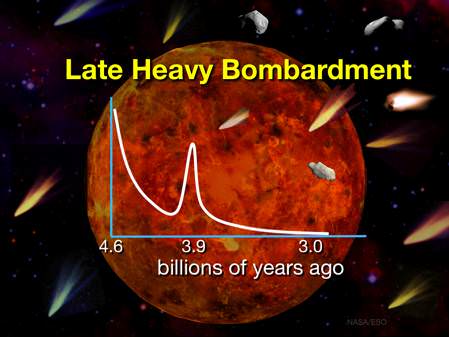
The asteroid that punched an “eye” in the Moon is about 10 times more massive than originally thought. Researchers say a protoplanet-sized body slammed into the Moon about 3.8 billion years ago, creating the area called Imbrium Basin that forms the right eye of the so-called “Man in the Moon.” Additionally, this large body also indicates that protoplanet-sized asteroids may have been common in the early solar system, putting the “heavy” into the Late Heavy Bombardment.
“We show that Imbrium was likely formed by an absolutely enormous object, large enough to be classified as a protoplanet,” said Pete Schultz from Brown University. “This is the first estimate for the Imbrium impactor’s size that is based largely on the geological features we see on the Moon.”
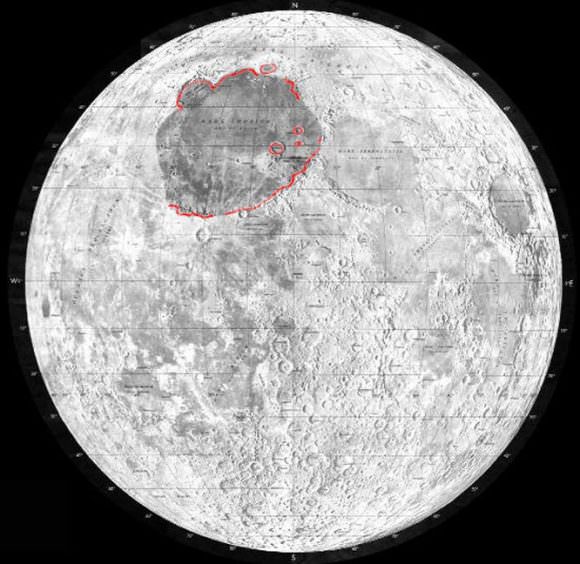
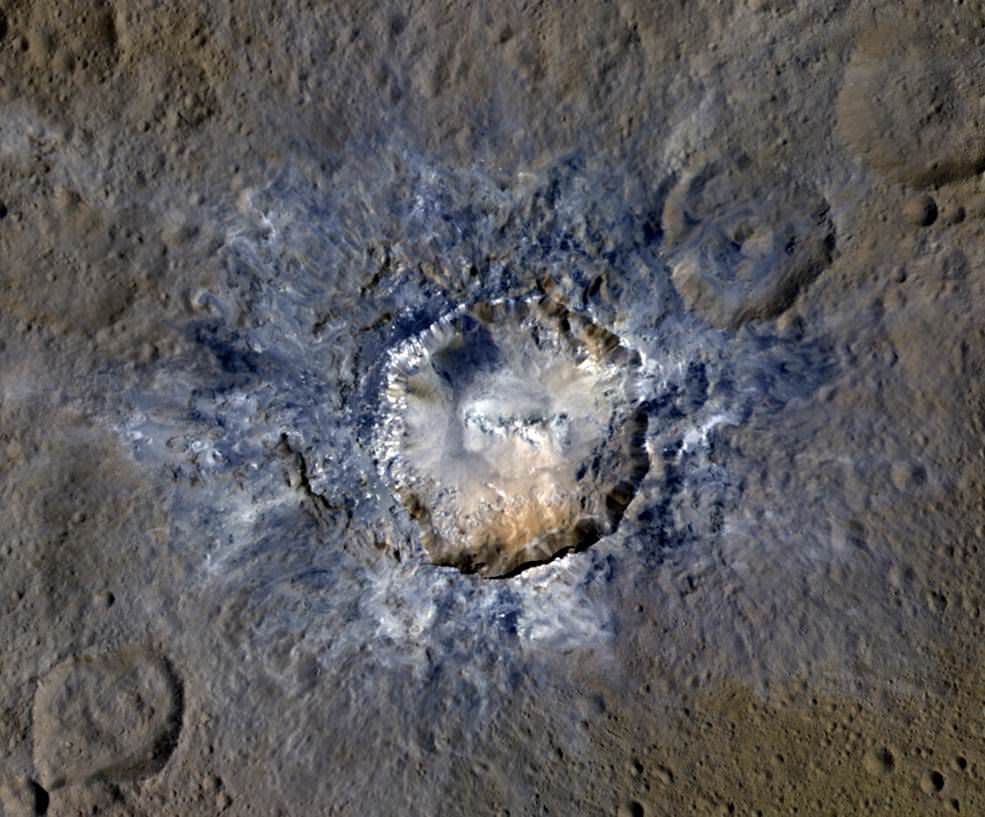
The Imbrium Basin is easily seen when the Moon is full, as a dark patch in the Moon’s northwestern quadrant. It is about 750 miles across, and a closer look shows the basin is surrounded by grooves and gashes that radiate out from the center of the basin, plus a second set of grooves with a different alignment that have puzzled astronomers for decades.
To re-enact the impact, Schultz used the Vertical Gun Range at the NASA Ames Research Center to conduct hypervelocity impact experiments. This facility has a 14-foot cannon that fires small projectiles at up to 25,750 km/hr (16,000 miles per hour), and high-speed cameras record the ballistic dynamics. During his experiments, Schultz noticed that in addition to the usual crater ejecta from the impact, the impactors themselves – if large enough — had a tendency to break apart when they first made contact with the surface. Then these chunks would continue to travel at a high speeds, skimming along and plowing across the surface, creating grooves and gouges.
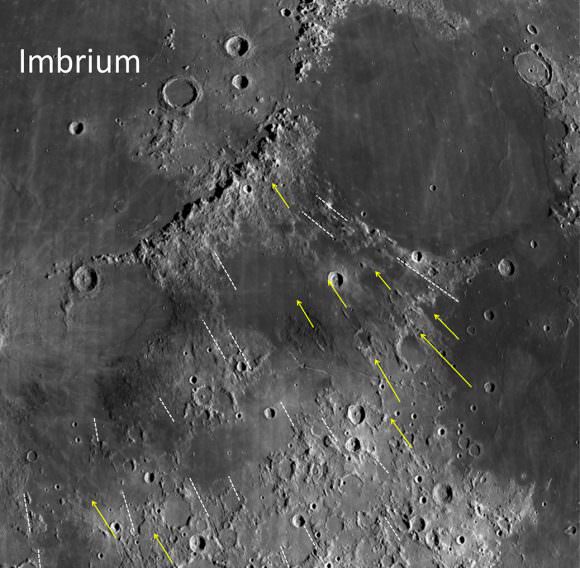
The results showed the second set of grooves were likely formed by these large chunks of the impactor that sheared off on initial contact with the surface.
“The key point is that the grooves made by these chunks aren’t radial to the crater,” Schultz said in a press release. “They come from the region of first contact. We see the same thing in our experiments that we see on the Moon — grooves pointing up-range, rather than the crater.”
The second set of groove trajectories could be used to estimate the impactor’s size. Schultz worked with David Crawford of the Sandia National Laboratories to generate computer models of the physics of various sizes of impactors, and they were able to estimate the impactor that created Imbrium Basin to be more than 250 km (150 miles) across, which is two times larger in diameter and 10 times more massive than previous estimates. This puts the impactor in the range of being the size of a protoplanet.
“That’s actually a low-end estimate,” Schultz said. “It’s possible that it could have been as large as 300 kilometers.”
Previous estimates, Schultz said, were based solely on computer models and yielded a size estimate of only about 50 miles in diameter.
Schultz and his colleagues also used the same methods to estimate the sizes of impactors related to several other basins on the Moon, for example, the Moscoviense and Orientale basins on the Moon’s far side, which yielded impactor sizes of 100 and 110 kilometers across respectively, larger than some previous estimates.
Combining these new estimates with the fact that there are even larger impact basins on the Moon and other planets, Schultz concluded that protoplanet-sized asteroids may have been common in the early solar system, and he called them the “lost giants” of the Late Heavy Bombardment, a period of intense comet and asteroid bombardment thought to have pummeled the Moon and all the planets including the Earth about 4 to 3.8 billion years ago.
“The Moon still holds clues that can affect our interpretation of the entire solar system,” he said. “Its scarred face can tell us quite a lot about what was happening in our neighborhood 3.8 billion years ago.”
Schultz’s study was published in Nature.
Source: Brown University