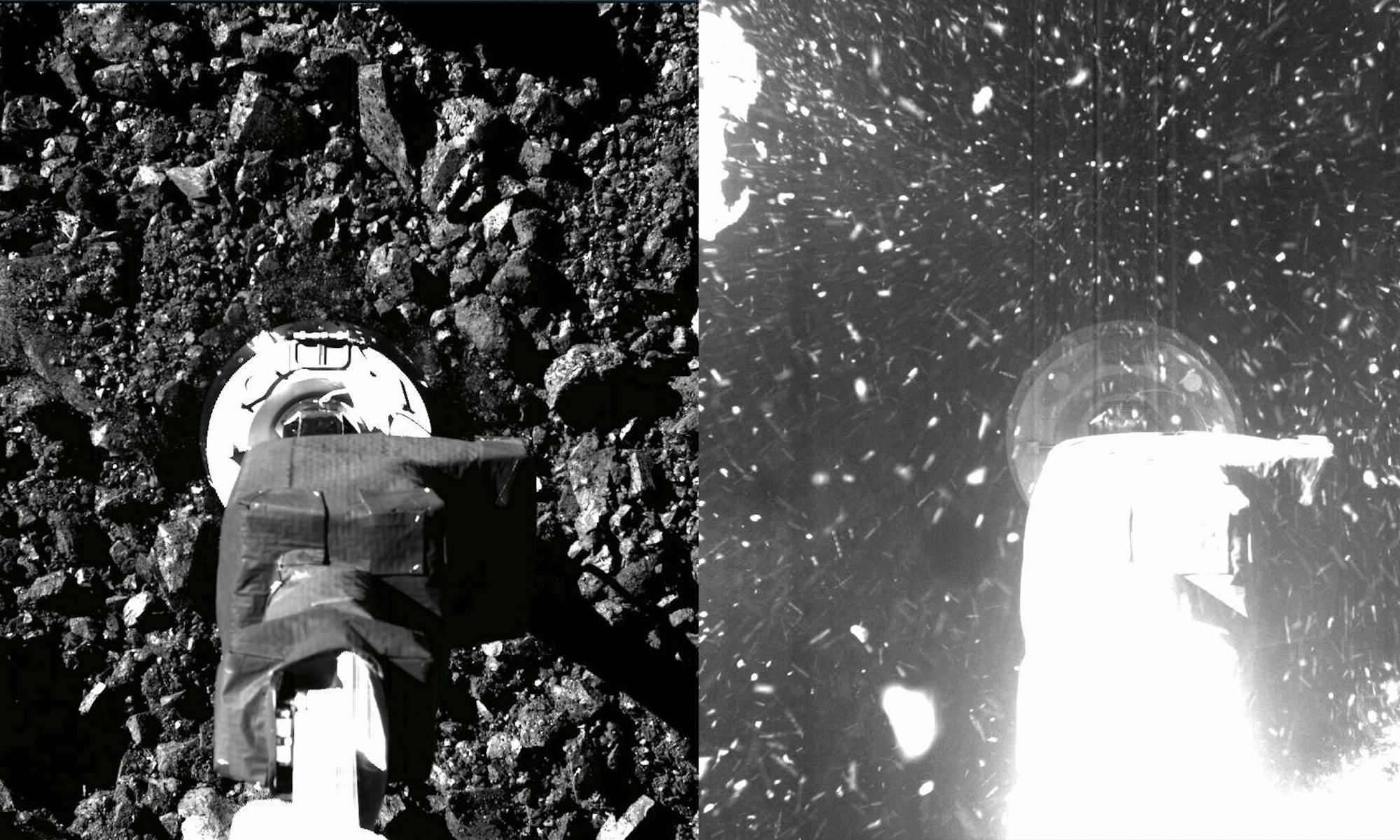
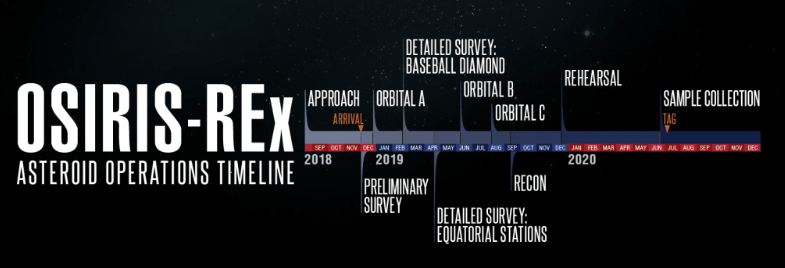
The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft conducted a two-year reconnaissance and sample collection at the asteroid Bennu, providing crucial data about the 500-meter-wide potentially hazardous rubble pile/space rock. When OSIRIS-REx arrived on Dec. 3, 2018, it needed some tricky navigation and precise maneuvers to make the mission work.
Experts at NASA Goddard’s Scientific Visualization Studio created an amazing visualization of the path the spacecraft took during its investigations. A short film called “A Web Around Asteroid Bennu” highlights the complexity of the mission, and the film is being shown at the SIGGRAPH computer graphics conference in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, a festival honoring standout works of computer animated storytelling.
Continue reading “Watch OSIRIS-REx's Complex Orbital Path Around Bennu in This Cool Animation”