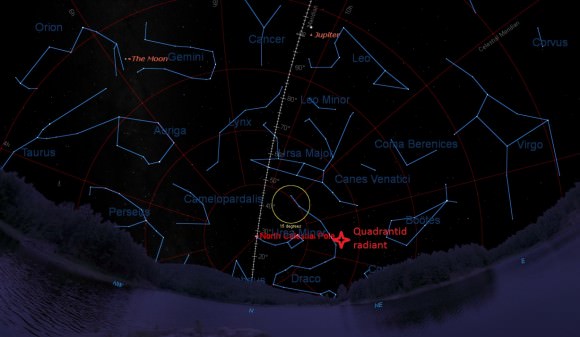
A new Avengers movie. A reboot of the Star Wars franchise. The final installment of the Hunger Games. The Martian makes it to the big screen. Yup, even if the zombie apocalypse occurs in 2015, it’ll still be a great year. But trading science fiction for fact, we’re also on track for a spectacular year in space science and exploration as well.
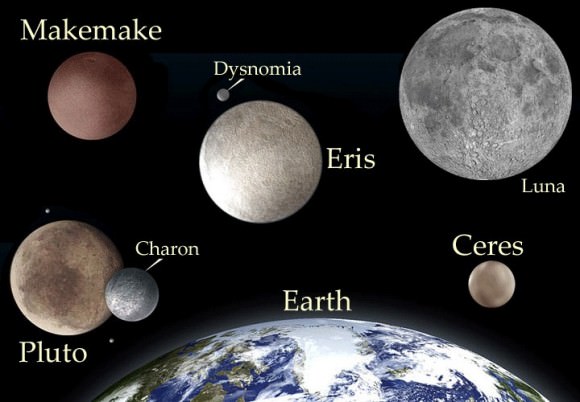
Humanity will get its first good look at Ceres and Pluto, giving us science writers some new pics to use instead of the same half dozen blurry dots and artist’s conceptions. SpaceX will also attempt a daring landing on a sea platform, and long duration missions aboard the International Space Station will get underway. And key technology headed to space and on Earth may lead the way to opening up the window of gravitational wave astronomy on the universe. Here’s 10 sure-fire bets to watch for in the coming year from Universe Today:
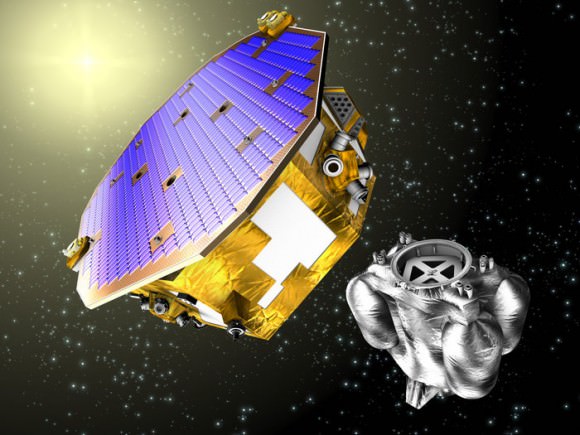

10. LISA Pathfinder
A precursor to a full-fledged gravitational wave detector in space, LISA Pathfinder will be launching atop a Vega rocket from Kourou, French Guiana in July 2015. LISA stands for the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna, and the Pathfinder mission will journey to the L1 Lagrange point between the Earth and the Sun to test key technologies. LISA Pathfinder will pave the way for the full fledged LISA space platform, a series of three free flying spacecraft proposed for launch in the 2030s.
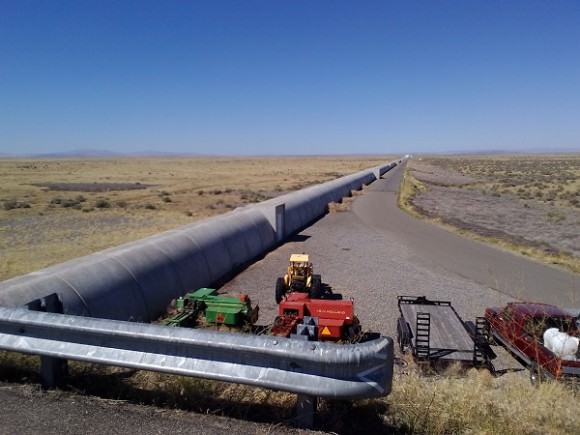

9. AdLIGO Goes Online
And speaking of gravitational waves, we may finally get the first direct detection of the same in 2015, when Advanced LIGO is set to go online. Comprised of two L-shaped detectors, one based in Livingston Louisiana, and another in Hanford Washington, AdLIGO will feature ten times the sensitivity of the original LIGO observatory. In fact, as was the case of the hunt for the Higgs-Boson by CERN, a non-detection of gravitational waves by AdLIGO would be a much stranger result!

8. Hubble Turns 25
Launched on April 24th, 1990 aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery, the Hubble Space Telescope celebrates 25 years in space in 2015. The final servicing mission in 2009 gave Hubble a reprieve from the space junk scrap heap, and the orbiting telescope is still going strong. Hubble has no less than pushed the limits in modern astronomy to become a modern icon of the space age.

7. The End of MESSENGER
NASA’s Mercury exploring spacecraft wraps up its mission next year. Launched in 2004, MESSENGER arrived in orbit around Mercury after a series of flybys on March 18th, 2011. MESSENGER has mapped the innermost world in detail, and studied the space environment and geology of Mercury. In late March 2015, MESSENGER will achieve one final first, when it impacts the surface of Mercury at the end of its extended mission.

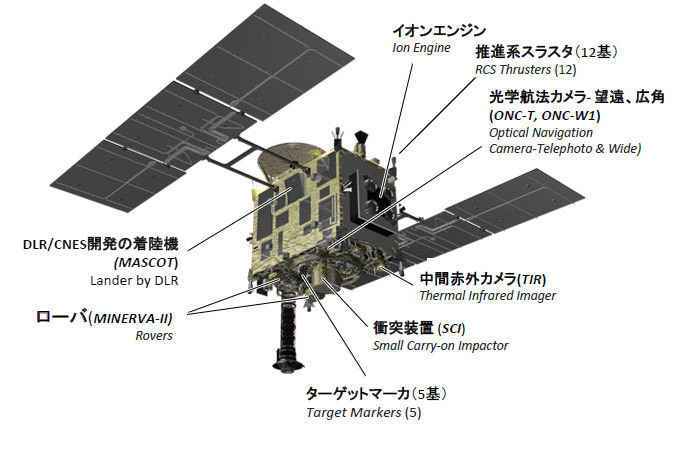
6. Akatsuki at Venus
This Japanese spacecraft missed orbital insertion a few years back, but gets a second chance at life in 2015. Launched in 2010 atop an H-IIA rocket from the Tanegashima Space Center in Japan, Akatsuki failed to enter orbit around Venus at the end of 2010, and instead headed out for a heliocentric path around the Sun. Some quick thinking by JAXA engineers led to a plan to attempt to place Akatsuki in Venusian orbit in November 2015. This would be a first for the Japanese space agency, as attempts by JAXA at placing a spacecraft in orbit around another planet – including the Mars Nozomi probe – have thus far failed.
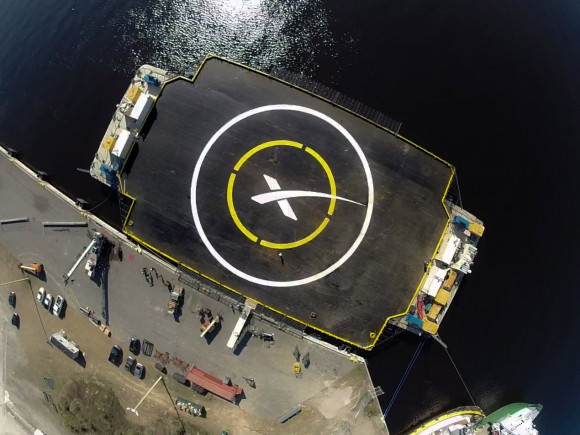

5. SpaceX to Attempt to Land on a Sea Platform
It’ll definitely rock if they pull it off next week: on January 6th, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will lift off from Cape Canaveral with its Dragon spacecraft headed to the International Space Station on mission CRS-5. Sure, these resupply missions are becoming routine, but after liftoff, SpaceX is attempting something new and daring: landing the Falcon-9 first stage Buck Rodgers style, “fins first” on a floating barge. This is the next step in ultimately proving the feasibility of having the rocket fly back to the launch site for eventual reuse. If nothing else, expect some stunning video of the attempt soon!
4. NASA to Decide on an Asteroid Mission
Some major decisions as to the fate and the future of manned space exploration are due next year, as NASA is expected to decide on the course of action for its Asteroid Redirect Mission. The current timeline calls for the test of the SLS rocket in 2018, and the launch of a spacecraft to recover an asteroid and place it in orbit around the Moon in 2019. If all goes according to plan – a plan which could always shift with the political winds and future changes in administrations – we could see astronauts exploring a captured asteroid by the early 2020s.

3. Long Duration ISS Missions
Beginning in 2015, astronauts and cosmonauts will begin year-long stays aboard the ISS to study the effects of long duration space missions. In March of 2015, cosmonaut Mikhail Korniyenko and U.S. astronaut Scott Kelly will launch as part of Expedition 43 headed to the ISS. The Russians have conducted stays in space longer than a year aboard the Mir space station, but Kelly’s stay aboard the ISS will set a duration record for NASA astronauts. Perhaps, a simulated “Mars mission” aboard the ISS could be possible in the coming years?

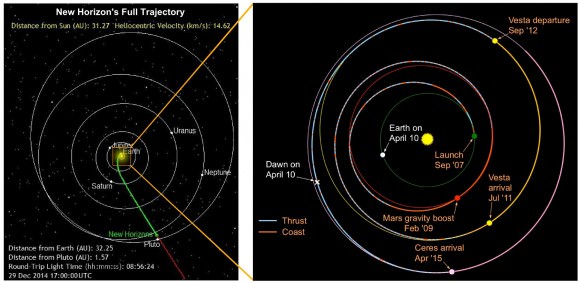
2. Dawn at Ceres
Fresh off of exploring Vesta, NASA’s Dawn spacecraft will become the first mission to enter orbit around a second object, the asteroid 1 Ceres next year in April 2015. The largest asteroid and the first object of its kind discovered on the first day of the 19th century, Ceres looks to be a fascinating world in its own right. Does it possess water ice? Active geology? Moons of its own? If Dawn’s performance at Vesta was any indication, we’re in for another exhilarating round of space exploration!
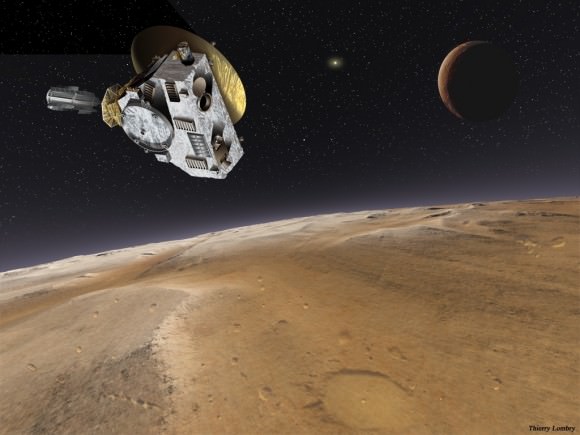

1. New Horizons at Pluto
An easy No. 1,we finally get our first good look at Pluto in July, as NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft flies less than 14,000 kilometres from the surface of the distant world. Launched in 2006, New Horizons will “thread the needle” between Pluto and Charon in a flurry of activity as it passes by. New Horizons will then turn back as it passes into the shadows of Pluto and Charon and actually view the two worlds as they occult the distant Sun. And from there, New Horizons will head out to explore Kuiper Belt Objects of opportunity.
And these are just the top stories that are slated to be big news in space in 2015. Remember, another Chelyabinsk meteor or the next big comet could drop by at any time… space news can be unpredictable, and its doubtless that 2015 will have lots more surprises in store.