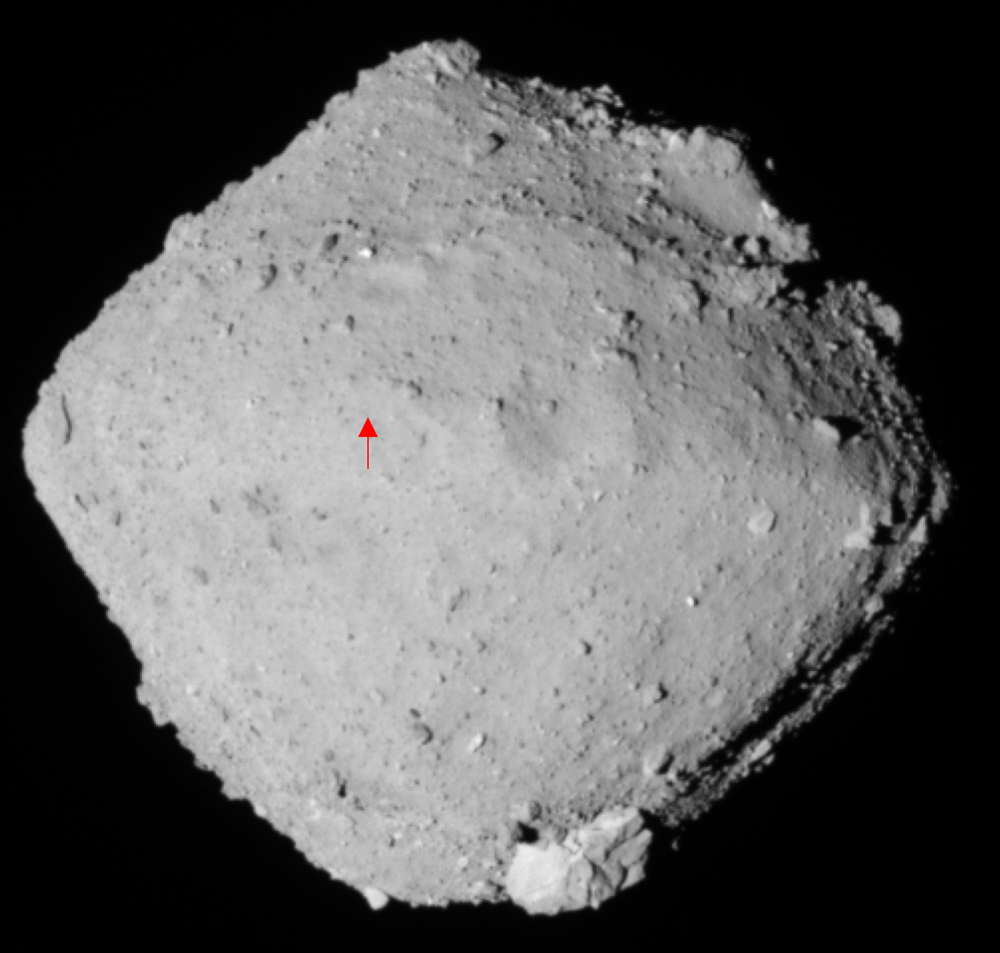
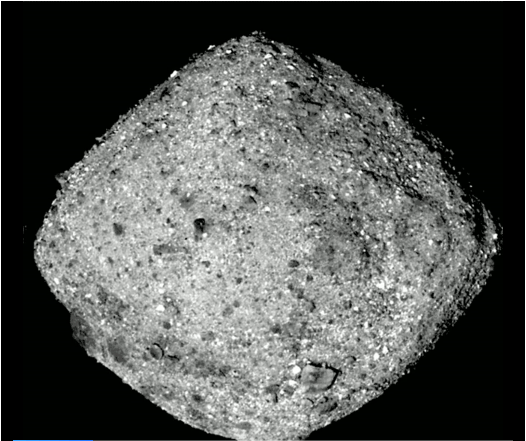
NASA’s OSIRIS-REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer) has found water on the asteroid Bennu. Bennu is OSIRIS-REx’s only target, and though the spacecraft arrived at the asteroid on December 3rd, some of its instruments have been trained on the asteroid since mid-August. And two of those instruments detected water on Bennu.
OSIRIS-REx wasn’t sent to Bennu just to find water. The mission is NASA’s first asteroid sample-return mission. The presence of water on Bennu confirms what the science team hoped would be true when they selected the asteroid as the spacecraft’s destination: Bennu is an excellent target for scientific inquiry into the early Solar System.
“The presence of hydrated minerals across the asteroid confirms that Bennu, a remnant from early in the formation of the solar system, is an excellent specimen for the OSIRIS-REx mission to study the composition of primitive volatiles and organics.” – Amy Simon, OVIRS deputy instrument scientist, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.
Continue reading “OSIRIS-REx Has Already Found Water on Bennu”