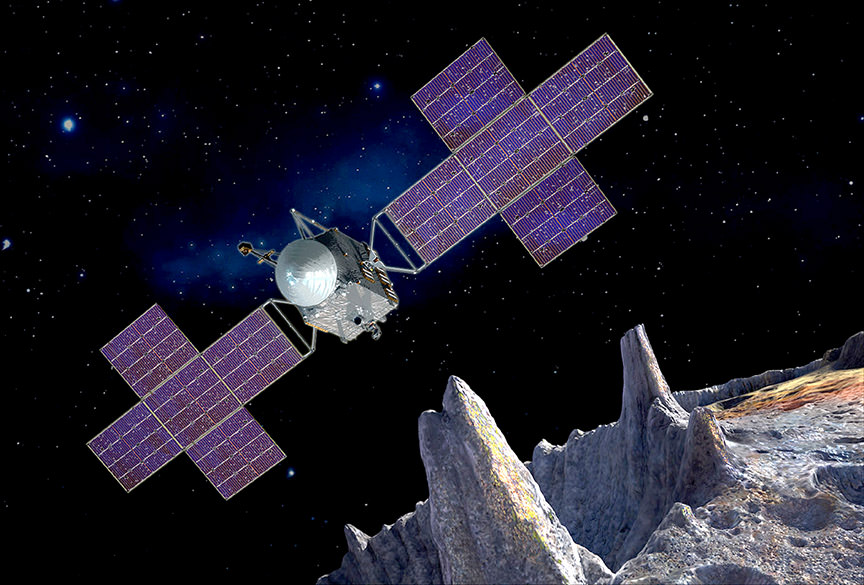
As NASA sets its sight on the next generation of space exploration, one area of focus is on missions that can teach us more about our Solar System. This was a major priority during the thirteenth round of NASA’s Discovery Program, which put out the call for proposals back in February of 2014. One of the proposals to make the cut was the Psyche mission, which will send an orbiter to the asteroid of the same name in 2o22.
This mission is unique in that it will entail visiting an asteroid that is entirely composed of metal, which scientists believe is the remnant core of an early planet. For the sake of the mission, NASA’s Glenn Research Center has been working hard to develop a cutting-edge, next-generation thruster that balances power with fuel efficiency. This thruster was recently subjected to tests designed to simulate its journey through space.
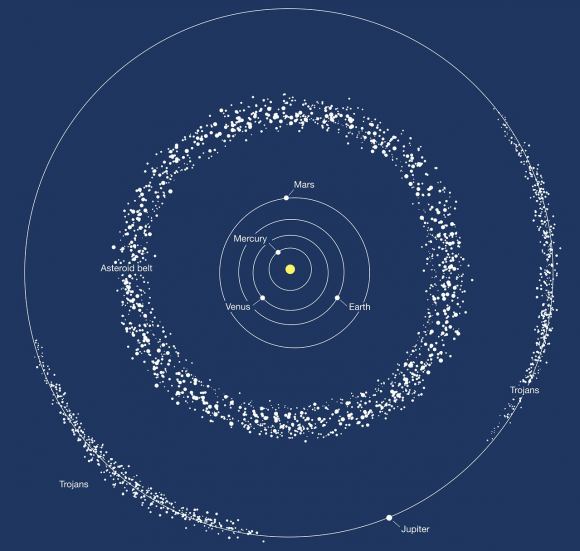
Originally discovered in 1852, the object known as 16 Psyche has been a source of fascination ever since astronomers were able to determine its composition. Unlike other asteroids that are largely carbonaceous (C-type), silicate (S-type), or composed of rock and metal (M-type), Psyche is the only asteroid to date that has been found to have an exposed nickel-iron surface.
Because of its unique nature, scientists have theorized that the metal asteroid is actually the core of a Mars-sized planet that formed during the early Solar System. This planet, they theorize, lost its outer layers after experiencing a massive collision, thus leaving an exposed core behind. The study of this asteroid is therefore expected to reveal a great deal about the interior of terrestrial planets and what powers their magnetic fields.
As David Oh, the mission’s lead project systems engineer, said in a recent NASA press release:
“Psyche is a unique body because it is, by far, the largest metal asteroid out there; it’s about the size of Massachusetts. By exploring Psyche, we’ll learn about the formation of the planets, how planetary cores are formed and, just as important, we’ll be exploring a new type of world. We’ve looked at worlds made of rock, ice and of gas, but we’ve never had an opportunity to look at a metal world, so this is brand new exploration in the classic style of NASA.”
The Psyche missions brings together researchers from Arizona State University and experts from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. For the sake of designing the engine that would send their spacecraft to its destination, the joint Arizona-JPL team turned to NASA’s Glenn Research Center, which has been conducting research into Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) for years.
SEP thrusters are essentially ion-engines that rely on electrically-charged inert gases (like xenon) to provide thrust. Like all Hall Effect ion-engines, this allows the thruster to provide a gentle, non-stop stream of thrust that gradually pushes a spacecraft up to greater and greater speeds. Such a system is ideal for deep-space missions where fuel-efficiency is a must.
As Carol Tolbert, the project manager for Psyche thruster testing at NASA Glenn, explained:
“For deep space missions, the type and amount of fuel required to propel a spacecraft is an important factor for mission planners. A SEP system, like the one used for this mission, operates more efficiently than a conventional chemical propulsion system, which would be impractical for this type of mission.”
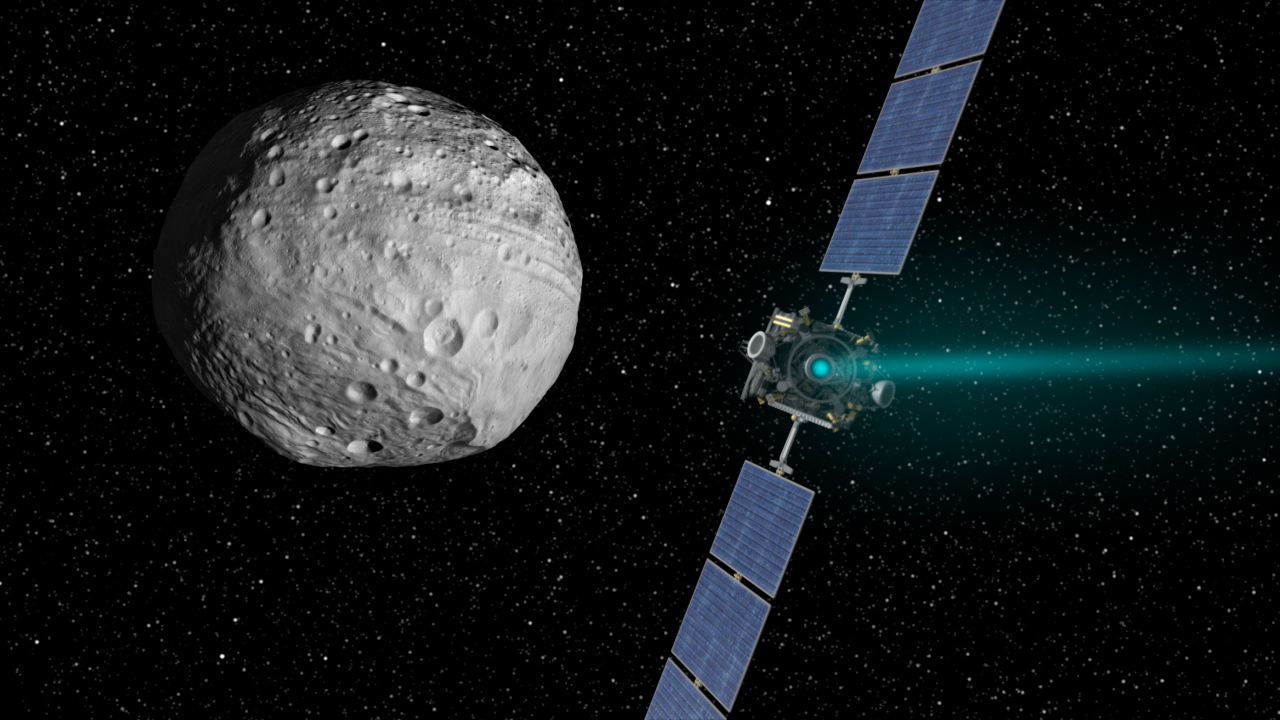
The Psyche mission, which will be built jointly by JPL and Space Systems Loral (SSL), will use a SPT-140 Hall effect thruster that relies on solar power to provide electrical charges. The reduced fuel mass of this thruster will allow the mission to enter orbit around the metal asteroid while also providing additional space for the mission’s suite of scientific instruments.
These include a multispectral imager, a magnetometer, and a gamma-ray spectrometer, all of which will help the science team to obtain vital information on the asteroid’s origin, composition and history. The SEP also provides flexibility and robustness in the mission flight plan, since it will allow Psyche to get to its destination with greater speed and efficiency than conventional propulsion would allow for.
To test how the thruster performs during low-power operations, engineers at NASA Glenn placed the thruster into a space environment chamber designed to generate the low-pressures and temperatures it will encounter in space. As Carol explained:
“This mission will be the first to use a Hall effect thruster system beyond lunar orbit, so the tests here at Glenn, which had never been conducted before, were needed to ensure the thruster could perform and operate as expected in the deep space environment.”

For decades, the Glenn center has used its compliment of chambers to simulate the conditions missions will encounter in space. However, this test is the first time that engineers have sought to determine how an SEP Hall-Effect thruster would fare. As Oh explained, this test is very important since it will simulate precisely how the spacecraft will fly, and the results have been encouraging so far:
“Glenn has a world-class facility that allowed us to go to very low pressures to simulate the environment the spacecraft will operate in and better understand how our thrusters will perform around Psyche. At first glance, the results confirm our predictions regarding how the thruster will perform, and it looks like everything is working as expected. But, we will continue to refine our models by doing more analysis.”
As the team works towards the mission’s proposed launch – which is scheduled for August 2022 – they will use the data collected at NASA Glenn to update their thruster modeling and incorporate it into mission trajectories. Once the spacecraft reaches its destination – the planned arrival will take place by 2026 – it is expected to reveal a great deal about this unique asteroid.
This data is also likely to teach us much about the history of the Asteroid Belt and the Solar System. If indeed 16 Psyche is the remnant of a Mars-sized planet that formed in the Main Belt, it could cause astronomers to rethink their notions of how the Solar System formed and evolved.
Further Reading: NASA