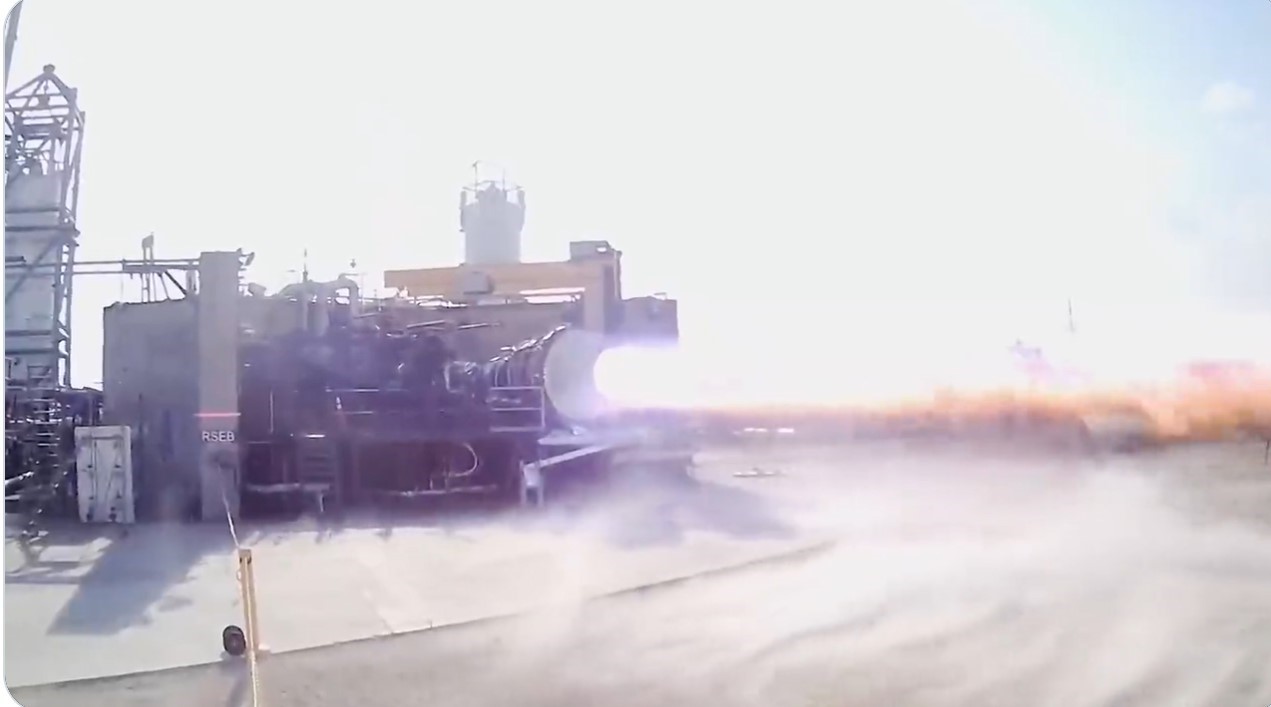
When NASA astronauts return to the surface of the Moon in the Artemis III mission, the plan is to use a modified SpaceX Starship as their lunar lander. NASA announced last week that SpaceX has now demonstrated an important capability of the vacuum-optimized Raptor engine that will be used for the lander: an extreme cold start.
A test last month successfully confirmed the engine can be started in the frigid conditions of space, even when the vehicle has spent an extended time in space, where temperatures will drop lower than a shorter low-Earth orbit mission. The Raptor vacuum engine was chilled to mimic conditions after a long coast period in space, and then was successfully fired.
Continue reading “SpaceX Test Fires a Raptor Engine, Simulating a Lunar Landing”