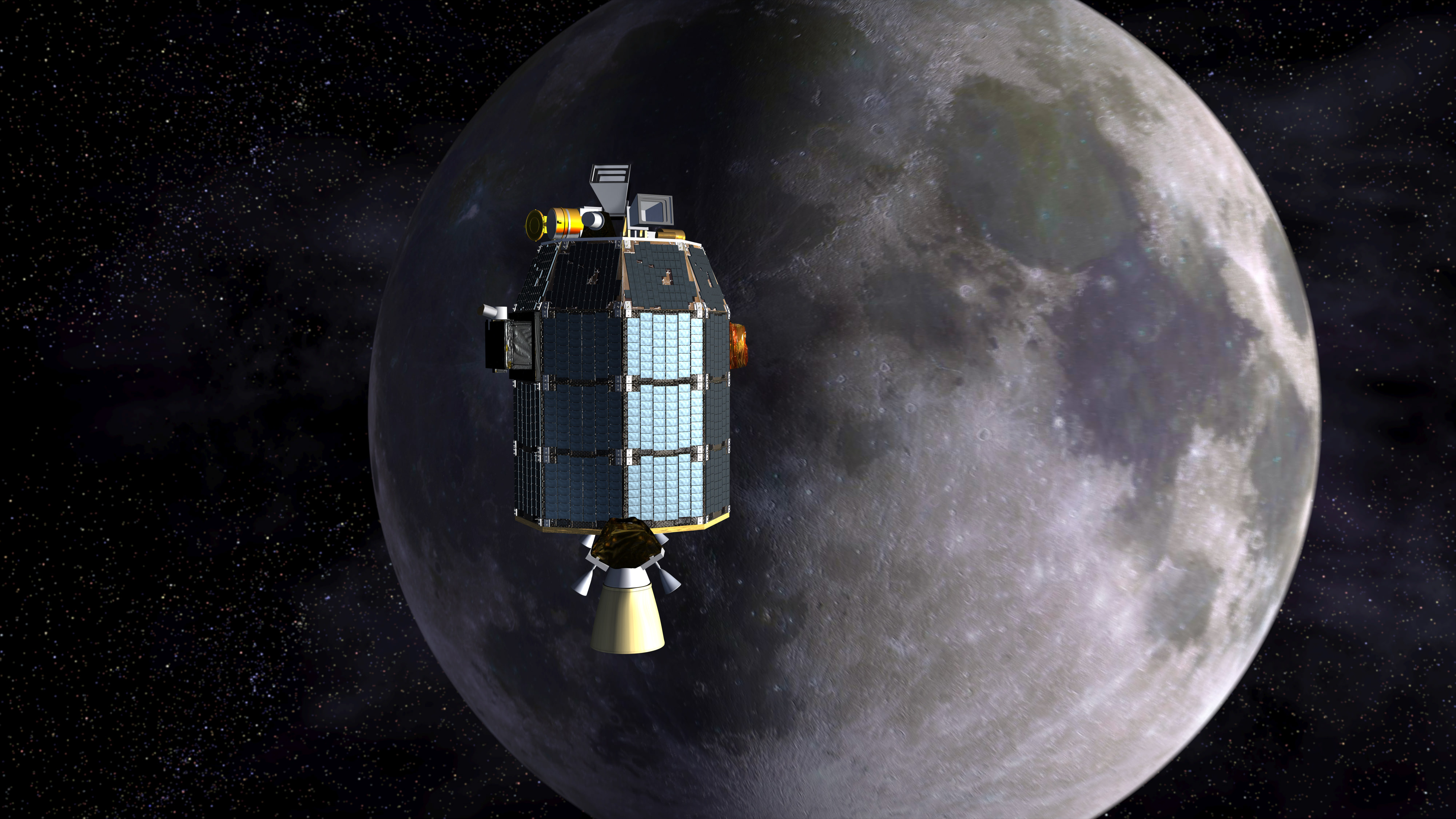
Depiction of NASA’s Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) observatory as it approaches lunar orbit.Credit: NASA Ames/Dana Berry
LADEE will now orbit far lower than ever before – details below![/caption]
LADEE, NASA’s latest lunar orbiter, is getting a new lease on life and will live a little longer to study the mysteries of the body’s tenuous atmosphere, or exosphere, and make surprising new discoveries while hugging Earth’s nearest neighbor even tighter than ever before, the team told Universe Today.
NASA has announced that the Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) mission will be granted a month long extension since the residual rocket fuel is more than anticipated due to the expertise of LADEE’s navigation engineers.
This is great news because it means LADEE’s three research instruments will collect a big bonus of science measurements about the pristine lunar atmosphere and dust during an additional 28 days in an ultra tight low orbit skimming around the Moon.
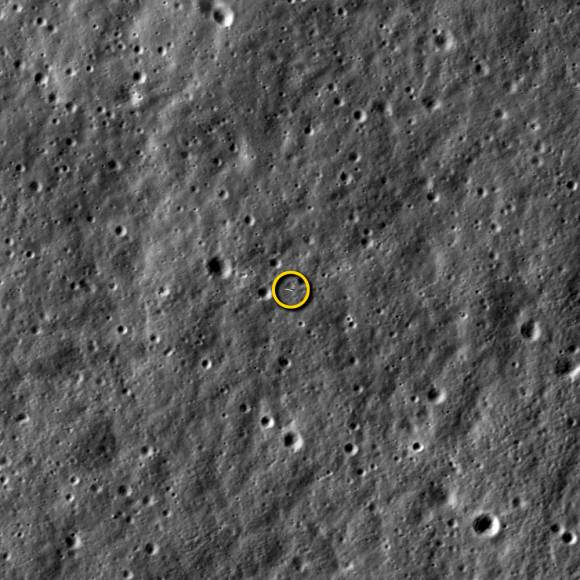
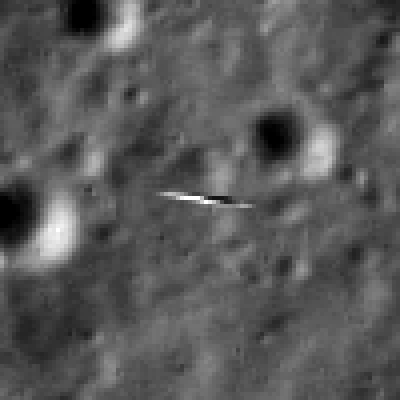
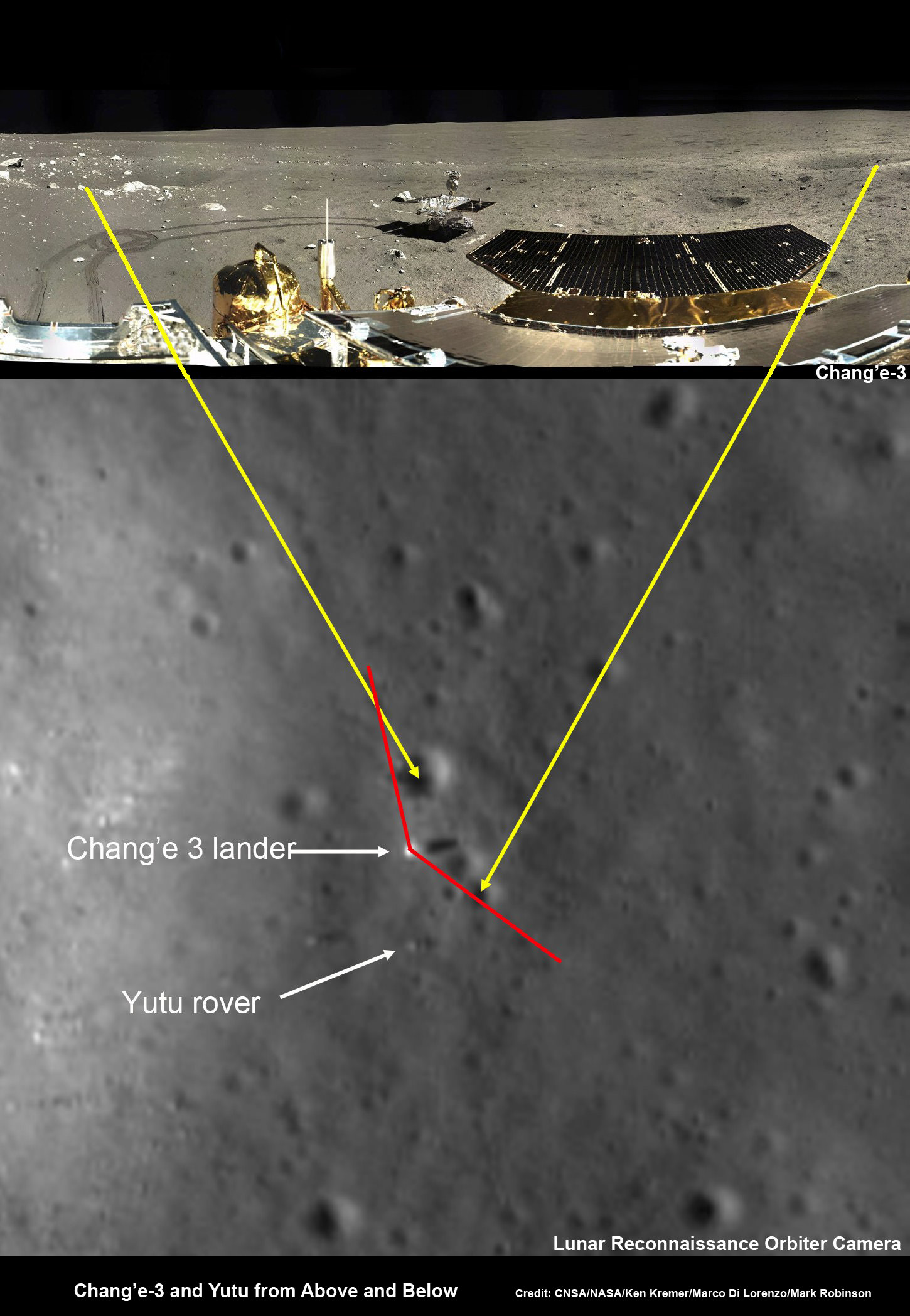
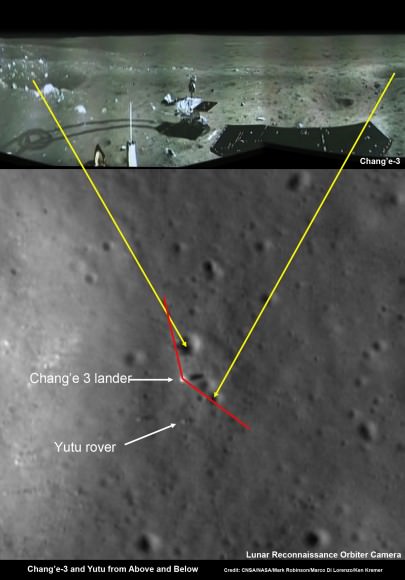
And the extension news follows closely on the heels of LADEE being photographed in lunar orbit for the first time by a powerful camera aboard NASA’s five year old Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), her orbital NASA sister – detailed here.

LADEE is currently flying around the moon’s equator at altitudes ranging barely eight to 37 miles (12-60 kilometers) above the surface which crosses over from lunar day to lunar night approximately every two hours.
During the extended mission lasting an additional full lunar cycle, LADEE will fly even lower to within a few miles (km) thereby allowing scientists an exceptional vantage point to unravel the mysteries of the moon’s atmosphere.
Just how low will LADEE fly?
I asked Rick Elphic, LADEE project scientist at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif.
“We will be taking LADEE from its nominal 20 to 50 kilometer periapsis right down to the treetops — we want to get data from 5 kilometers or even less!” Elphic told me.
“So far we’ve been keeping a healthy margin for spacecraft safety, but after the nominal mission is completed, we will relax those requirements in the interest of new science.”
With the measurements collected so far the science team has already established a baseline of data for the tenuous lunar atmosphere, or exosphere, and dust impacts, says NASA.
Therefore the LADEE team is free to fly the spacecraft much lower than ever before.
And why even go to lower altitudes? I asked Elphic.
Basically because the team hopes to see changes in the particle density and composition.
“The density depends on the species. For instance, argon-40 is heavier than neon-20, and has a lower scale height. That means we should see a big increase in argon compared to neon.”
“And we may see the heavier species for the first time at these really low altitudes.”
“It’s remotely possible we’ll see krypton, for instance.”
“But the real boon will be in the dust measurements.”
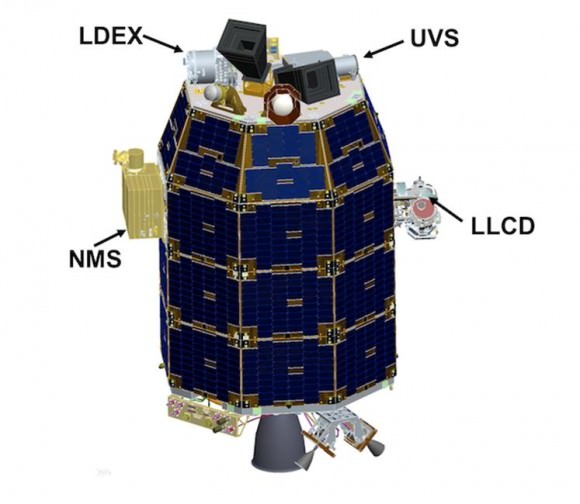
“LDEX (The Lunar Dust Experiment) will be measuring dust densities very close to the surface, and we will see if something new shows up. Each time we’ve dropped our orbit down to lower altitudes, we’ve been surprised by new things,” Elphic told Universe Today.
The Neutral Mass Spectrometer (NMS) instrument will measure the identity and abundances of the exospheres constituents, such as argon, neon and krypton.
With the extension, LADEE is expected to continue capturing data in orbit until about April 21, 2014, depending on the usage of the declining on board fuel to feed its maneuvering thrusters.
“LADEE is investigating the moons tenuous exosphere, trace outgases like the sodium halo and lofted dust at the terminator,” Jim Green, Planetary Science Division Director at NASA HQ, told me earlier in an exclusive interview.
“The spacecraft has a mass spectrometer to identify the gases, a physical dust detector and an imager to look at scattered light from the dust. These processes also occur at asteroids.”
The Lunar Dust Experiment (LDEX) recorded dust impacts as soon as its cover opened, says NASA and is also seeing occasional bursts of dust impacts caused by meteoroid showers, such as the Geminids.
By studying the raised lunar dust, scientists also hope to solve a 40 year old mystery – Why did the Apollo astronauts and early unmanned landers see a glow of rays and streamers at the moon’s horizon stretching high into the lunar sky.
The science mission duration had initially been planned to last approximately 100 days and finish with a final impact on the Moon on about March 24th.
And the team had told me before launch that an extension was rather unlikely since the spacecraft would be flying in such a very low science orbit of about 50 kilometers altitude above the moon that it will require considerable fuel to maintain.
“LADEE is limited by the amount of onboard fuel required to maintain orbit,” Doug Voss, launch manager, Wallops, told me.
So what accounts for the extension?
Basically it’s because of the expert navigation by NASA’s engineers and the Orbital Sciences Minotaur V rocket and upper stages following the spectacular night time LADEE blastoff from NASA Wallops, VA, on Sept. 6, 2013 and subsequent insertion into lunar orbit.
“The launch vehicle performance and orbit capture burns using LADEE’s onboard engines were extremely accurate, so the spacecraft had significant propellant remaining to enable extra science,” said Butler Hine, LADEE project manager at NASA’s Ames where the mission was designed, built, tested, in a NASA statement.
“This extension represents a tremendous increase in the amount of science data returned from the mission.”

“LADEE launched with 134.5 kilograms of fuel. After the third lunar orbit insertion burn (LOI-3), 80% of our fuel had been consumed,” said Dawn McIntosh, LADEE deputy project manager at NASA Ames Research Center, in an exclusive interview with Universe Today.
“Additional orbit-lowering maneuvers with the orbital control system (OCS) and reaction control system (RCS) of approximately 40 seconds were used to get LADEE into the science orbit.
And LADEE’s orbit capture was accomplished amidst the ridiculous US government shutdown with a skeleton crew.
The spacecraft finally entered its planned two hour science orbit around the moon’s equator on Nov. 20.
So LADEE’s orbital lifetime depends entirely on the remaining quantity of rocket fuel.
“LADEE has about 20 kg of propellant remaining today,” Butler Hine told Universe Today.
The 844 pound (383 kg) robot explorer is the size of a couch and was assembled at NASA’s Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif., and is a cooperative project with NASA Goddard Spaceflight Center in Maryland.

The $280 million probe is built on a revolutionary ‘modular common spacecraft bus’, or body, that could dramatically cut the cost of exploring space and also be utilized on space probes to explore a wide variety of inviting targets in the solar system.
“LADEE is the first in a new class of interplanetary exploration missions,” NASA Ames Center Director Pete Worden told me in an interview. “It will study the pristine moon to study significant questions.”
“This is probably our last best chance to study the pristine Moon before there is a lot of human activity there changing things.”
To date LADEE has traveled over 1 million miles and in excess of 1200 equatorial orbits around the Moon.
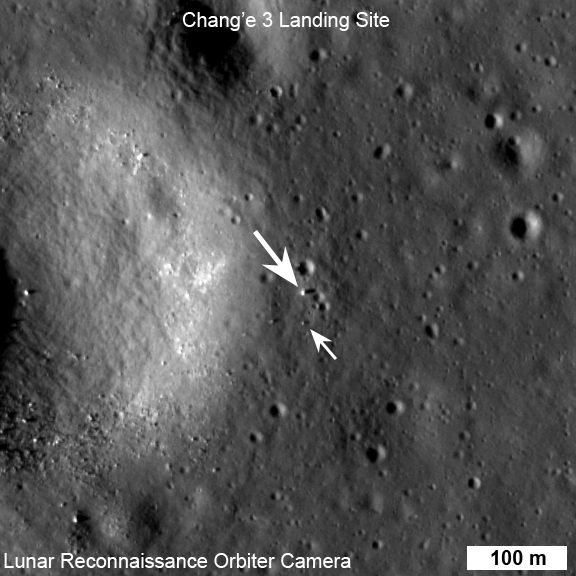
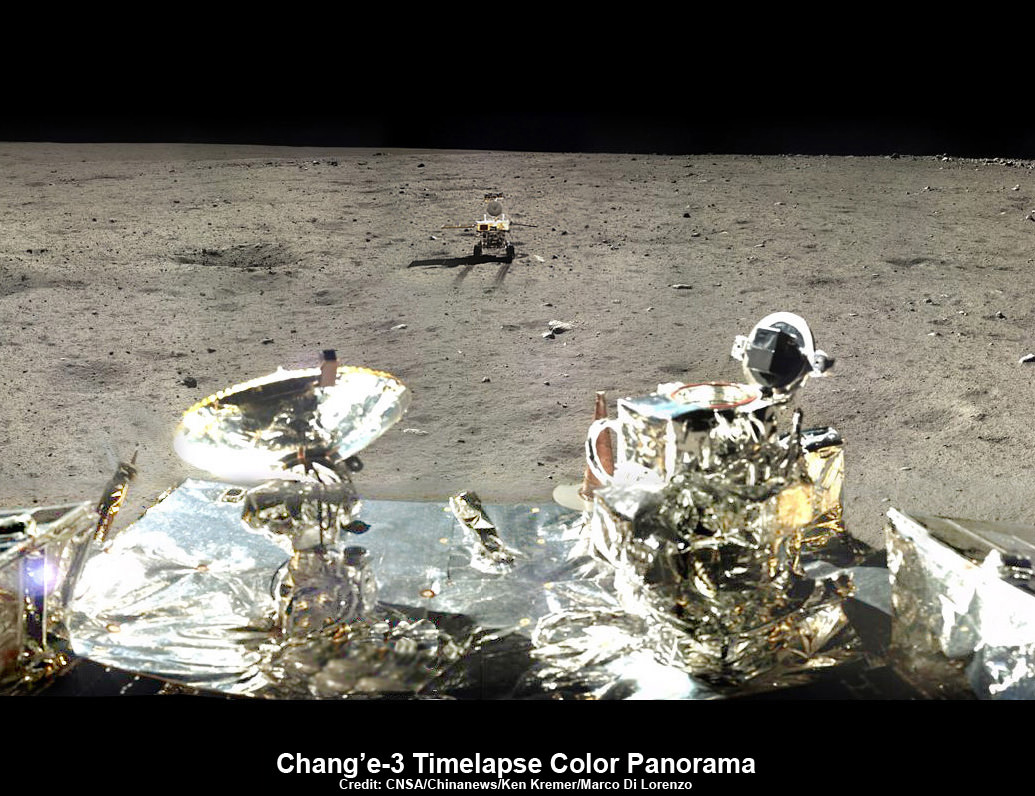
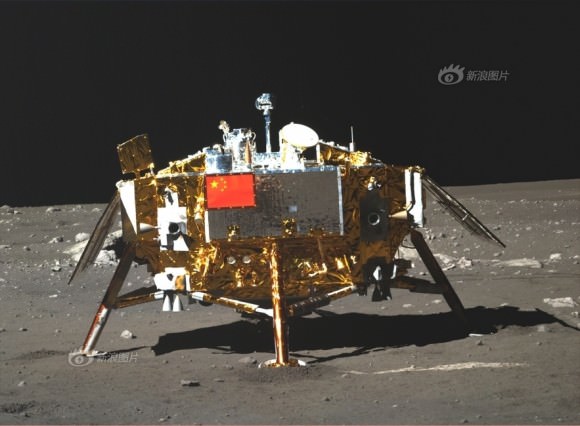
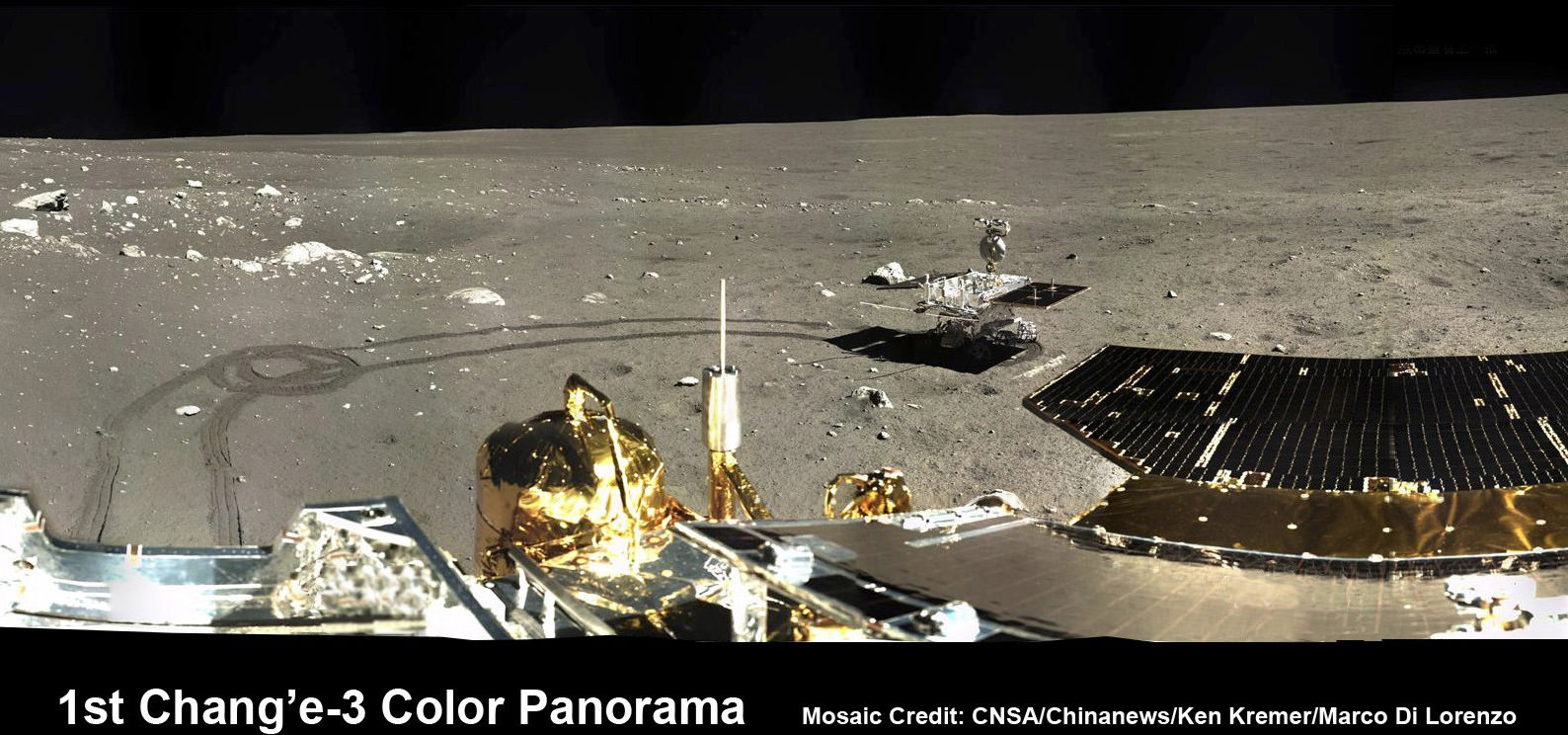
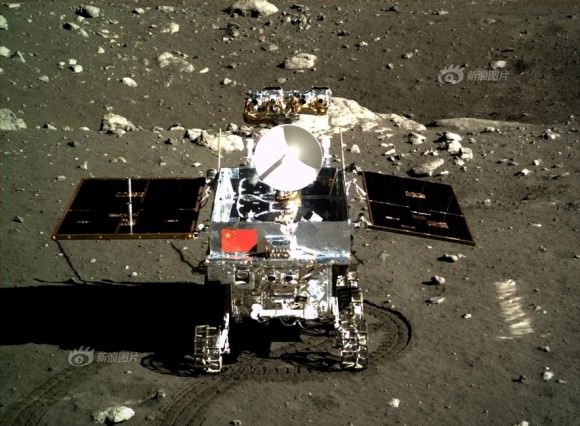
LADEE is also searching for any changes caused to the exosphere and dust by the landing of China’s maiden Chang’e-3 lander and Yutu moon rover in December 2013.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing LADEE, Chang’e-3, Orion, Orbital Sciences, SpaceX, commercial space, Mars rover and more news.