All systems appear to be “GO” for the world’s first attempt to soft land a space probe on the Moon in nearly four decades.
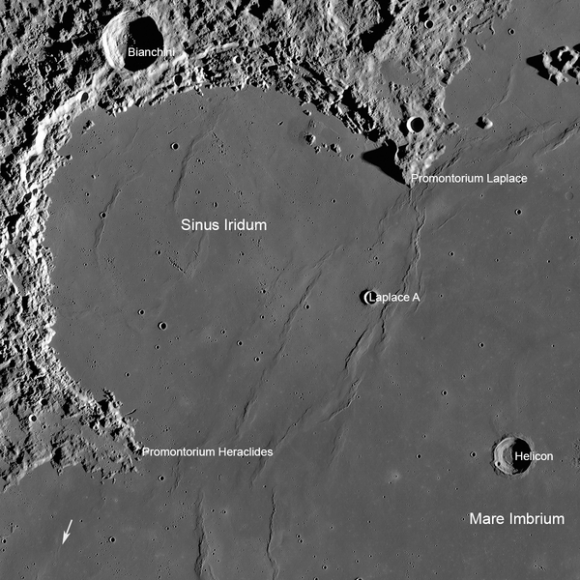
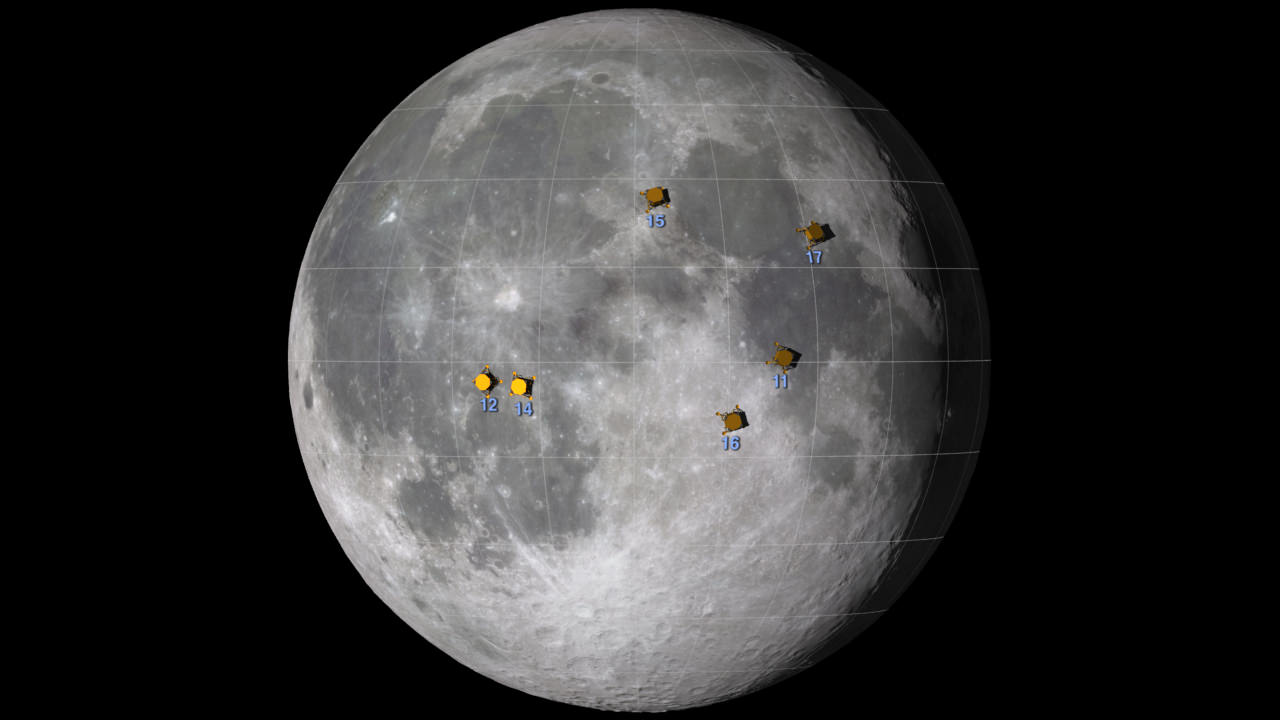
China’s maiden moon landing probe – Chang’e-3 – is slated to attempt the history making landing this weekend on a lava plain in the Bay of Rainbows, or Sinus Iridum region.
Chinese space engineers at the Beijing Aerospace Control Center (BACC) paved the way for the historic touchdown by successfully commanding Chang’e-3 to descend from the 100 km-high lunar circular orbit it reached just one week ago on Dec. 6, to “an elliptical orbit with its nearest point about 15 km away from the moon’s surface”, according to a statement from China’s State Administration of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense (SASTIND).
UPDATE: CCTV is providing live landing coverage
The first pictures taken from the alien lunar surface in some 37 years are expected to be transmitted within days or hours of touchdown planned as early as Saturday, Dec. 14, at 9:40 p.m. Beijing local time, 8:40 a.m. EST.
CCTV, China’s state run network, carried the launch live. It remains to be seen whether they will have live coverage of the landing since there have been no programming announcements.
SASTIND said the orbit lowering thruster firing was “conducted above the dark side of the moon at 9:20 p.m.” on Dec. 10, Beijing local time.
Confirmation of the Chang’e-3 probes new, lower orbit was received four minutes later.

If successful, the Chang’e-3 mission will mark the first soft landing on the Moon since the Soviet Union’s unmanned Luna 24 sample return vehicle landed back in 1976.
China would join an elite club of three, including the United States, who have mastered the critical technology to successfully touch down on Earth’s nearest neighbor.
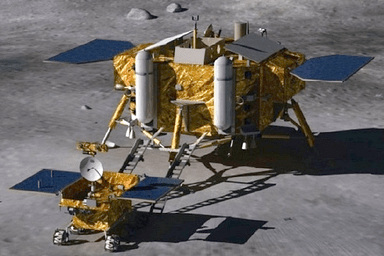
The Chang’e-3 mission is comprised of China’s ‘Yutu’ lunar lander riding piggyback atop a much larger four legged landing probe.
The voyage from the Earth to the Moon began 12 days ago with the flawless launch of Chang’e-3 atop China’s Long March 3-B booster at 1:30 a.m. Beijing local time, Dec. 2, 2013 (12:30 p.m. EST, Dec. 1) from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center, in southwest China.
Chang’e-3 will make a powered descent to the Moon’s surface on Dec. 14 by firing the landing thrusters at the altitude of 15 km (9 mi) for a soft landing in a preselected area on the Bay of Rainbows.
The powered descent will take about 12 minutes.
The variable thrust engine can continuously vary its thrust power between 1,500 to 7,500 newtons, according to Xinhua.
The Bay of Rainbows is located in the upper left portion of the moon as seen from Earth. It was imaged in high resolution by China’s prior lunar mission – the Chang’e-2 lunar orbiter.
The 1200 kg lander is equipped with terrain recognition equipment and software to avoid rock and boulder fields that could spell catastrophe even in the final seconds before touchdown if the vehicle were to land directly on top of them.
Chang’e-3 is powered by a combination of solar arrays and a nuclear device in order to survive the two week long lunar nights.
The six-wheeled ‘Yutu’ rover, with a rocker bogie suspension, will be lowered in stages to the moon’s surface in a complex operation and then drive off a pair of landing ramps to explore the moon’s terrain.
Yutu measures 150 centimeters high and weighs approximately 120 kilograms and sports a robotic arm equipped with science instruments.
The rover and lander are equipped with multiple cameras, spectrometers, an optical telescope, ground penetrating radar and other sensors to investigate the lunar surface and composition.
The radar instrument installed at the bottom of the rover can penetrate 100 meters deep below the surface to study the Moon’s structure and composition in unprecedented detail.
China’s Chang’e-3 probe joins NASA’s newly arrived LADEE lunar probe which entered lunar orbit on Oct. 6 following a spectacular night time blastoff from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Chang’e-3, LADEE, MAVEN, MOM, Mars rover and more news.