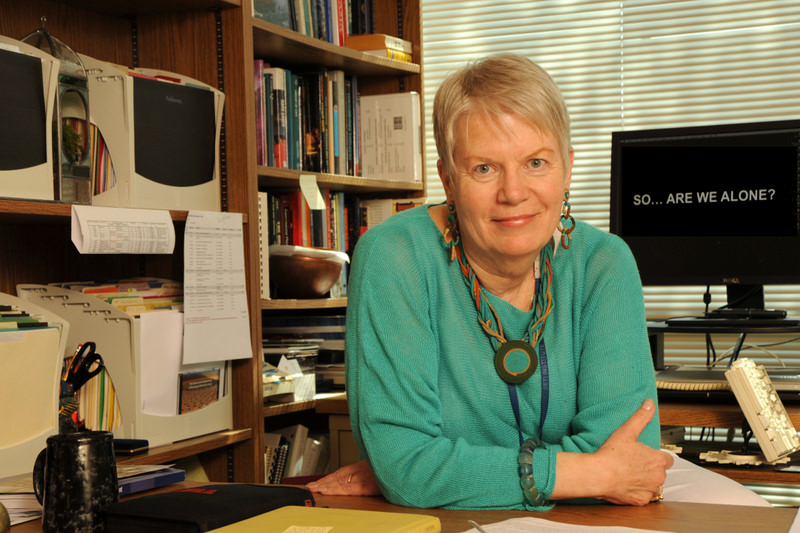
In 1985, famed astronomer, author and TV host Carl Sagan invited Jill Tarter to dinner at his house near Cornell University. Tarter, heavily involved with the Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence, gladly accepted the chance to speak with Sagan, a member of SETI’s board of trustees.
Seated with Sagan and his wife, Ann Druyan, Tarter learned that Sagan had a fiction book on the go.
“Annie said, ‘You may recognize someone in the book, but I think you’ll like her,'” Tarter recalled in an interview with Universe Today.
Suspecting the character was based on herself, Tarter’s response to Druyan was: “‘Just make sure she doesn’t eat ice cones so much.’ It was something I was teased about.”
Female, in a male-dominated field
It was 15 years ago this month that the movie Contact, based on Sagan’s book of the same title, expanded to a run in international theatres after a successful summer in North America. The movie explores the implication of aliens making contact with Earth, but does it from more of a scientific perspective than most films.
While Contact, the movie did not talk about the pi sequences or advanced mathematical discussions in Contact, the book, it did bring concepts such as prime numbers, interference with radio telescopes, and the religion vs. science debate to theatres in 1997.
Tarter, who has just retired as the long-time director of the SETI Institute, said she was stunned by the parallels between her own life and that of Ellie Arroway, the character based on her in Contact. Both lost parents at an early age. Both also had to make their way in a field aggressively dominated by males.
Tarter recalls a meeting with fellow female scientists of her generation some years ago.
“A huge percentage of us had been, in high school, either cheerleaders or drum majorettes. This is so counterintuitive, right? Because we’re the nerds, we’re the brainy ones … (it was because) we were all competitors, and there weren’t any (female) sports to compete at. These sports were open, and we competed, and we generally won.”
Working on set
Tarter cautions the parallels did not totally match. The hopes and aspirations of Ellie in the book, and also the movie, were products of Sagan’s imagination. But the producers and actors of the film did want to get a close sense of what it was like to work with SETI.
After Jodie Foster was cast as Ellie, there were multiple phone calls between the actress and Tarter to discuss SETI.
“From her point of view, she was clear she wasn’t going to teach anyone astronomy. She was interested, in a personal way, about what the scientists were like,” Tarter said.
When the crew was filming at the Arecibo Observatory in Puerto Rico, Tarter flew there to observe the work, meet with Foster and also show the actress around. Tarter recalls bringing Foster up in a cabin that had a perfect view of the telescope, some 500 feet above the dish.
Microphones and walkie-talkies
Filming was an interesting process for Tarter, as well. There were the microphones, and the tools the crew used to check continuity. Most amusingly for Tarter, she observed Foster (reported height 5 feet, 2 inches) needing to stand on a box for most of the close-up shots with actor Matthew McConaughey (reported as 6 feet tall).
Two errors still irk Tarter today. There is a scene when Ellie gives a modified version of the Drake Equation, which calculates the odds of intelligent life who are capable of communicating with other life forms, and the calculations are all wrong. “It’s really infuriating,” Tarter said.
The other large mistake is a scene where Ellie gets a potential signal from space, while working at the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array set of radio telescopes in New Mexico.
“She’s sitting in the middle of the array, in a car, with her laptop, and she gets the signal. And the first thing she does is pick up a walkie-talkie and start broadcasting. That signal is going to wipe out the signal from the sky. You don’t transmit by walkie-talkie.”
But overall, Tarter said the movie did a great job at portraying the feel of SETI. And Foster appreciated Tarter’s help. “She would write me handwritten thank-you notes, which was a kind of manner that most people have lost. A great courtesy.”
Hollywood outreach
Tarter walked the red carpet at the movie premiere and spent most of her time watching the film in tears of happiness. That euphoria evaporated when she saw the SETI Institute was not credited at the end of the film. When she talked to one of the film producers, she said she was informed that lawyers usually draft agreements specifying the length of time the credit appears, and the compensation received for doing so.
“We don’t have a lawyer at the SETI Institute,” she said. “When I write a paper, I acknowledge my collaborators. We got that wrong, so we never got any credit. We might have gotten even more recognition.”
But the professional connection with Foster still remains. Foster happily responded to a request from Tarter to do voice-overs for a video clip used for a SETI high school curriculum for integrated science. She also narrated a show, Life: A Cosmic Story, for the California Academy of Sciences Morrison Planetarium.
Tarter is now shifting into full-time outreach for SETI, saying the budgetary problems that shut down the organization’s Allen Telescope Array for several months last year were a warning call.
One of the organization’s newest initiatives is SETILive.org, which crowdsources analysis of signals from the Kepler Field. SETI solicits the public to take some time looking at the signal patterns, one at a time, in search of extraterrestrial communications.
“SETI is too important to allow it to fail,” Tarter said, adding her focus is finding substantial, stable funding from “that individual or institution that is capable of taking a long view.”