If you want to know where you are in space, you’d better bring along a map. But it’s a little more complicated than riding shotgun on a family road trip.
Spacecraft navigation beyond Earth orbit is usually carried out by mission control. A series of radio communication arrays across the planet, known as the Deep Space Network, allows operators to check in with space probes and update their navigational status. The system works, but it could be better. What if a spacecraft could autonomously determine its position, without needing to phone home? That’s been a dream of aerospace engineers for a long time, and it’s getting close to fruition.
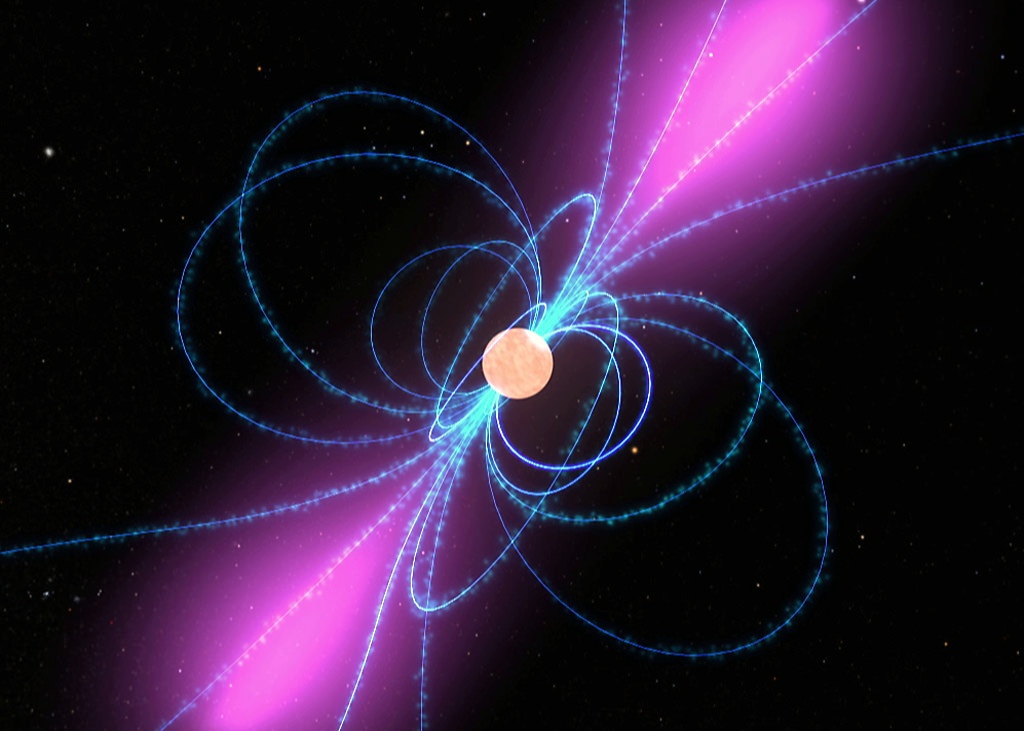
Pulsars are the key.
Continue reading “Soon Every Spacecraft can Navigate the Solar System Autonomously Using Pulsars”