The fields of astronomy and astrophysics are poised for a revolution in the coming years. Thanks to next-generation observatories like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), scientists will finally be able to witness the formation of the first stars and galaxies in the Universe. In effect, they will be able to pierce the veil of the Cosmic Dark Ages, which lasted from roughly 370,000 years to 1 billion years after the Big Bang.
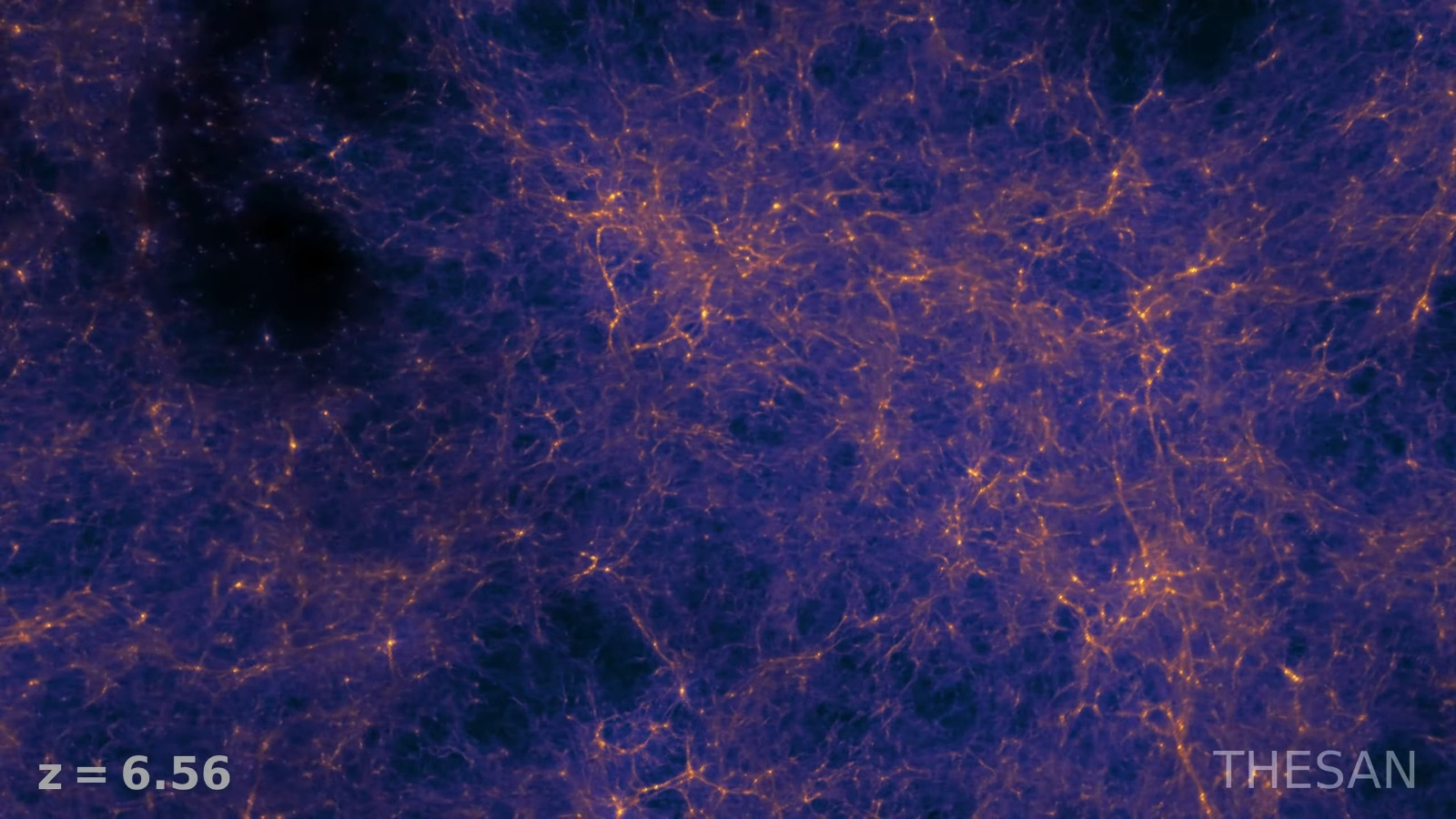
During this period, the Universe was filled with clouds of neutral hydrogen and decoupled photons that were not visible to astronomers. In anticipation of what astronomers will see, researchers from the Harvard & Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA), the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics (MPIA) created a new simulation suite called Thesan that simulates the earliest period of galaxy formation.
Continue reading “New Simulation Recreates an Early Time in the Universe That Still Hasn't Been Seen Directly”