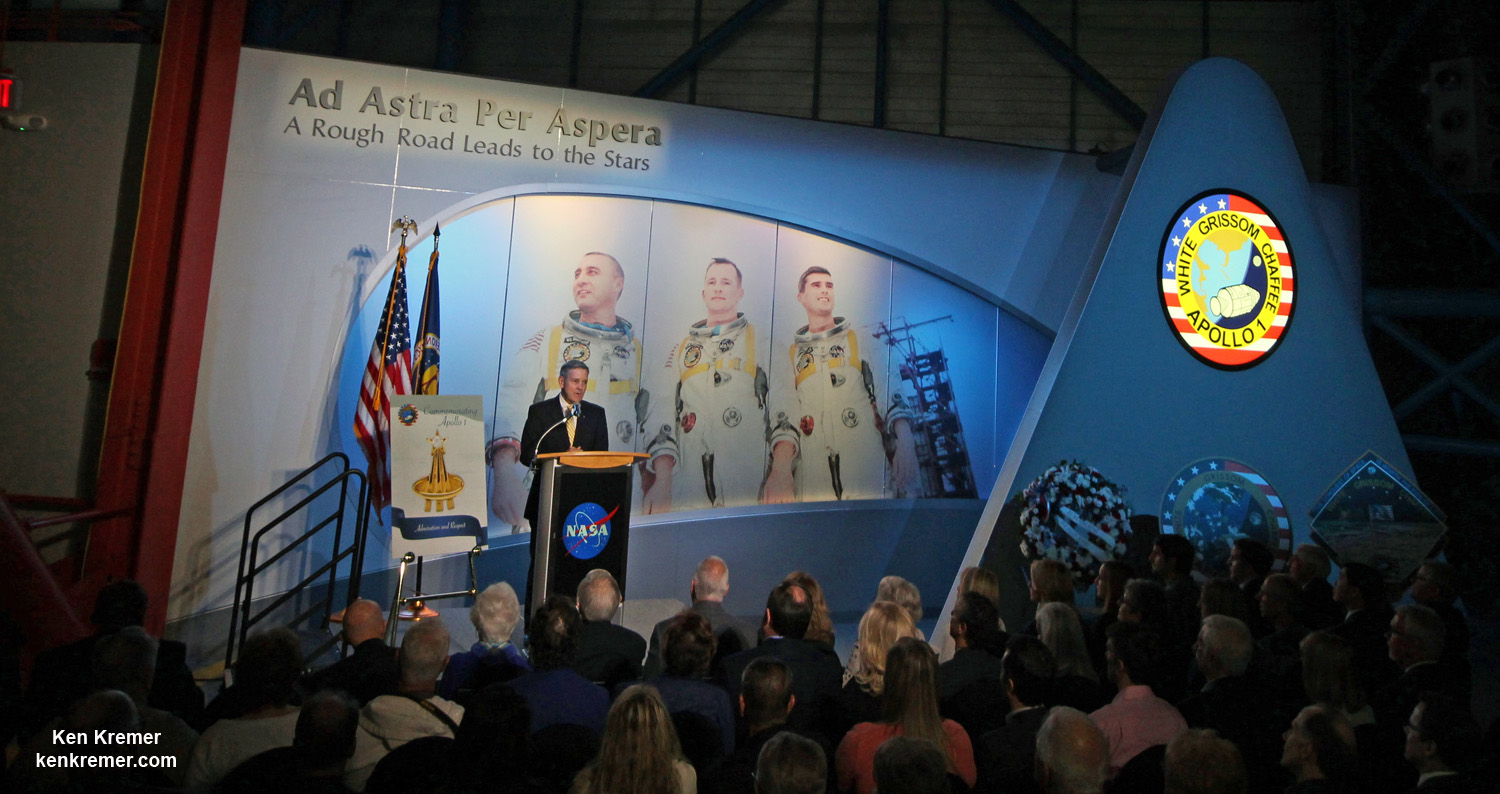
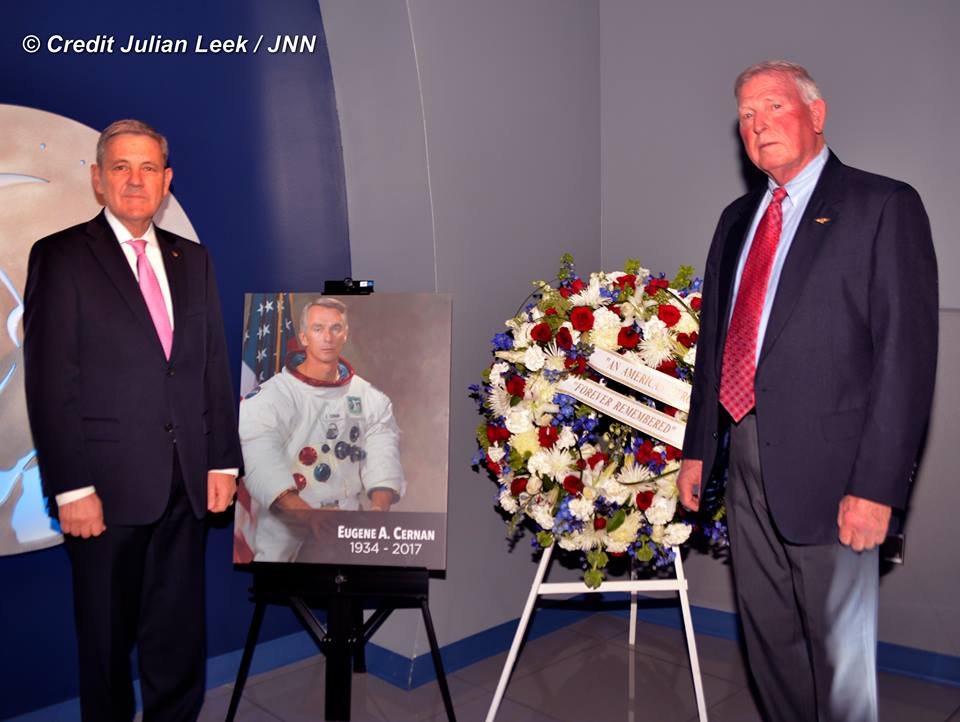
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER VISITOR COMPLEX, FL – NASA unveiled a new tribute exhibit honoring three fallen astronaut heroes 50 years to the day of the Apollo 1 tragedy on January 27, 1967 when the three man crew perished in a flash fire on the launch pad during a capsule test that was not considered to be dangerous.
The Apollo 1 prime crew comprising NASA astronauts Gus Grissom, Ed White II and Roger Chaffee were killed during routine practice countdown testing when a fire suddenly erupted inside the cockpit as they were strapped to their seats in their Apollo command module capsule, on a Friday evening at 6:31 p.m. on January 27, 1967.
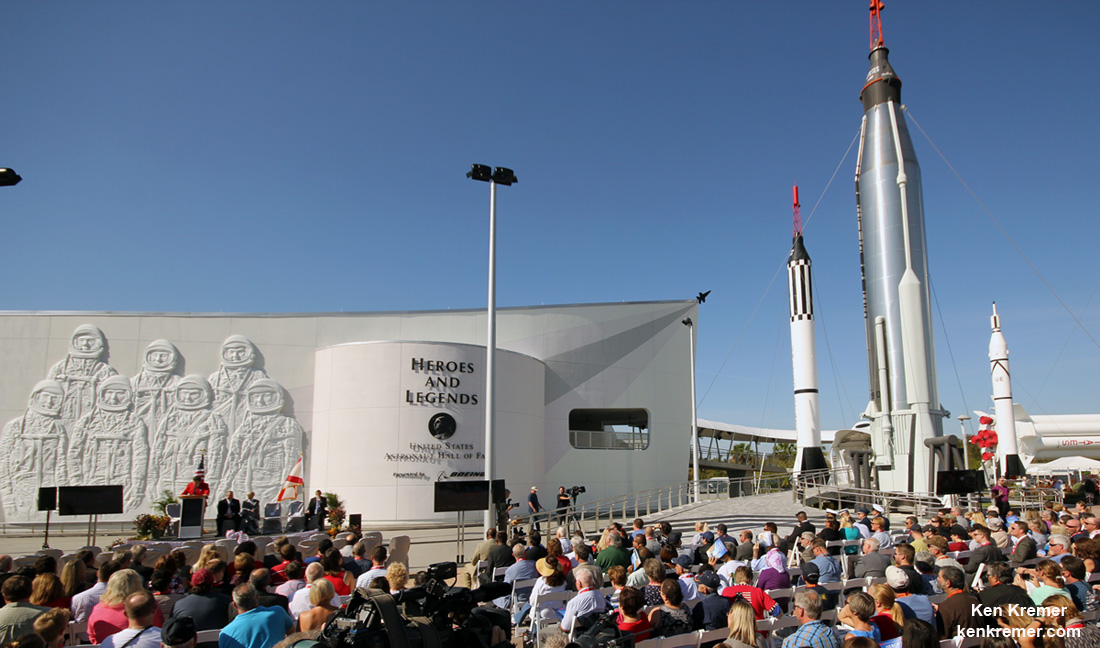
“It’s been 50 years since the crew of Apollo 1 perished in a fire at the launch pad, but the lives, accomplishments and heroism of the three astronauts are celebrated in a dynamic, new tribute that is part museum, part memorial and part family scrapbook,” says a NASA narrative that aptly describes the exhibit and the memorial ceremony I attended at the Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Jan. 27, 2017 on behalf of Universe Today.
It was the first disaster with a human crew and the worst day in NASA’s storied history to that point.
The tribute is named called “Ad Astra Per Aspera – A Rough Road Leads to the Stars.”

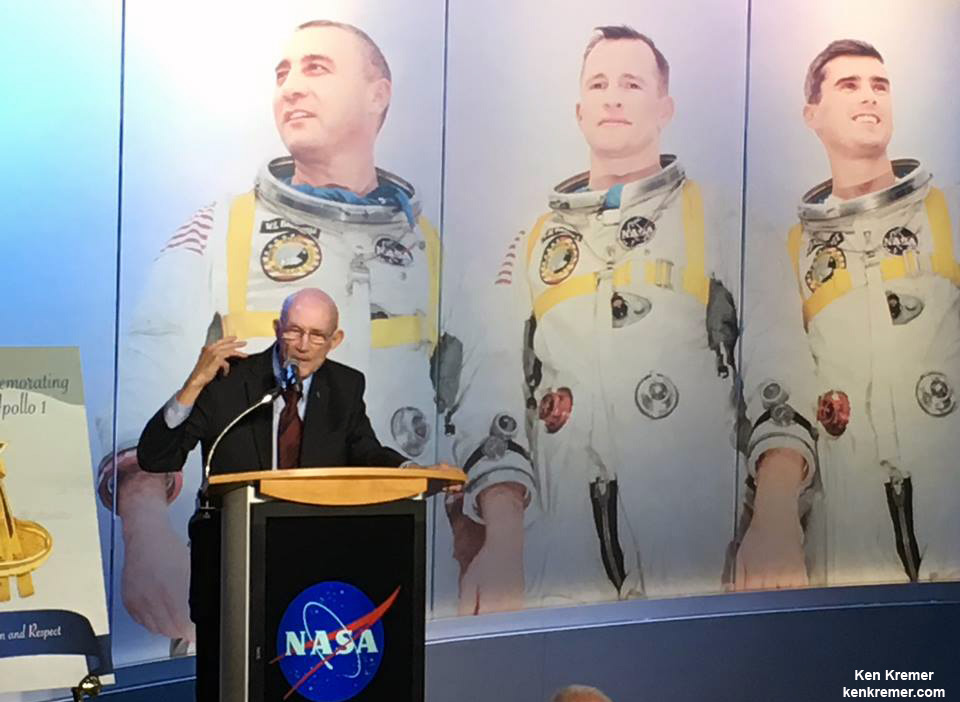
At the tribute dedication ceremony Kennedy Space Center Director and former astronaut Bob Cabana said the families of the fallen crew gave their approvals and blessing to the efforts that would at last tell the story of Apollo 1 to all generations – those who recall it and many more to young or not yet born to remember the tragedy of the early days of America’s space program.
“It’s long overdue,” said KSC center director and former astronaut Bob Cabana at the KSC dedication ceremony to family, friends and invited guests colleagues. “I’m proud of the team that created this exhibit.”
“Ultimately, this is a story of hope, because these astronauts were dreaming of the future that is unfolding today,” said Cabana. Generations of people around the world will learn who these brave astronauts were and how their legacies live on through the Apollo successes and beyond.”
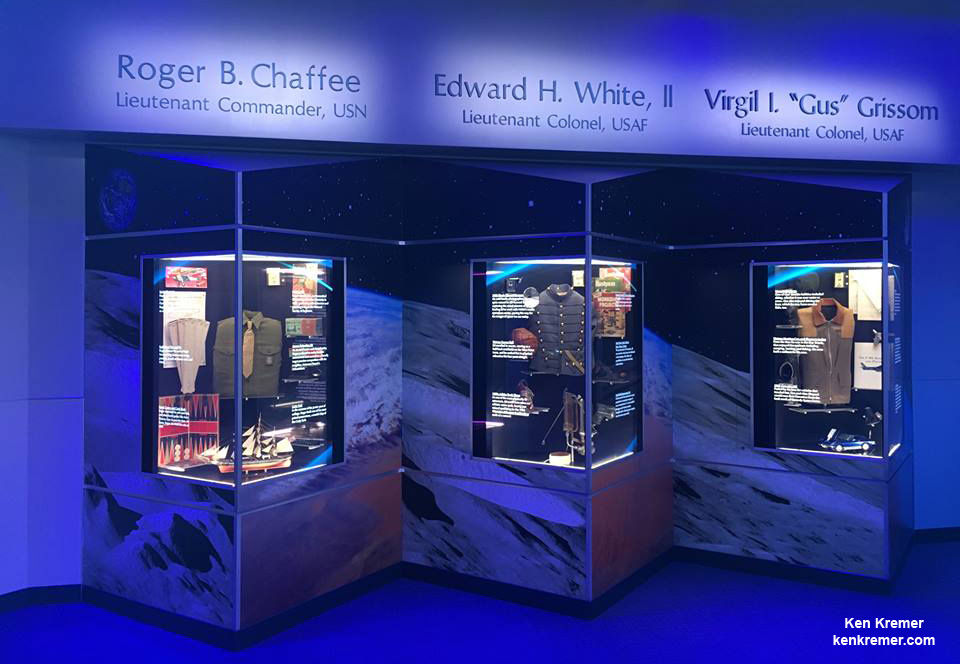
The exhibit “showcases clothing, tools and models that define the men as their parents, wives and children saw them as much as how the nation viewed them.”
The main focus was to introduce the astronauts to generations who never met them and may not know much about them or the early space program, says NASA.
“This lets you now meet Gus Grissom, Ed White and Roger Chaffee as members of special families and also as members of our own family,” said NASA’s Luis Berrios, who co-led the tribute design that would eventually involve more than 100 designers, planners and builders to realize.
“You get to know some of the things that they liked to do and were inspired by. You look at the things they did and if anyone does just one of those things, it’s a lifetime accomplishment and they did all of it and more.”
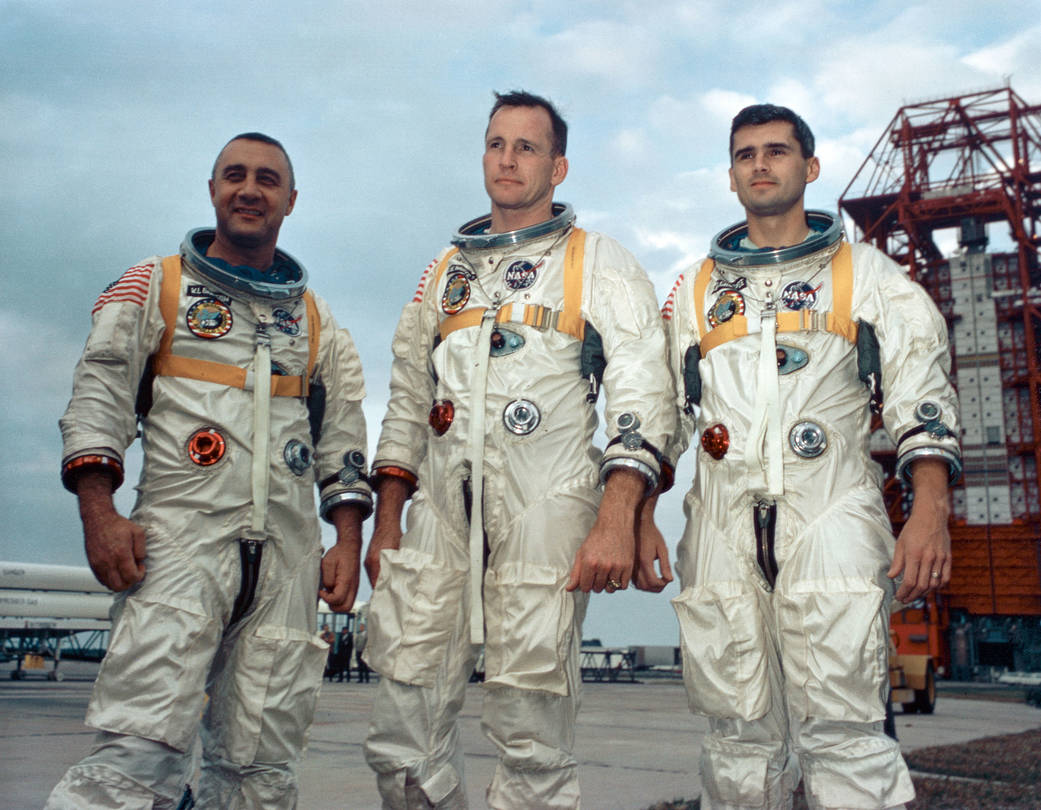

The crew and the Apollo 1 command module were stacked atop the Saturn 1B rocket at Launch Complex 34 on what is now Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
During the “plugs out” test the Saturn 1B rocket was not fueled. But the fatal flaw was the atmosphere of pure oxygen for the astronauts to breath inside the sealed Apollo 1 command module which was pressurized to 16.7 psi.

Another significantly contributing fatal flaw was the inward opening three layered hatch that took some 90 seconds to open under the best of conditions.
After working all afternoon through the practice countdown and encountering numerous problems, something went terribly awry. Without warning a flash fire erupted in the cockpit filled with 100 percent oxygen and swiftly spread uncontrollably creating huge flames licking up the side of the capsule, acrid smoke and a poisonous atmosphere that asphyxiated, burned and killed the crew.
With the scorching temperatures spiking and pressures rapidly rising in a closed system, the capsule exploded some 20 seconds after the fire started. And because of the pressure buildup inside with flames licking up the sides and the toxic atmosphere generated from burning materials, the crew succumbed and could not turn the latch to pull open the hatch against the pressure.
The pad crew tried bravely in vain to save them, fighting heavy smoke and fire and fearing that the attached launch abort system on top of the capsule would ignite and kill them all too.
An investigation would determine that the fire was likely caused by a spark from frayed wiring, perhaps originating under Grissom’s seat.
“An electrical short circuit inside the Apollo Command Module ignited the pure oxygen environment and within a matter of seconds all three Apollo 1 crewmembers perished,” NASA concluded.
NASA and contractor North American Aviation completely redesigned the capsule with major engineering changes including an atmosphere of 60 percent oxygen and 40 percent nitrogen at 5 psi blower pressure, new hatch that could open outwards in 5 seconds, removing flammable materials among many others that would make the Apollo spacecraft much safer for the upcoming journeys to the moon.
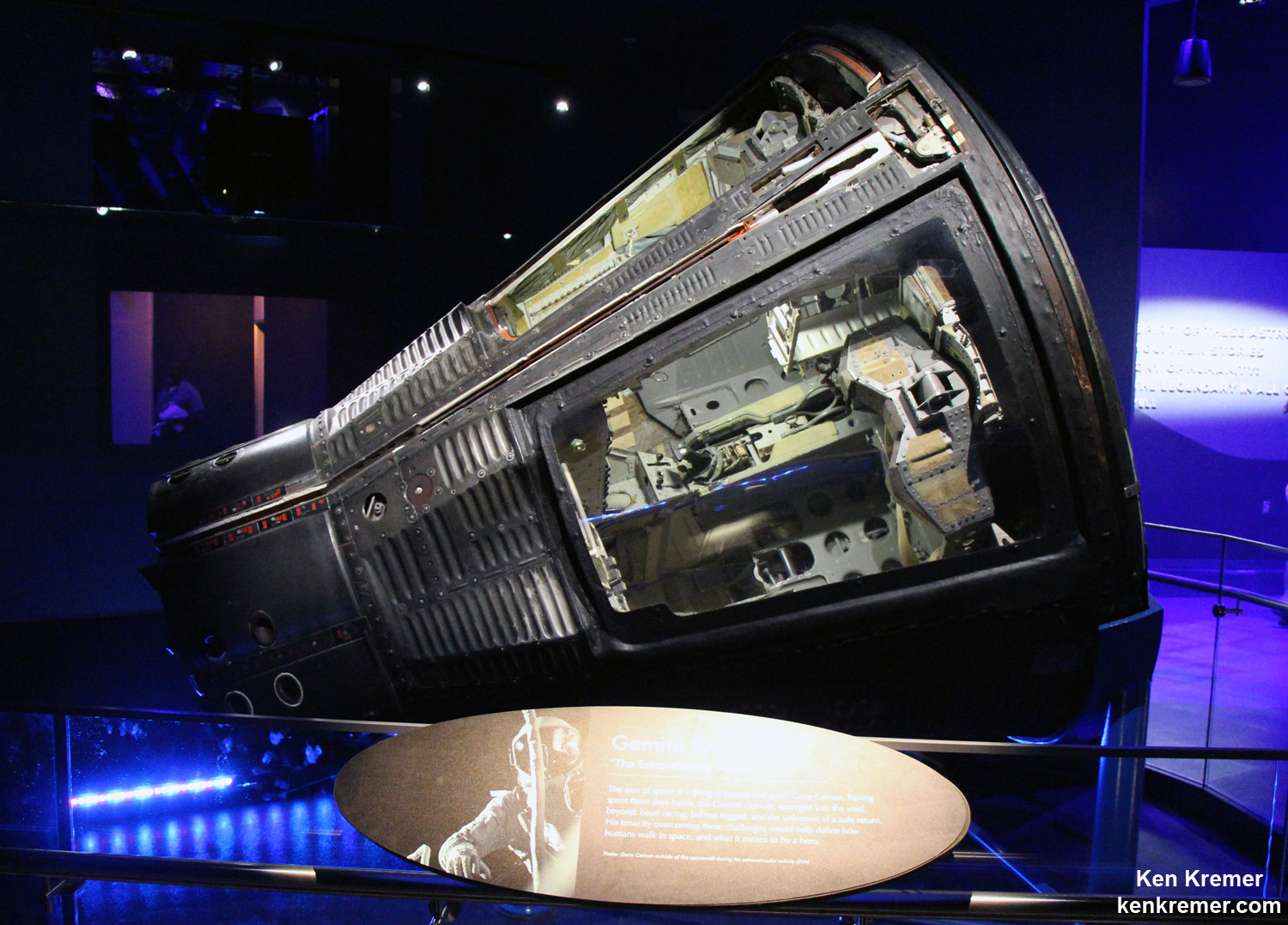
The multi-layed hatch serves as the centerpiece of the tribute exhibit. No piece of Apollo 1 has ever before been put on public display. Alongside the old hatch, the new hatch is displayed that was used on all the remaining Apollo missions.

Display cases highlights the lives and careers of the three astronauts in these NASA descriptions.
Gus Grissom was “one of NASA’s Original Seven astronauts who flew the second Mercury mission, a hunting jacket and a pair of ski boots are on display, along with a small model of the Mercury spacecraft and a model of an F-86 Sabre jet like the one he flew in the Korean War. A slide rule and engineering drafts typify his dedication to detail.”
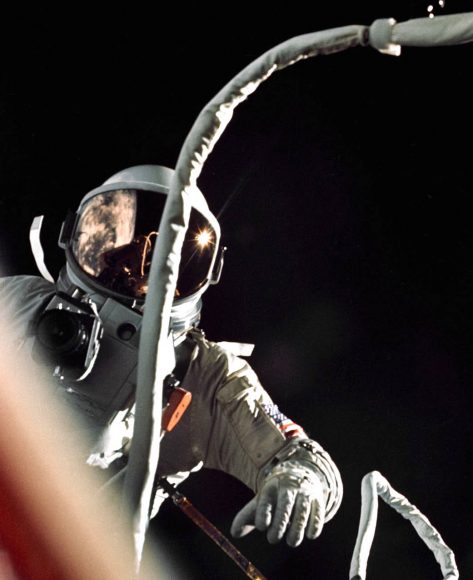
“The small handheld maneuvering thruster that Ed White II used to steer himself outside his Gemini capsule during the first American spacewalk features prominently in the display case for the West Point graduate whose athletic prowess nearly equaled his flying acumen. An electric drill stands alongside the “zip gun,” as he called the thruster.”
“It was great to juxtaposition it with a drill which was also a tool that Ed loved to use,” Berrios said. “He had a tremendous passion for making things for his family.”
“Roger Chaffee, for whom Apollo 1 would have been his first mission into space, was an esteemed Naval aviator who became a test pilot in his drive to qualify as an astronaut later. Displayed are board games he played with his wife and kids on rare evenings free of training.”
Grissom, White and Chaffee composed NASA’s first three person crew following the one man Mercury program and two man Gemini program, that had just concluded in November 1966 with Gemini 12.
The trio had been scheduled to blastoff on February 21, 1967 on a 14 day long mission in Earth orbit to thoroughly check out the Apollo command and service modules.
Apollo 1 was to be the first launch in NASA’s Apollo moon landing program initiated by President John F. Kennedy in 1961.
Apollo 1 was planned to pave the way to the Moon so that succeeding missions would eventually “land a man on the Moon and return him safely to Earth before this decade is out” as Kennedy eloquently challenged the nation to do.

I remember seeing the first news flashes about the Apollo 1 fire on the TV as a child, as it unfolded on the then big three networks. It is indelibly marked in my mind. This new exhibit truly tells the story of these astronaut heroes vividly to those with distant memories and those with little or no knowledge of Apollo 1.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.