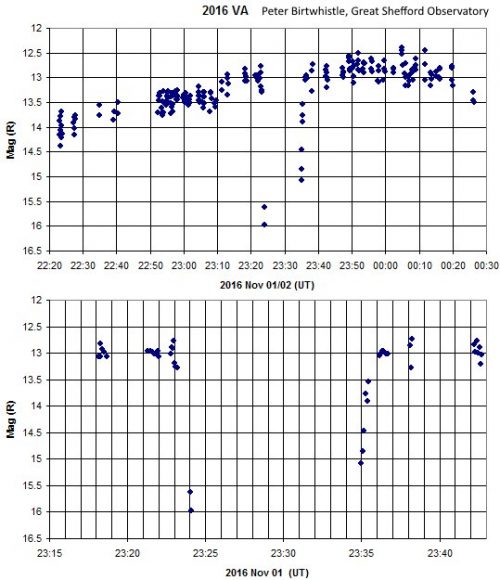
Oklahoma’s Beaver River is an incredibly historic place. Anthropologists estimate that as early as 10,500 years ago, human beings hunted bison in the region. Being without horses, the hunter-gatherers would funnel herds into narrow, dead-end gullies cut into the hillside by the river. Once there, they would kill them en masse, taking the meat and organs and leaving the skeletons behind.
Sadly, no visible trace of this history remains in the region today, thanks to weathering and erosion. But according to a recent story released by NASA, the same technology that powers the Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer (OSIRIS-REx) mission has made the ancient history of this region visible for all to see.
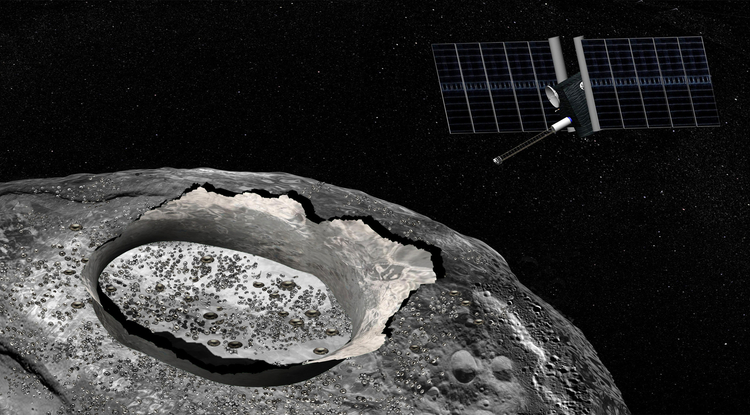
Having launched back in September of 2016, the robotic spacecraft OSIRIS-REx is scheduled to rendezvous with the Near-Earth Asteroid Bennu in 2023. The purpose of the mission is to obtain samples of the carbonaceous object and return them to Earth, thus helping scientists to get a better understanding of the formation and evolution of the Solar System, as well as the source of organic compounds that led to the formation of life on Earth.
Once it reaches Bennu, it will rely on light-detection and ranging (aka. lidar) to map the asteroid and help the mission team select a landing site. This technology uses one or more lasers to send out short pulses that bounce off of nearby objects. The instrument then measures how long it takes for the signal to return to get an accurate assessment of distance and generate topographical information.
The OSIRIS-REx Laser Altimeter (OLA) instrument was designed by Teledyne Optech, a company that has worked with NASA many times in the past. Their work includes the laser instrument that was used by the Phoenix Lander to detect snow in the Martian atmosphere back in 2008. And more recently, it was used by an archeological research team in the Beaver River area to create a detailed picture of its past.
Using an airborne version of the Teledyne Optech lidar device, the team was able to create a 3-D model of the surface. They were also able to generate as a ‘bare-earth” version of the area that showed what the land looked like without all of the concealing features – i.e. rocks, trees and grass – that hide its past.
In so doing, they were able to figure out where they should dig to find evidence that the region was once a major hunting ground. As Paul LaRoque, vice president of special projects at Teledyne Optech, explained, this process allowed the archaeologists to “see structures or features that were so overgrown that they wouldn’t be obvious at all to someone on the ground.”

This sort of process has also been used by other archaeological teams to make major finds, like uncovering the lost “Ciudad Blanca” (aka. the “City of the Monkey God”) of Honduras. This ancient Mesoamerican settlement, which is believed to have been built between the 1st and 2nd millennium CE, had remained the stuff of legend for centuries. Despite multiple claims by explorers, no confirmed discovery was ever made.
But thanks to a joint effort by archaeologists from the University of Florida and the Houston-based National Center for Airborne Laser Mapping, an archaeological team was able to create images that stripped away the lush rainforest to revealed multiple structures – including pyramids, a plaza, a possible ball court, and many houses.
Lidar was also used by a research team from the University of Connecticut for the sake of studying the dynamics between human settlement and the historic landscape of New England. Using publicly available data, they were able to peer beneath all the current vegetation to detect the remnants of stone walls, building foundations, abandoned roads and what was once cleared farm land.
The revealing look at Beaver River is one of 50 stories that will be released on Dec. 5th, as part of a NASA Spinoff publication. Each year, Spinoff profiles about 50 NASA technologies that have transformed into commercial products and services, demonstrating the wider benefits of America’s investment in its space program. Spinoff is a publication of the Technology Transfer Program in NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate.
Further Reading: NASA






















![Distribution of new impact craters (yellow dots) discovered by analyzing 14,000 NAC temporal pairs. The two red dots mark the location of the 17 March 2013 and the 11 September 2013 impacts that were recorded by Earth-based video monitoring [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Moon-new-crater-distribution-NASA-GSFC-ASU-1024x367.jpg)


![Example of a low reflectance (top) and high reflectance (bottom) splotch created either by a small impactor or more likely from secondary ejecta. In either case, the top few centimeters of the regolith (soil) was churned [NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University].](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Moon-craters-splotches-NASA.gif)