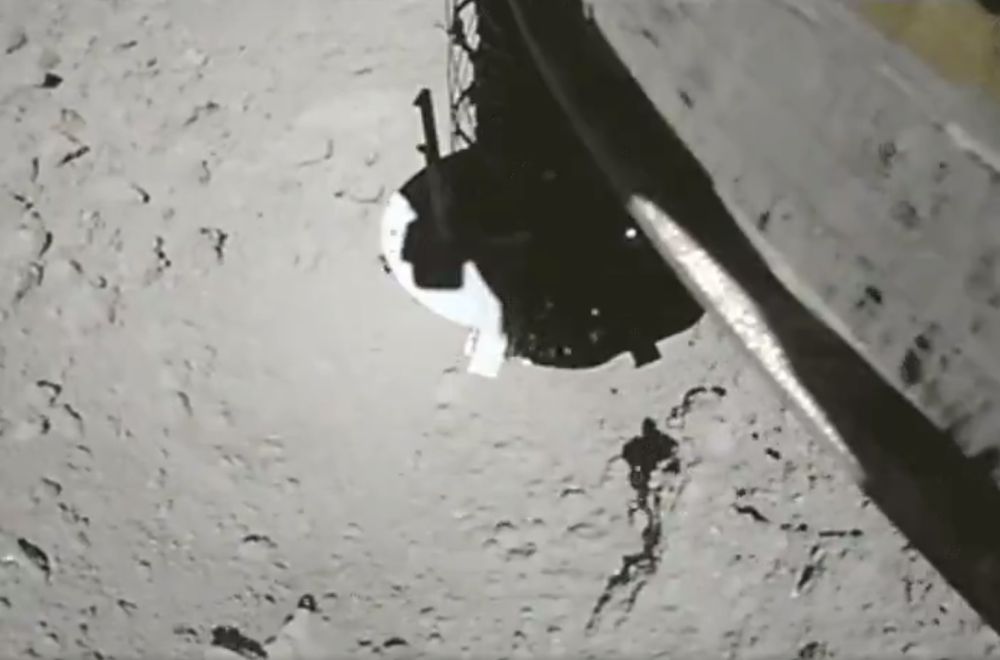
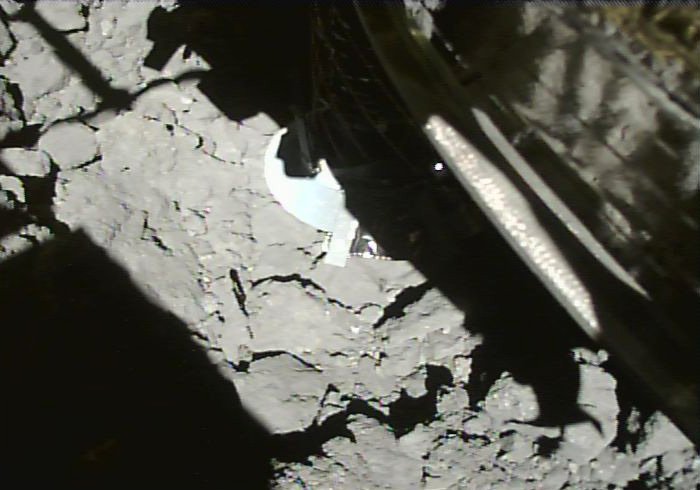
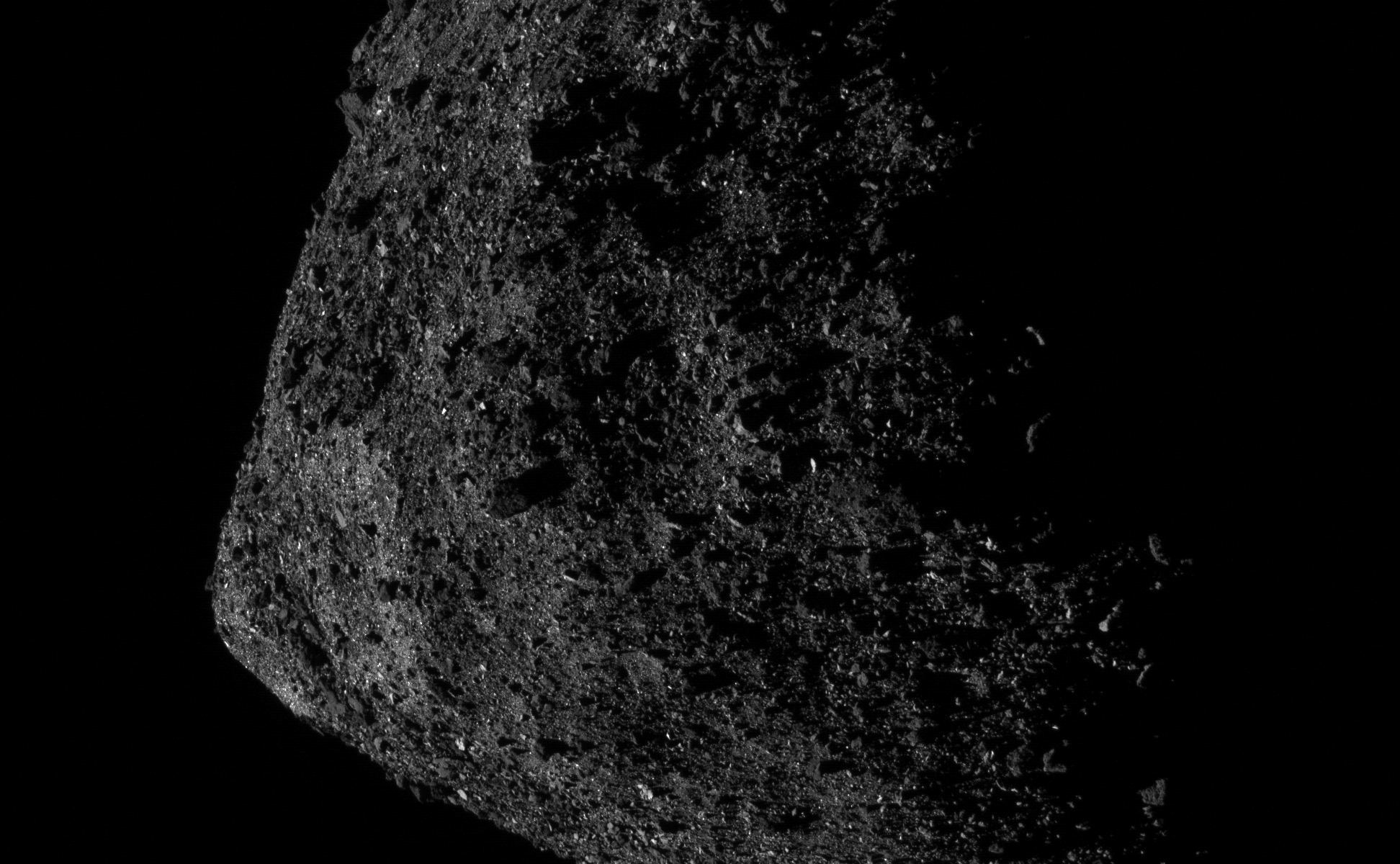
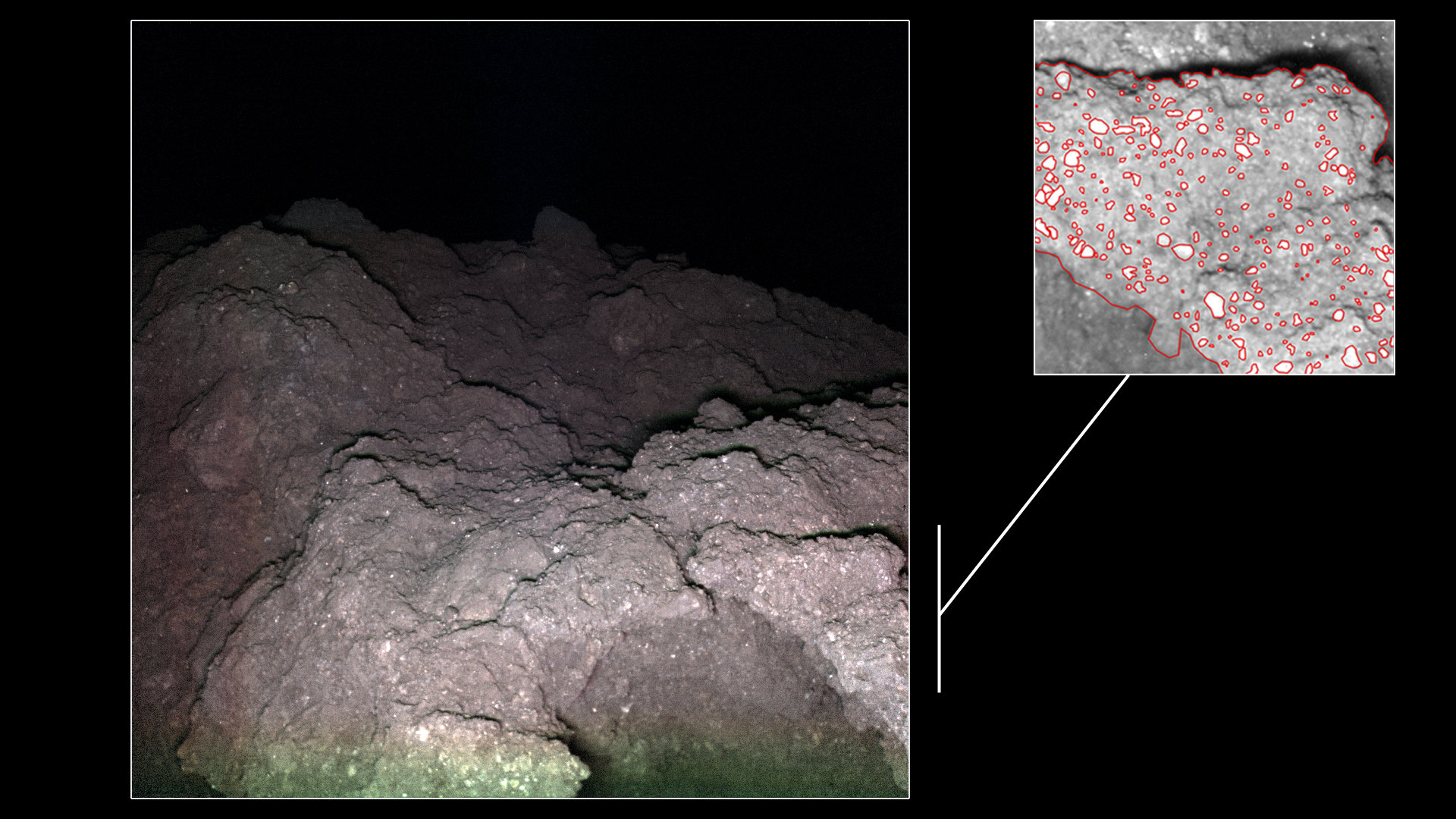
When Japan’s Hayabusa 2 spacecraft arrived at asteroid Ryugu in June 2018, it carried four small rovers with it. Hayabusa 2 is primarily a sample-return mission, but JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) sent rovers along to explore the asteroid’s surface and learn as much as they could from their visit. There’s also no guarantee that the sample return will be successful.
They chose Ryugu because the asteroid is classified as a primitive carbonaceous asteroid. This type of asteroid is a desirable target because it represents the primordial matter that formed the bodies in our Solar System. It’s also pretty close to Earth.
The sample from Ryugu, which will make it to Earth in December 2020, is the big science prize from this mission. Analyzing it in Earth-based laboratories will tell us a lot more than spacecraft instruments can. But the rovers that landed on Ryugu’s surface have already revealed a lot about Ryugu.
Continue reading “Asteroid Ryugu is a “Fragile Rubble Pile””