We do not yet know how, where, or why life first appeared on our planet. Part of the difficulty is that “life” has no strict, universally agreed-upon definition.
Continue reading “The Improbable Origins of Life on Earth”The Galactic Habitable Zone
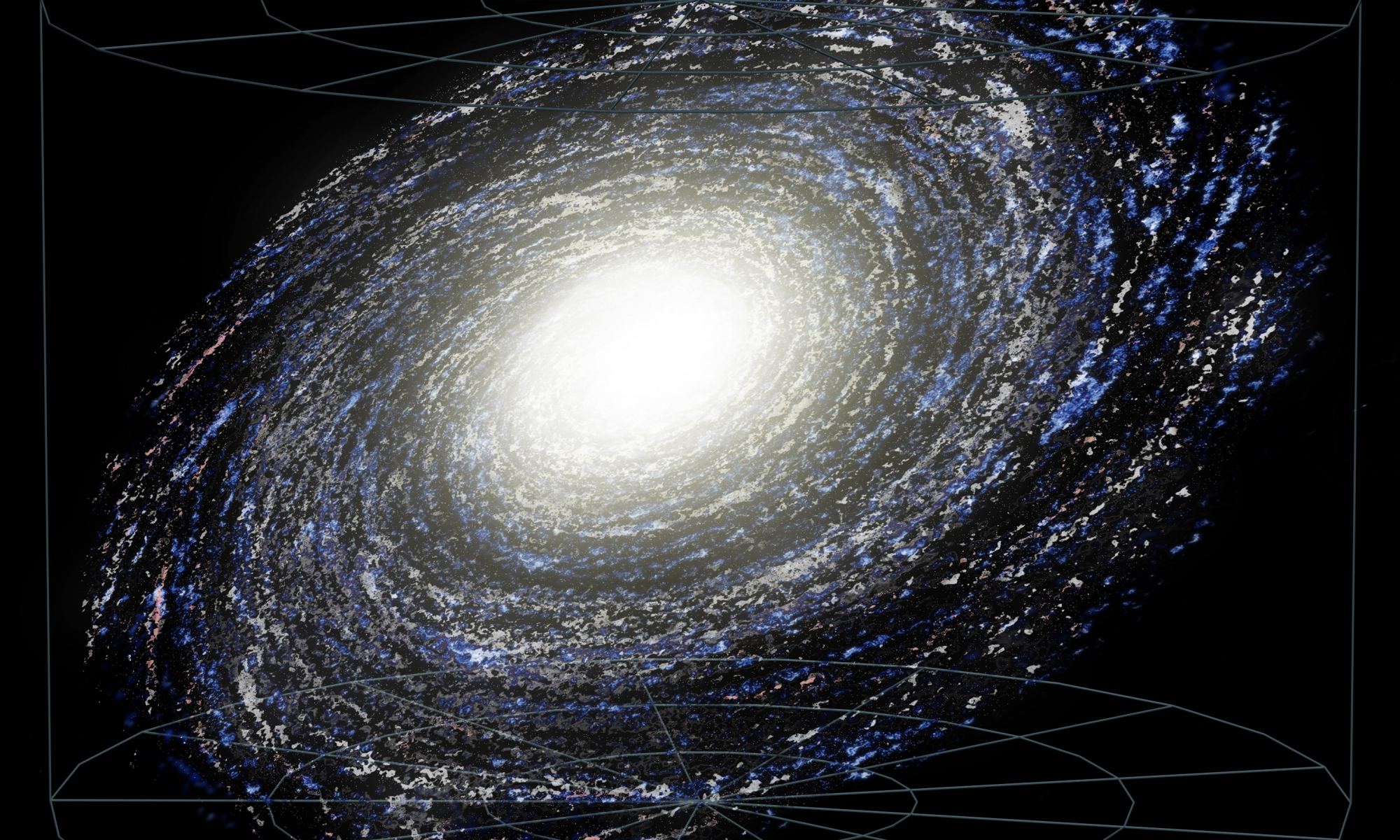
Our planet sits in the Habitable Zone of our Sun, the special place where water can be liquid on the surface of a world. But that’s not the only thing special about us: we also sit in the Galactic Habitable Zone, the region within the Milky Way where the rate of star formation is just right.
Continue reading “The Galactic Habitable Zone”Early Life Was Radically Different Than Today

All modern life shares a robust, hardy, efficient system of intertwined chemicals that propagate themselves. This system must have emerged from a simpler, less efficient, more delicate one. But what was that system, and why did it appear on, of all places, planet Earth?
Continue reading “Early Life Was Radically Different Than Today”Why Venus Died
Venus is only slightly smaller than the Earth, and so has enjoyed billions of years of a warm heart. But for this planet, sometimes called Earth’s sister, that heat has betrayed it. That planet is now wrapped in suffocating layers of a poisonous atmosphere made of carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid. The pressures on the surface reach almost 100 times the air pressure at Earth’s sea level. The average temperatures are over 700 degrees Fahrenheit, more than hot enough to melt lead, while the deepest valleys see records of over 900 degrees.
Continue reading “Why Venus Died”Why Mars Died
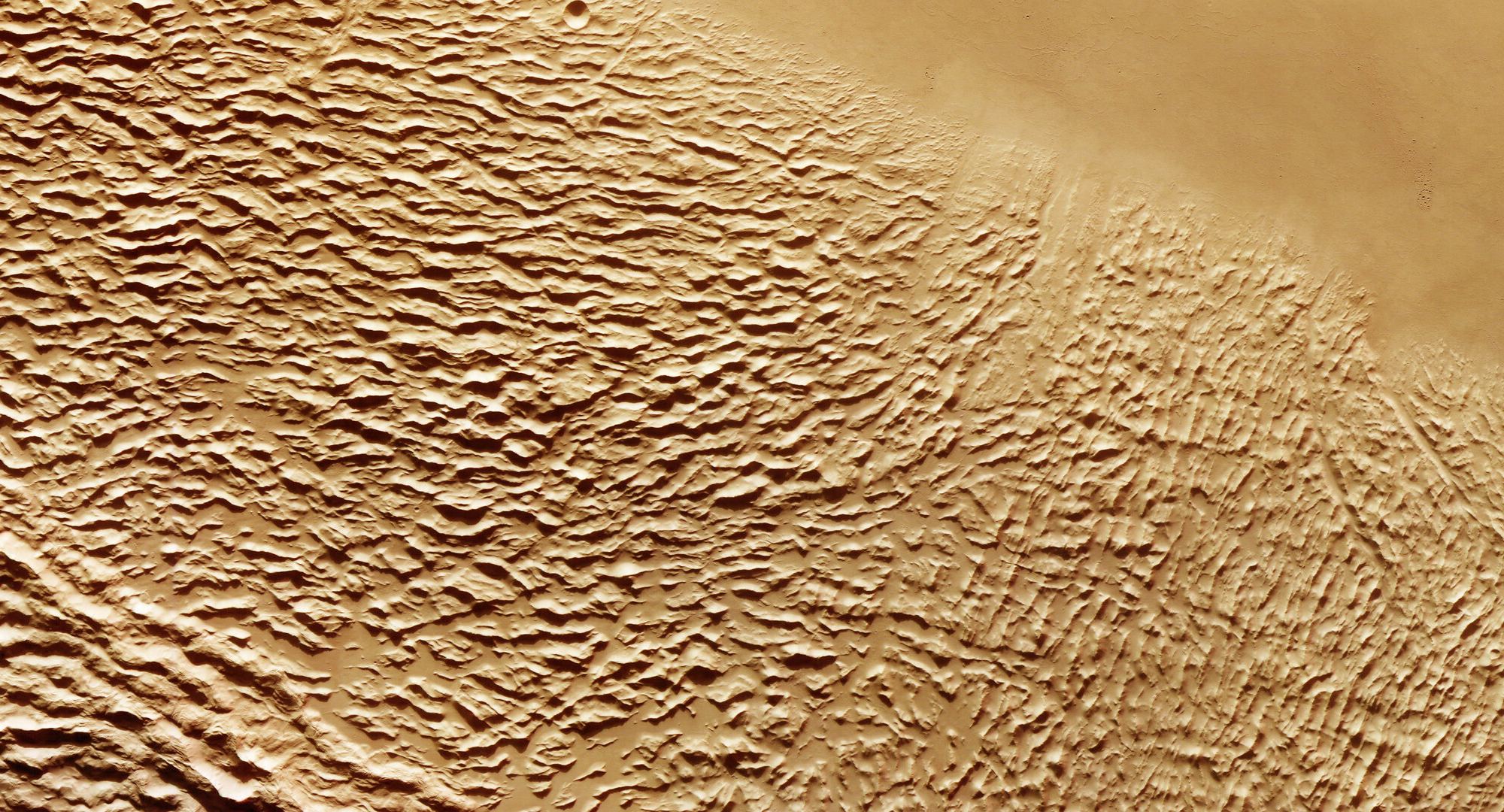

We know of Mars as the Red Planet, for its surface and atmosphere is caked in endless swirling dust of rusted iron, the rusting action provided by the always-eager oxygen. But this was not always so.
Continue reading “Why Mars Died”Thirsty? Water is More Common than you Think

Water is the most common chemical molecule found throughout the entire universe. What water has going for it is that its constituents, hydrogen and oxygen, are also ridiculously common, and those two elements really enjoying bonding with each other. Oxygen has two open slots in its outmost electron orbital shell, making it very eager to find new friends, and each hydrogen comes with one spare electron, so the triple-bonding is a cinch.
Continue reading “Thirsty? Water is More Common than you Think”Why Quantum Mechanics Defies Physics
The full, weird story of the quantum world is much too large for a single article, but the period from 1905, when Einstein first published his solution to the photoelectric puzzle, to the 1960’s, when a complete, well-tested, rigorous, and insanely complicated quantum theory of the subatomic world finally emerged, is quite the story.
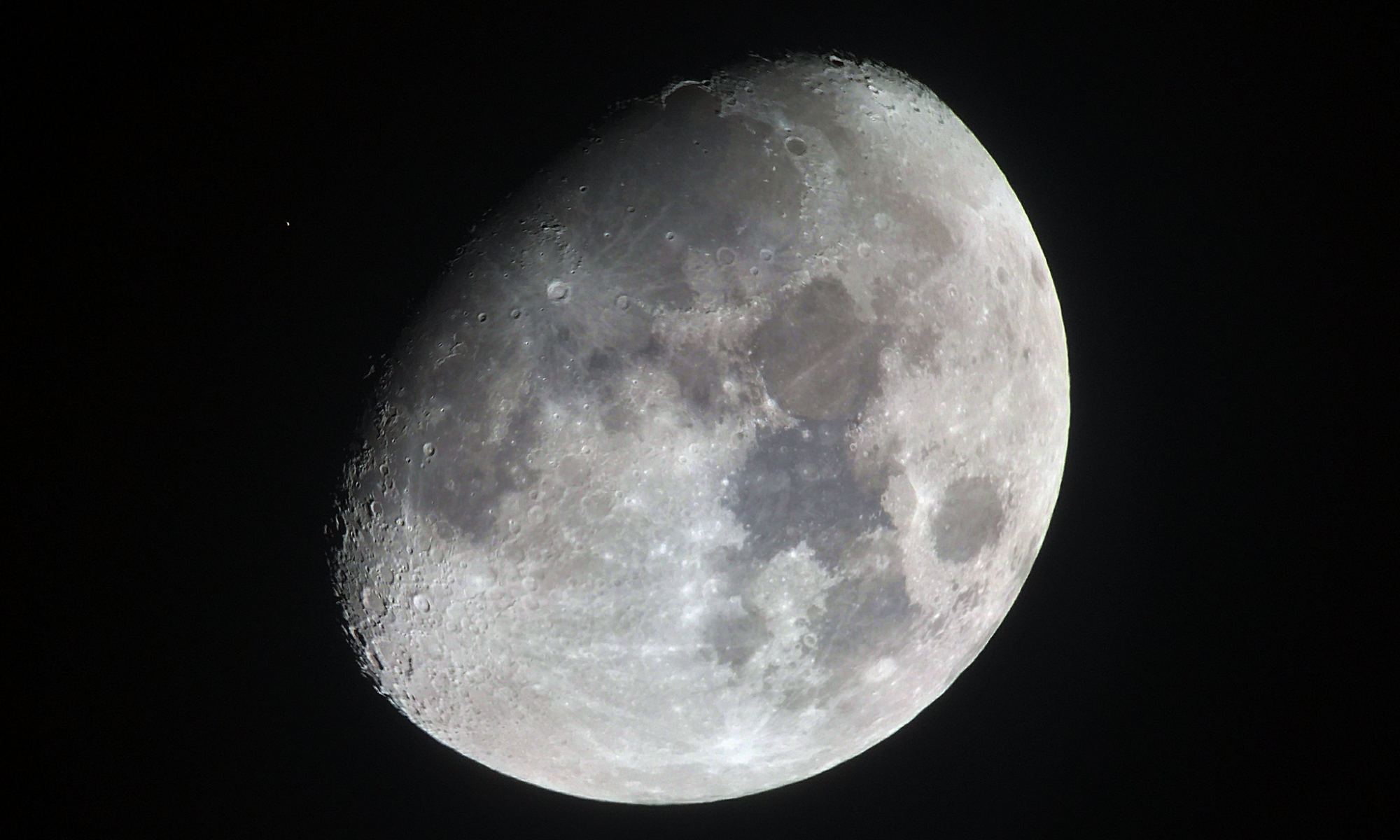
Continue reading “Why Quantum Mechanics Defies Physics”We Owe Our Lives to the Moon
Life appeared on Earth through a series of lucky coincidences, and that luck started with our Moon. None of the other planets of the inner solar system have significant moons. Space is lonely around Mercury and Venus. Mars does have two small moons, Phobos and Deimos (Fear and Despair, befitting companions for the God of War), but those are simply captured asteroids, lassoed in the not-too-distant past and doomed to eventually come close enough to their unloving parent to be torn to shreds by gravitational forces.
Continue reading “We Owe Our Lives to the Moon”How Supersymmetry Saved String Theory
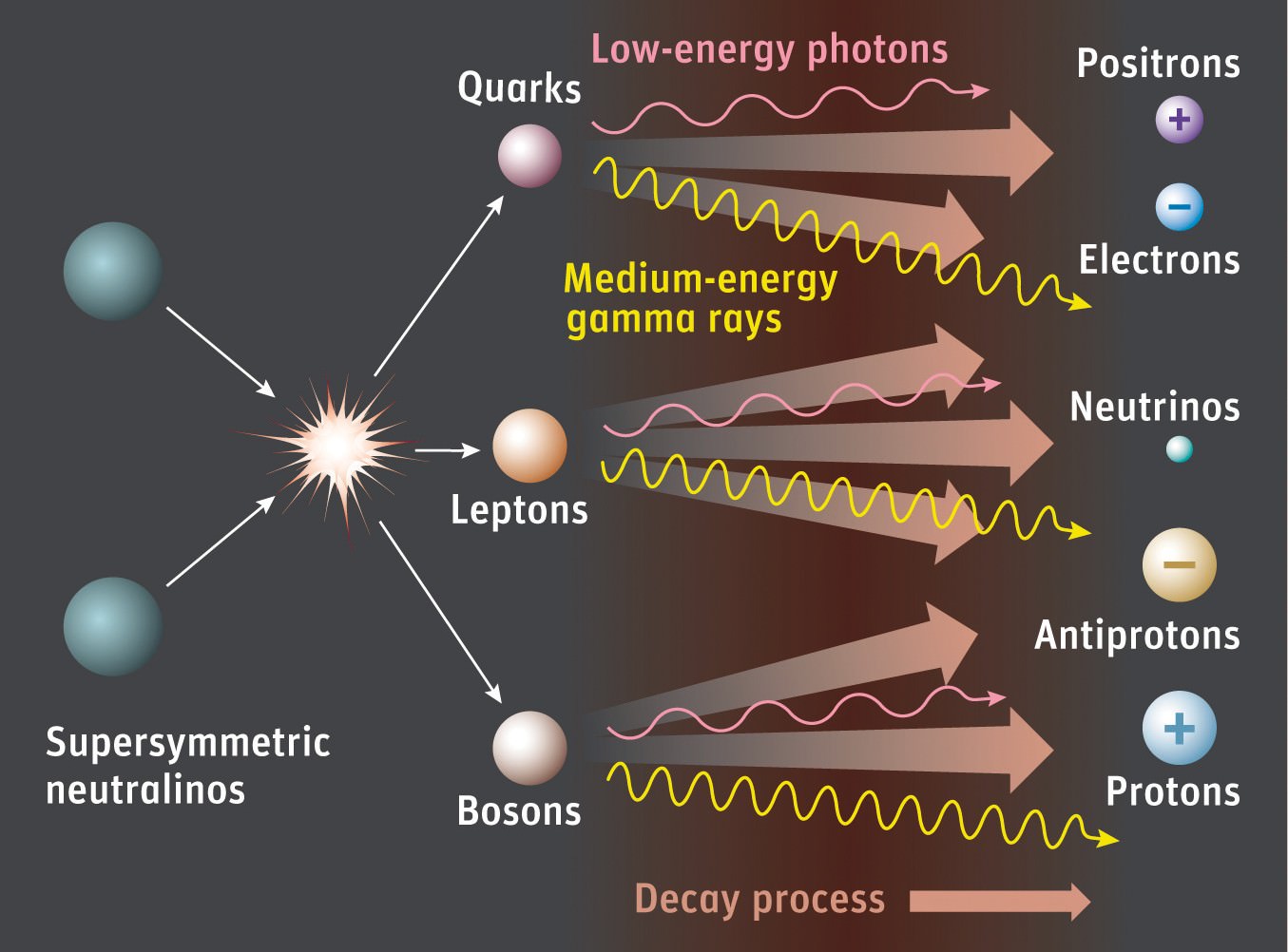
String theory, like most revolutions, had humble origins. It started all the way back in the 1960’s as an attempt to understand the workings of the strong nuclear force, which had only recently been discovered. Quantum field theory, which had been used successfully to explain electromagnetism and the weak nuclear force, wasn’t seeming to cut it, and so physicists were eager for something new.
Continue reading “How Supersymmetry Saved String Theory”Holograms Might Save Physics
Even though the guts of General Relativity are obtusely mathematical, and for decades was relegated to math departments rather than proper physics, you get to experience the technological gift of relativity every time you navigate to your favorite restaurant. GPS, the global positioning system, consists of a network of orbiting satellites constantly beaming out precise timing data. Your phone compares those signals to figure out where you are on the Earth. But there is a difference in spacetime between the surface of the Earth and the orbit of the satellites. Without taking general relativity into account, your navigation would simply be incorrect, and you’d be late for dinner.
Continue reading “Holograms Might Save Physics”




