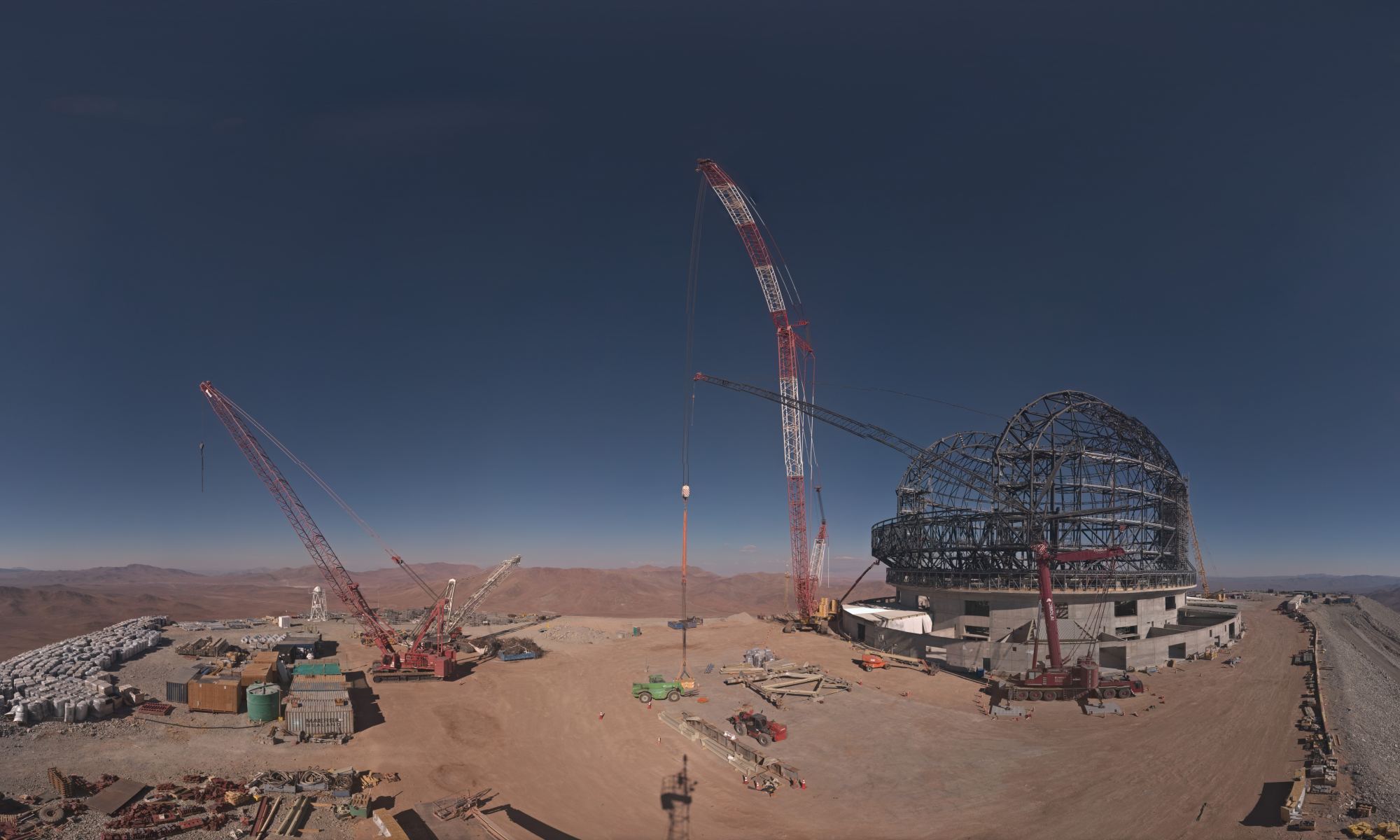
Construction of the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) reached a milestone, with the structure of the dome completed just enough where engineers were able to rotate the dome’s skeleton for the first time.
ESO released a timelapse video this week of the dome’s movement, sped up from the actual snail’s pace of 1 centimeter per second. When the telescope is completed – currently set for sometime in 2028 — the rotation of the dome will allow the telescope to track objects in the night sky over the Chilean Atacama desert. The final operating speed will be at pace of 5 kilometers per hour.
Take note of the size of the humans moving about on the video. They appear like tiny ants compared to the immense size of the aptly named ELT.
Continue reading “The Extremely Large Telescope’s Dome is on the Move”