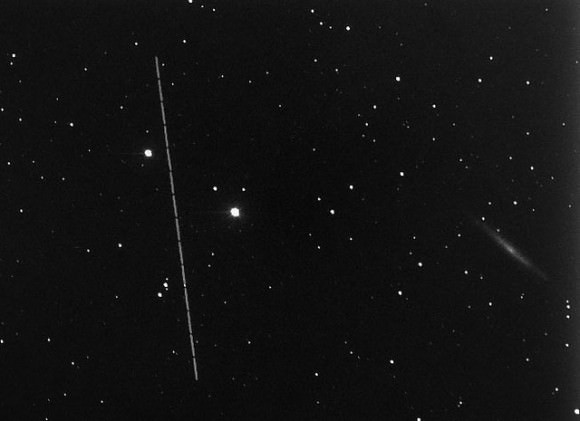
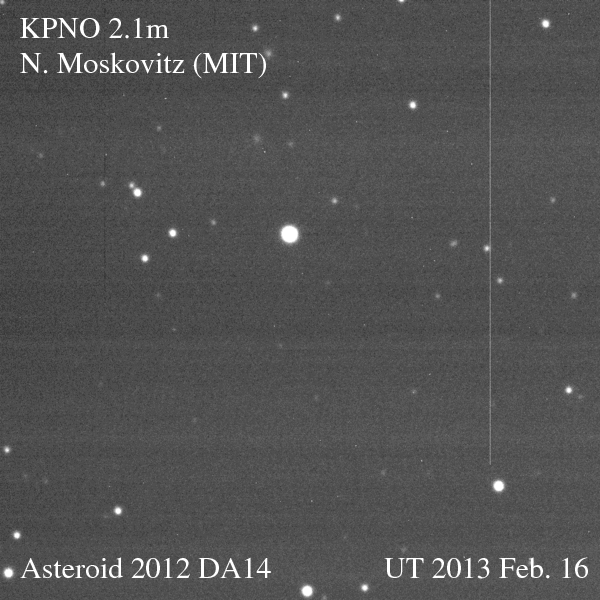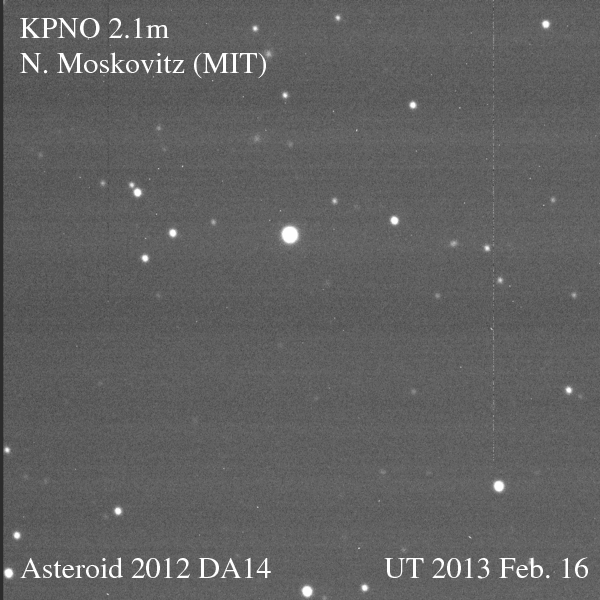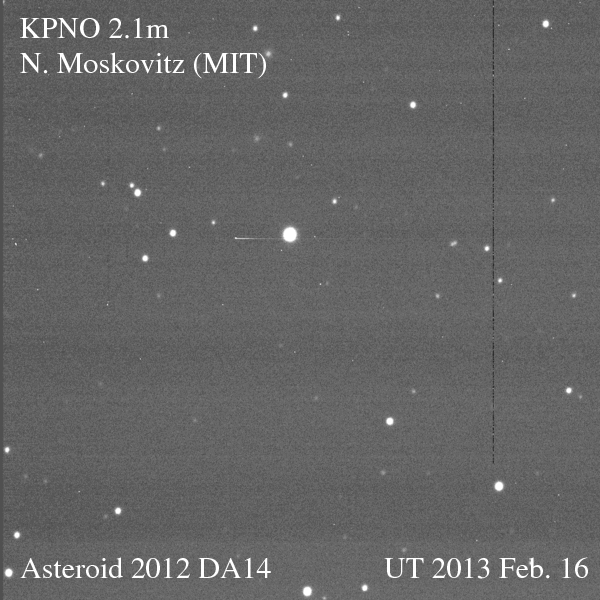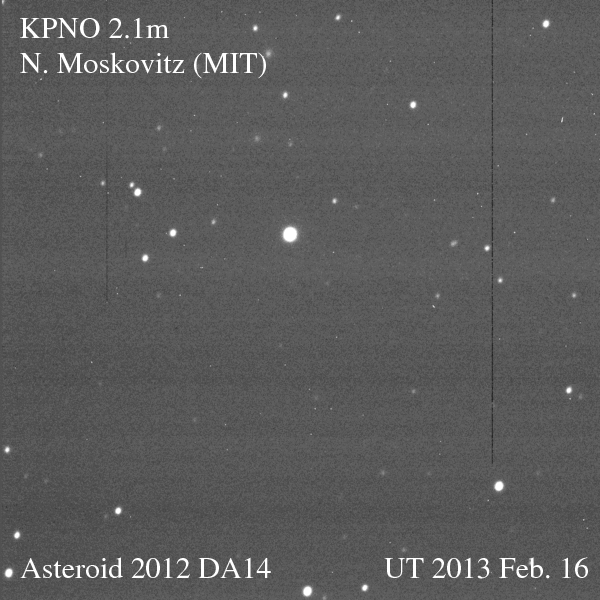
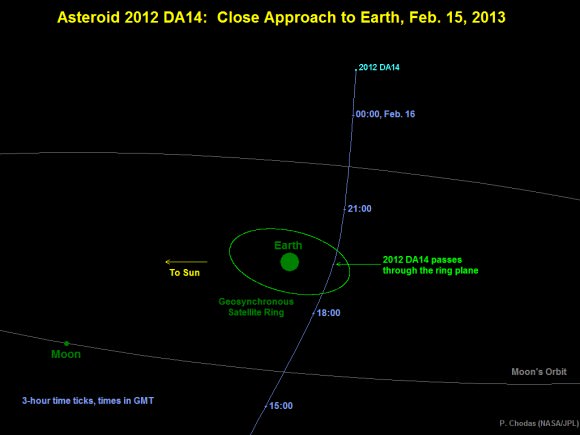
Just as anticipated, on Friday, Feb. 15, asteroid 2012 DA14 passed us by, zipping 27,000 kilometers (17,000 miles) above Earth’s surface — well within the ring of geostationary weather and communications satellites that ring our world. Traveling a breakneck 28,100 km/hr (that’s nearly five miles a second!) the 50-meter space rock was a fast-moving target for professional and amateur observers alike. And even as it was heading away from Earth DA14 was captured on camera by a team led by MIT researcher Dr. Nicholas Moskovitz using the 2.1-meter telescope at the Kitt Peak National Observatory in Tucson, AZ. The team’s images are shown above as an animated gif (you may need to click the image to play it.)
This object’s close pass, coupled with the completely unexpected appearance of a remarkably large meteor in the skies over Chelyabinsk, Russia on the morning of the same day, highlight the need for continued research of near-Earth objects (NEOs) — since there are plenty more out there where these came from.
“Flybys like this, particularly for objects smaller than 2012 DA14, are not uncommon. This one was special because we knew about it well in advance so that observations could be planned to look at how asteroids are effected by the Earth’s gravity when they come so close.”
– Dr. Nicholas Moskovitz, MIT
The animation shows 2012 DA14 passing inside the Little Dipper, crossing an area about a third the size of the full Moon in 45 minutes. North is to the left.
(For a high-resolution version of the animation, click here.)

According to the National Optical Astronomy Observatory, which operates the Kitt Peak Observatory, Dr. Moskovitz’ NSF-supported team “are analyzing their data to measure any changes in the rotation rate of the asteroid after its close encounter with the Earth. Although asteroids are generally too small to resolve with optical telescopes, their irregular shape causes their brightness to change as they rotate. Measuring the rotation rate of the asteroid in this way allows the team to test models that predict how the earth’s gravity can affect close-passing asteroids. This will lead to a better understanding of whether objects like 2012 DA14 are rubble piles or single solid rocks.
“This is critical to understanding the potential hazards that other asteroids could pose if they collide with the Earth.”
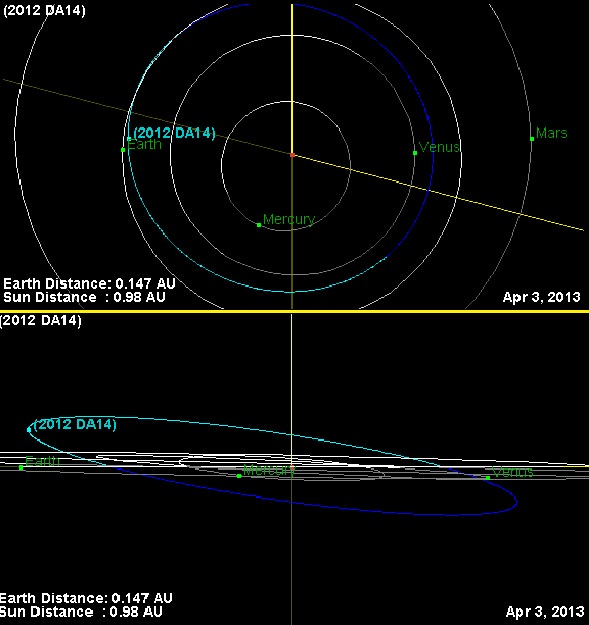
So just how close was DA14’s “close pass?” Well, if Earth were just a few minutes farther along in its orbit, we would likely be looking at images of its impact rather than its departure.*
Although this particular asteroid isn’t expected to approach Earth so closely at any time in the foreseeable future — at least within the next 130 years — there are lots of such Earth-crossing objects within the inner Solar System… some we’re aware of, but many that we’re not. Identifying them and knowing as many details as possible about their orbits, shapes, and compositions is key.
Even this soon after the Feb. 15 flyby observations of 2012 DA14 have provided more information on its orbit and characteristics., allowing for fine-tuning of the data on it.
According to the Goldstone Radar Observatory web page, the details on 2012 DA14 are as follows:
Semimajor axis 1.002 AU
Eccentricity 0.108
Inclination 10.4 deg
Perihelion distance 0.893 AU
Aphelion distance 1.110 AU
Absolute magnitude (H) 24.4
Diameter ~50 meters (+- a factor of two)
Rotation period ~6 h (N. Moskovitz, pers. comm.)
Pole direction unknown
Lightcurve amplitude ~1 mag (N. Moskovitz, pers. comm.)
Spectral class Ld (N. Moskovitz, pers. comm.)
Goldstone is currently conducting radar observations on the asteroid. A radar map of its surface and motion is anticipated in the near future.
Read more about Dr. Moskovitz’ observations on the NOAO website here, and see more images of 2012 DA14 captured by astronomers around the world in our previous article.

Also, in an encouraging move by international leaders in the field, during the fiftieth session of the Scientific and Technical Subcommittee of the Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space, currently being held from at the United Nation Office in Vienna, near-Earth objects are on the agenda with a final report to be issued by an Action Team. Read the report PDF here.
*According to astronomer Phil Plait, while the orbits of Earth and DA14 might intersect at some point, on the 15th of February 2013 the asteroid slipped just outside of Earth’s orbit — a little over 17,000 miles shy. “It was traveling one way and the Earth another, so they could not have hit each other on this pass no matter where Earth was in its orbit,” he wrote in an email. Still, 17,000 miles is a very close call astronomically, and according to Neil deGrasse Tyson on Twitter, it “will one day hit us, like the one in Russian [sic] last night.” When? We don’t know yet. That’s why we must keep watching.