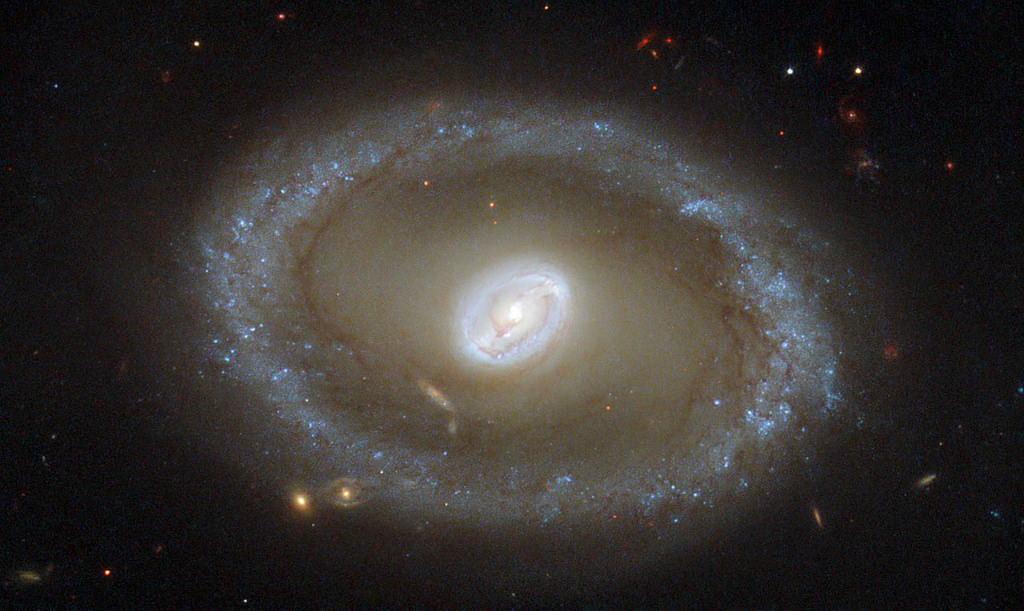
Let’s just casually look at this image of a galaxy 86 million light-years away from us. In the center of this incredible image is a bright loop that you can see surrounding the heart of the galaxy. That is where stars are being born, say the scientists behind this new Hubble Space Telescope image.
“Compared to other spiral galaxies, it looks a little different,” NASA stated. “The galaxy’s barred spiral center is surrounded by a bright loop known as a resonance ring. This ring is full of bright clusters and bursts of new star formation, and frames the supermassive black hole thought to be lurking within NGC 3081 — which glows brightly as it hungrily gobbles up in-falling material.”
A “resonance ring” refers to an area where gravity causes gas to stick around in certain areas, and can be the result of a ring (like you see in NGC 3081) or close-by objects with a lot of gravity. Scientists added that NGC 3081, which is in the constellation Hydra or the Sea Serpent, is just one of many examples of barred galaxies with this type of resonance.
By the way, this image is a combination of several types of light: optical, infrared and ultraviolet.
Source: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center