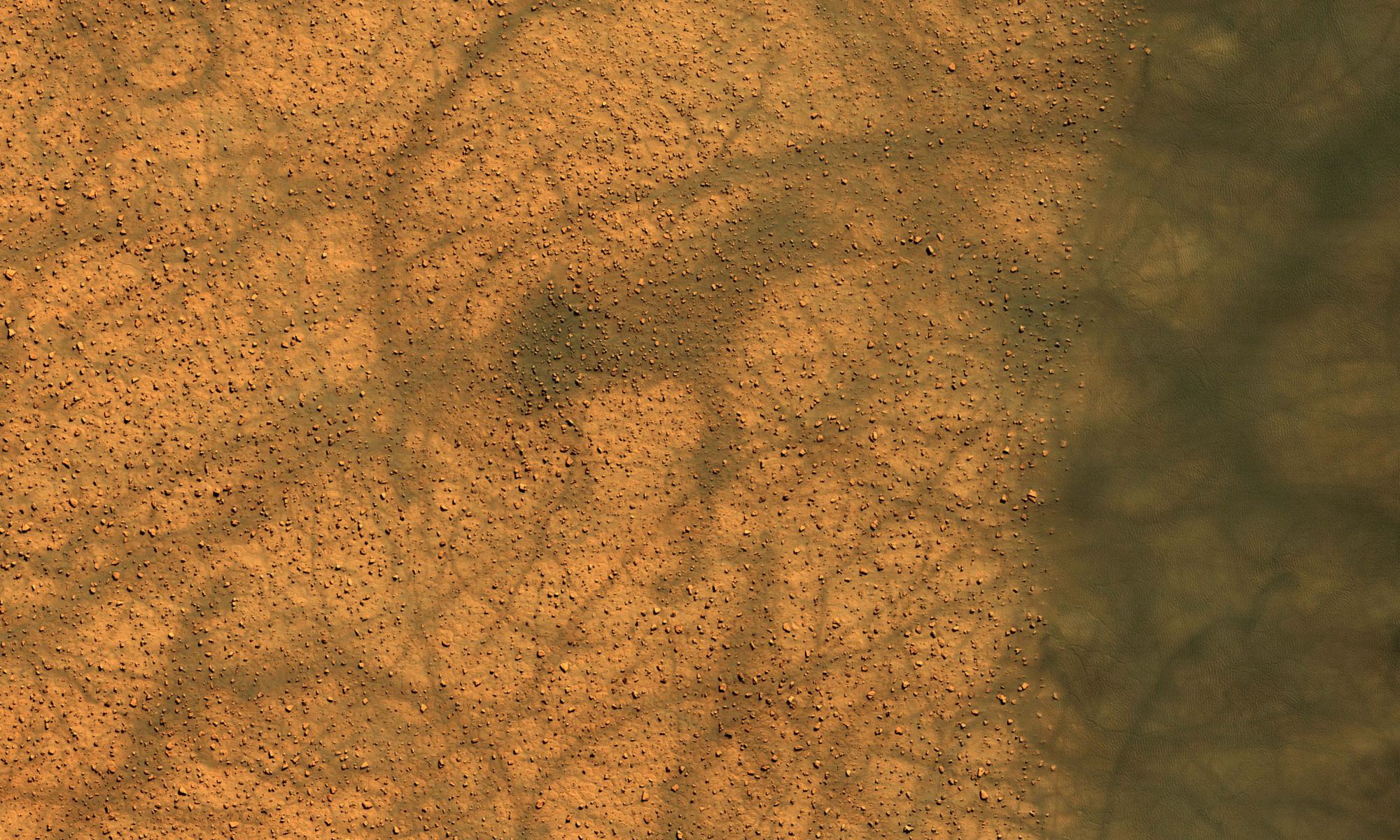
Just like Earth, Mars undergoes seasonal changes due to its axial tilt. And while summer heat on Mars can’t compare with Earth’s, along with the Martian summer warmth comes an increase in small whirling storms known as dust devils.
Continue reading “Summer is Dust Devil Time on Mars”This is a Landslide… on the Moon
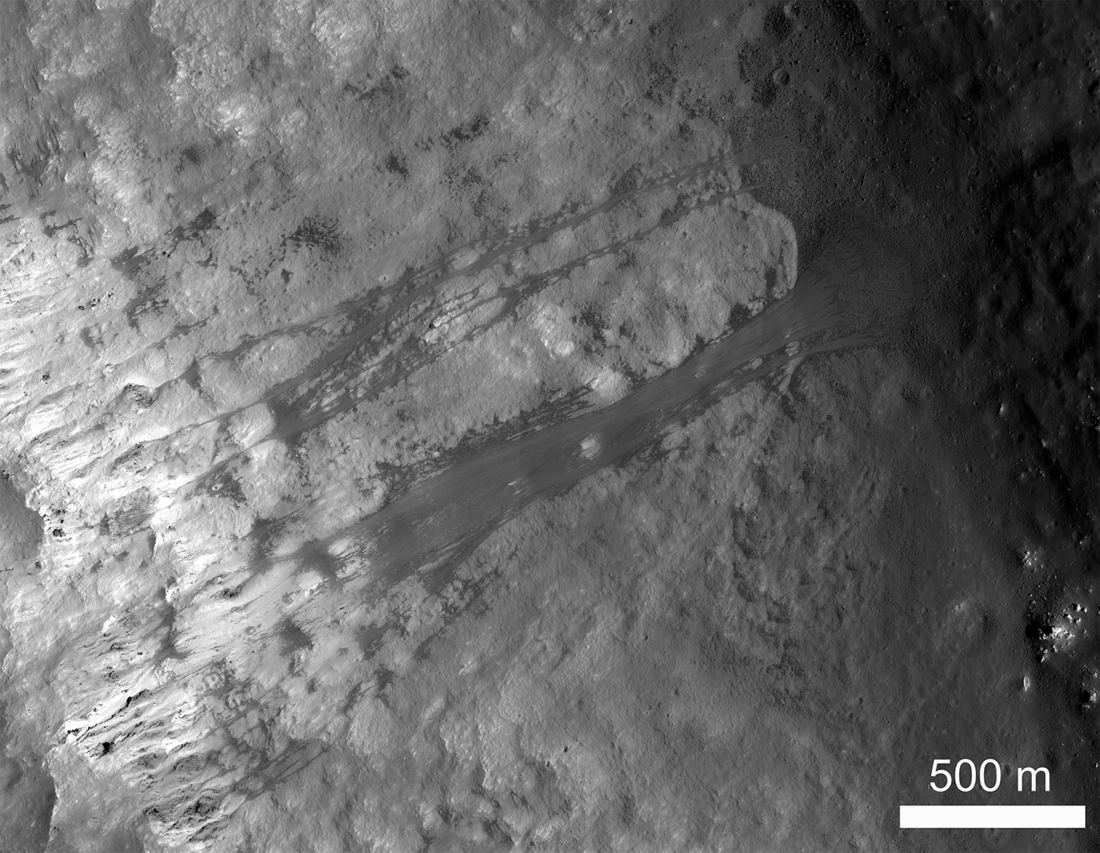

Landslides bringing you down?
Landslides can be found all across our own planet Earth, on all seven continents plus the ocean floors. Similar large mass movements have been spotted around the Solar System on rocky worlds, including our companion, the Moon.
This image from the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) shows an example of lunar landslides, with translational slides of regolith on the walls of Kepler Crater.
Continue reading “This is a Landslide… on the Moon”Simulation Helps Explain Saturn’s Mysterious Hexagon

A new study of the mysterious hexagon-shaped storm at Saturn’s north pole suggests this phenomenon is actually the result of activity occurring across the entire planet.
Continue reading “Simulation Helps Explain Saturn’s Mysterious Hexagon”The Colorful Walls of an Exposed Impact Crater on Mars
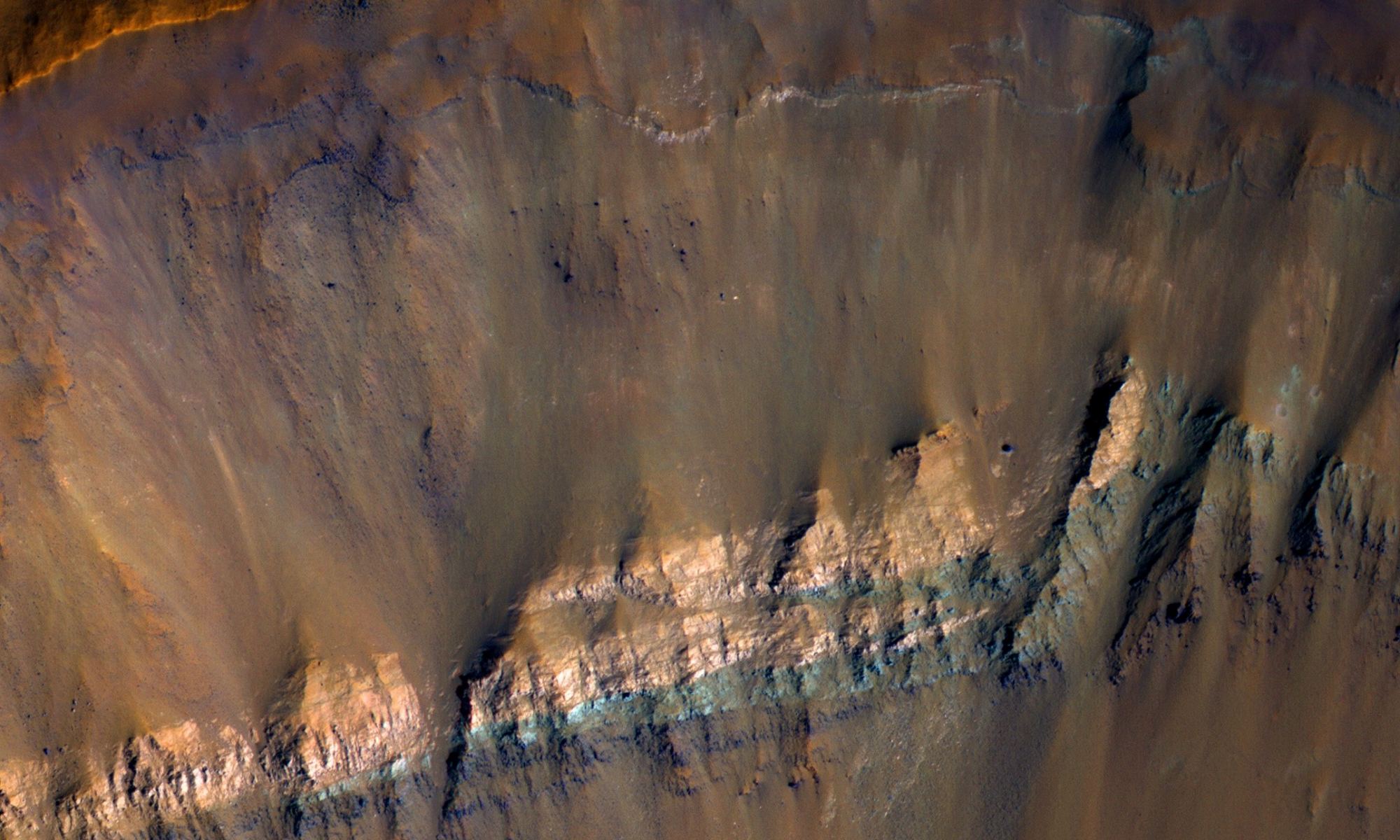

Impact craters have been called the “poor geologists’ drill,” since they allow scientists to look beneath to the subsurface of a planet without actually digging down. It’s estimated that Mars has over 600,000 craters, so there’s plenty of opportunity to peer into the Red Planet’s strata – especially with the incredible HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) camera on board the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter which has been orbiting and studying Mars from above since 2006.
Continue reading “The Colorful Walls of an Exposed Impact Crater on Mars”What the Astronauts Saw as They Orbited the Moon During Apollo 17
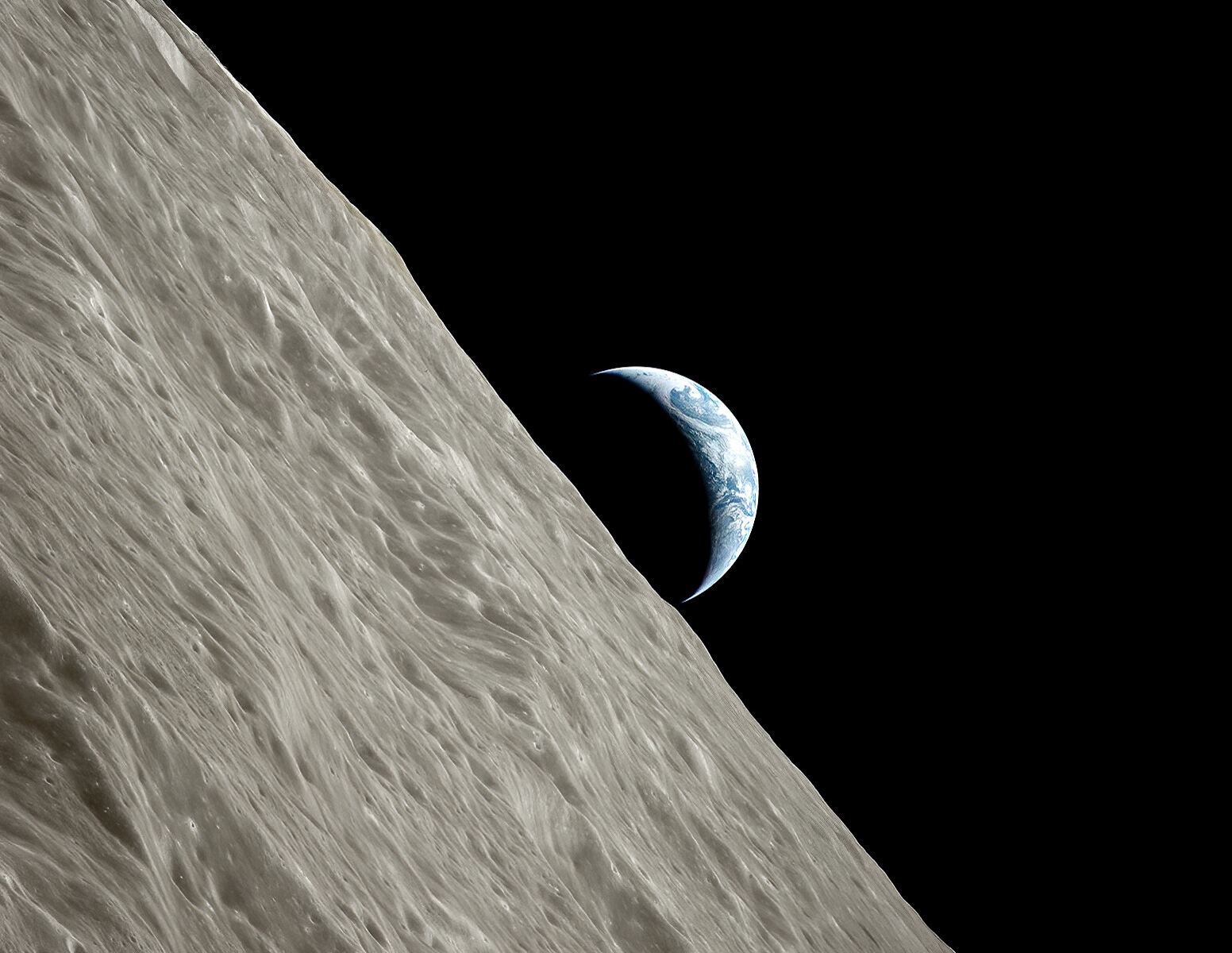

This view always gets me *right there.* But this new version really gets me.
This is what Apollo 17 astronauts saw in December of 1972 as they came around the farside of the Moon: the blue and white crescent Earth rising above the stark lunar horizon. And now image editing guru Kevin Gill has sharpened the image, giving it more texture, color and contrast. I can imagine this sharp, spectacular view must be close to what the astronauts saw with their own eyes.
“There I was, and there you are, the Earth – dynamic, overwhelming…” said Apollo 17 astronaut Gene Cernan.
Continue reading “What the Astronauts Saw as They Orbited the Moon During Apollo 17”A Galaxy has been Found That’s as Bright as a Quasar… But it’s Not a Quasar
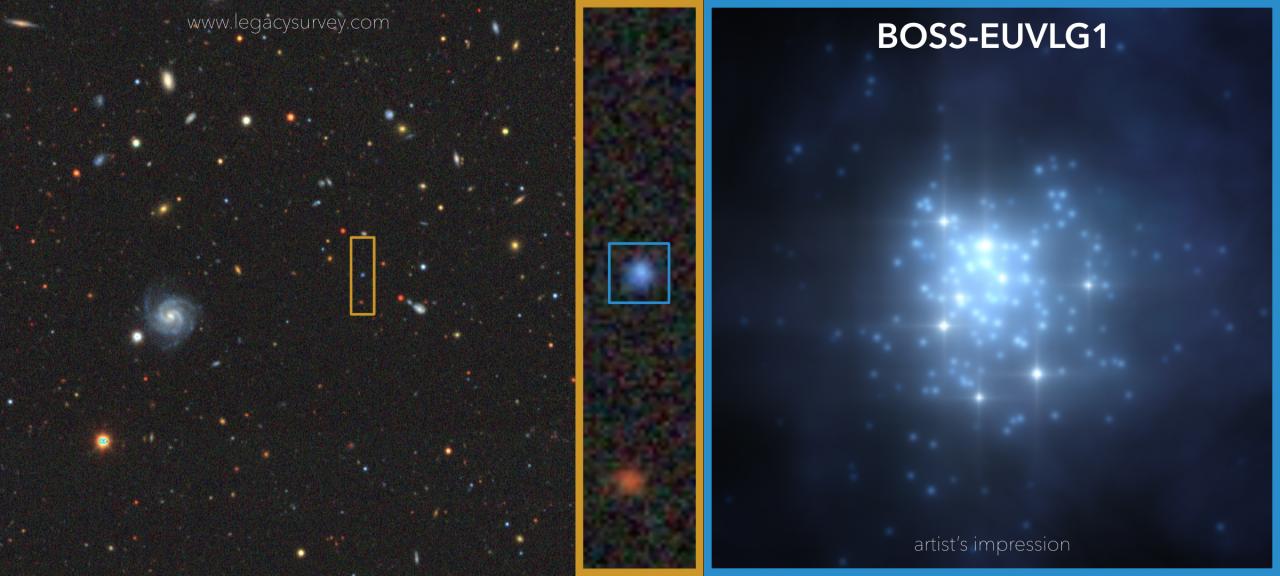
Astronomers have found a new type of galaxy that is very old, very distant and very bright in ultraviolet light. This is somewhat an unusual combination, and so when this bright galaxy was first detected, the team of researchers who found it first thought it was a quasar. But detailed study revealed it was actually a galaxy with some other unusual features, which contributes to its brightness: it is busy with star formation, it has almost no dust.
As of now, this galaxy – with the license plate-type name of BOSS-EUVLG1 – appears to be the only one of its kind.
Continue reading “A Galaxy has been Found That’s as Bright as a Quasar… But it’s Not a Quasar”We Might Have a New Mini-Moon Soon
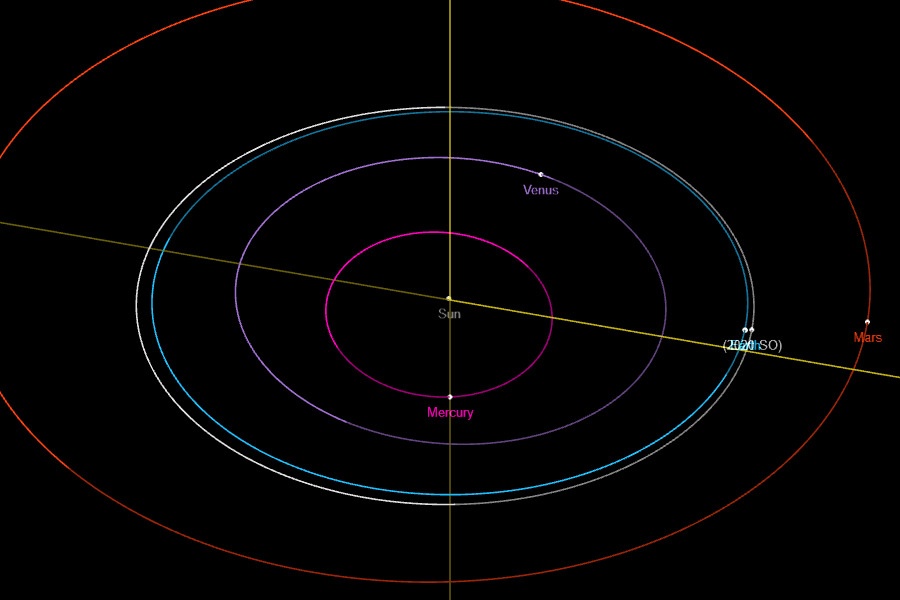
Is it a new asteroid mini–moon or a human-made mini-moon? That’s the question about a small object approaching Earth, called 2020 SO. NASA’s Small Body Database predicts the object will captured by Earth’s gravity in October 2020 and temporarily be trapped in orbit.
Continue reading “We Might Have a New Mini-Moon Soon”Video Shows a Meteoroid Skipping off Earth’s Atmosphere
Here’s something we don’t see very often: an Earth-grazing meteoroid.
On September 22, 2020, a small space rock skipped through Earth’s atmosphere and bounced back into space. The meteoroid was spotted by the by a camera from the Global Meteor Network, seen in the skies above Northern Germany and the Netherlands. It came in as low as 91 km (56 miles) in altitude – far below any orbiting satellites – before it skipping back into space.
Continue reading “Video Shows a Meteoroid Skipping off Earth’s Atmosphere”Astronauts are Getting a New Toilet Next Week
When astronauts have to go, NASA wants them to boldly go.
A new space toilet is heading to the International Space Station, with official name “Universal Waste Management System” (UWMS). (If it’s NASA, there has to be an acronym). The new toilet is smaller than the current toilets aboard the station, is more user-friendly, and includes 3-D printed titanium parts.
Continue reading “Astronauts are Getting a New Toilet Next Week”