In this series we are exploring the weird and wonderful world of astronomy jargon! You’ll feel balanced with today’s topic: hydrostatic equilibrium!
Continue reading “Astronomy Jargon 101: Hydrostatic Equilibrium”The Object About to Hit the Moon isn’t a SpaceX Booster After All
Last month, astronomers reported that a discarded upper stage of a Falcon 9 rocket, launched 7 years ago, was on a collision course with the Moon. The rocket in question carried NASA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR) to the Sun-Earth L1 Lagrange point, where the still-operating observatory provides advance warning on solar wind activities. The leftover rocket stage, meanwhile, became a floating piece of space junk orbiting the Sun. Its ultimate fate was unknown, until last month, when astronomer Bill Gray predicted that it was bound for an impact with the Moon sometime on March 4th, 2022.
This week, Gray, who has been tracking the object ever since, released an update on the situation. He confirmed that there is indeed a rocket stage on course to crash into the far side of the Moon, but it’s not a SpaceX rocket at all. Instead, it’s a Chinese booster: the upper stage of the rocket that carried China’s Chang’e 5-T1 mission to the Moon in 2014.
Continue reading “The Object About to Hit the Moon isn’t a SpaceX Booster After All”Astronomers Scan the Center of the Milky Way for Any Sign of Intelligent Civilizations. Nothing but Silence.
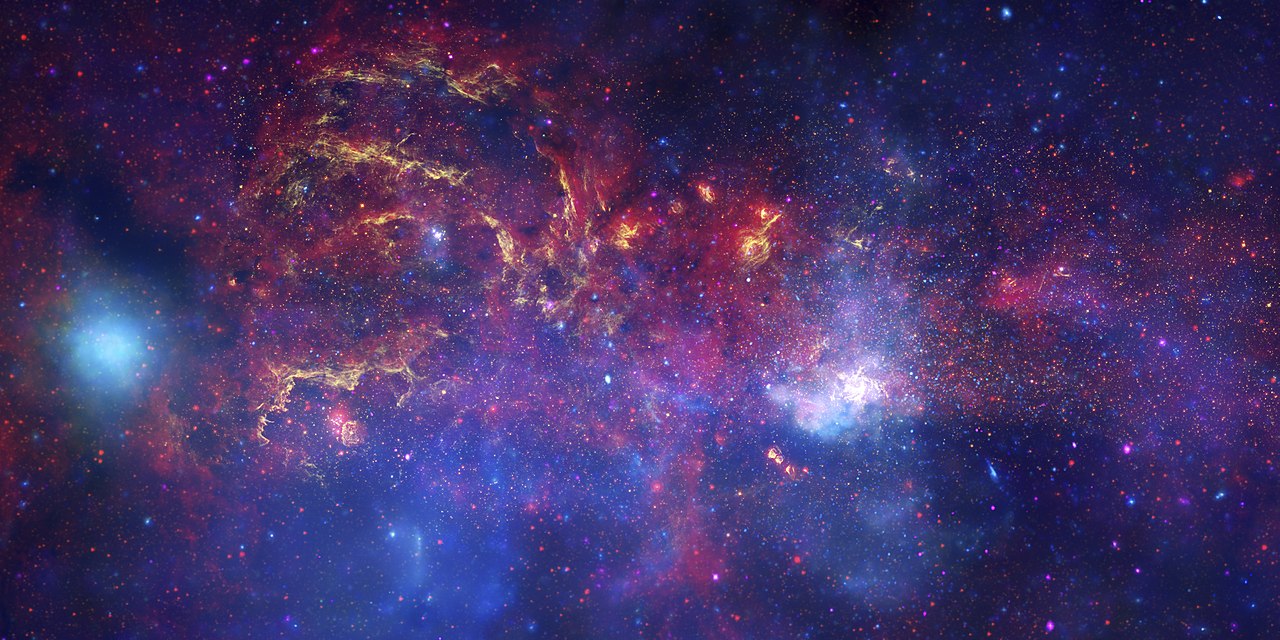

Are there civilizations somewhere else in the Universe? Somewhere else in the Milky Way? That’s one of our overarching questions, and an answer in the affirmative would be profound.
Humanity’s pursued the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) in one form or another since shortly after the advent of radio waves in the early 20th century. Efforts have waxed and waned over the decades, but the search has never been completely abandoned.
The search detected transient hints in the form of unexplained radio waves in the past, but nothing that comprises reliable evidence. Now a new search for technosignatures in the Milky Way’s center has turned up nothing.
Continue reading “Astronomers Scan the Center of the Milky Way for Any Sign of Intelligent Civilizations. Nothing but Silence.”Astronomy Jargon 101: Hubble’s Law
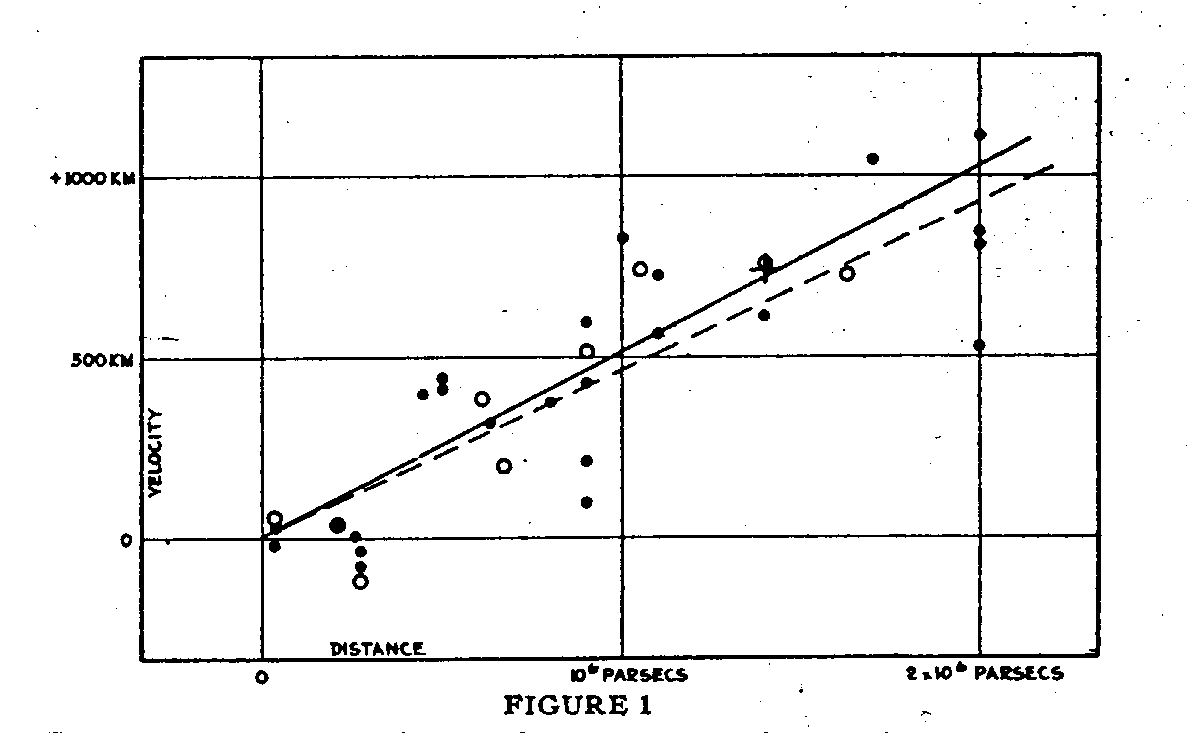
In this series we are exploring the weird and wonderful world of astronomy jargon! You’ll expand your horizons with today’s topic: Hubble’s Law!
Continue reading “Astronomy Jargon 101: Hubble’s Law”Astronomy Jargon 101: Heliosphere

In this series we are exploring the weird and wonderful world of astronomy jargon! You’ll push the boundaries with today’s topic: the heliosphere!
Continue reading “Astronomy Jargon 101: Heliosphere”A THIRD Planet Found Orbiting Nearby Proxima Centauri
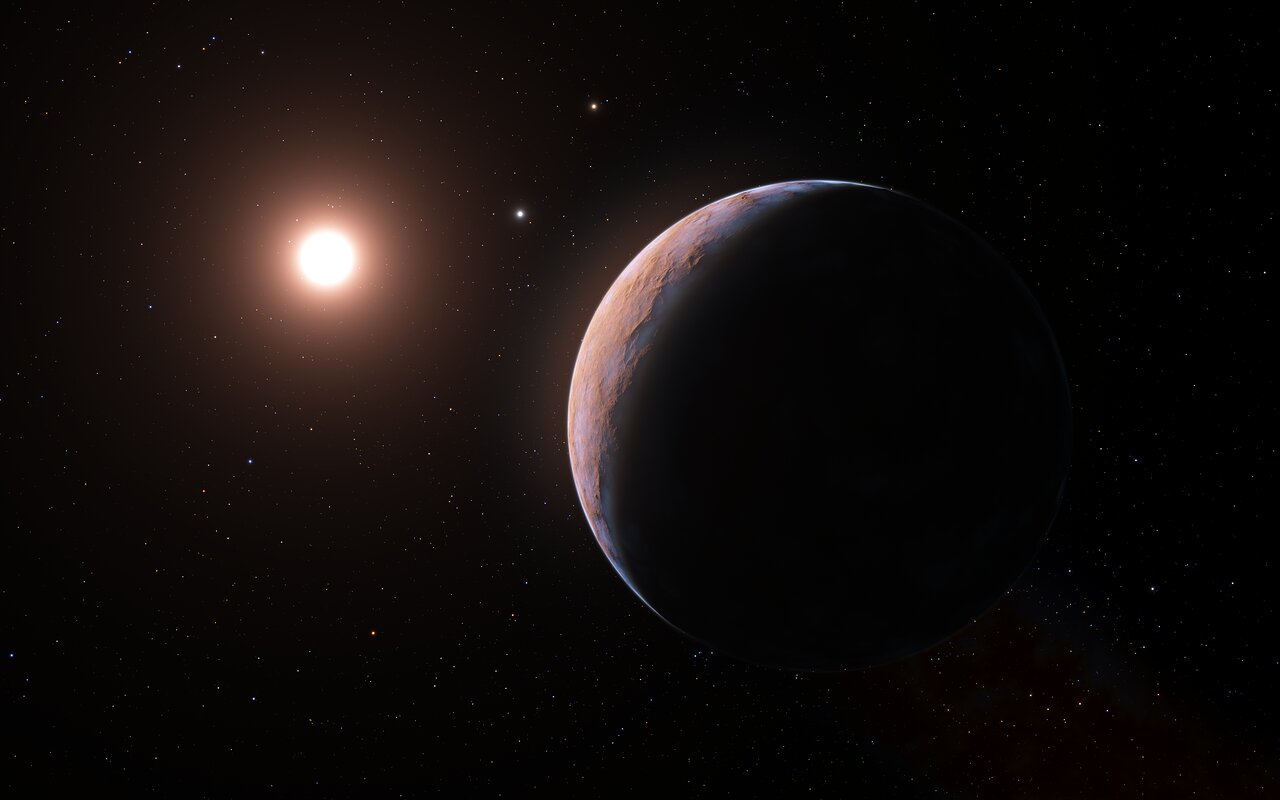

In August of 2016, astronomers with the European Southern Observatory (ESO) announced that they had discovered an exoplanet orbiting in neighboring Proxima Centauri. Based on Radial Velocity measurements (aka. Doppler Photometry), the discovery team estimated that the planet was roughly the same size and mass as Earth and orbited with Proxima Centauri’s Circumsolar Habitable Zone (HZ). In 2020, this planet was confirmed by follow-up observations.
In that same year, a second exoplanet (Proxima c) roughly seven times the mass of Earth (a Super-Earth or mini-Neptune) was confirmed. As if that wasn’t enough, an international team of astronomers with the ESO recently announced that they detected a third exoplanet around Proxima Centauri – Proxima d! This Mars-sized planet orbits about halfway between its host star and Proxima b and is one of the lightest exoplanets ever discovered.
Continue reading “A THIRD Planet Found Orbiting Nearby Proxima Centauri”Astronomy Jargon 101: Gravitational Lens
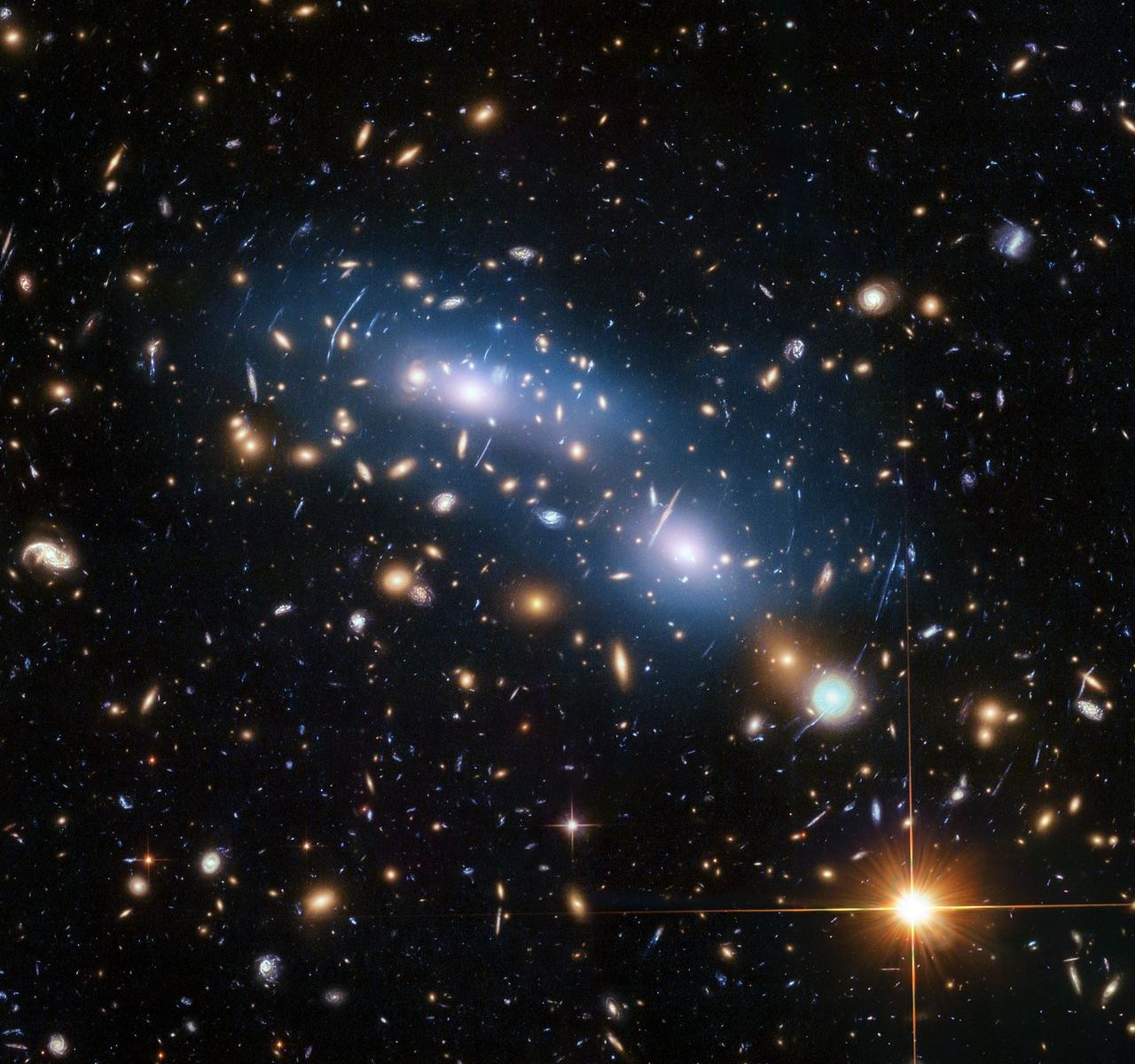

In this series we are exploring the weird and wonderful world of astronomy jargon! You’ll be seeing double with today’s topic: gravitational lens!
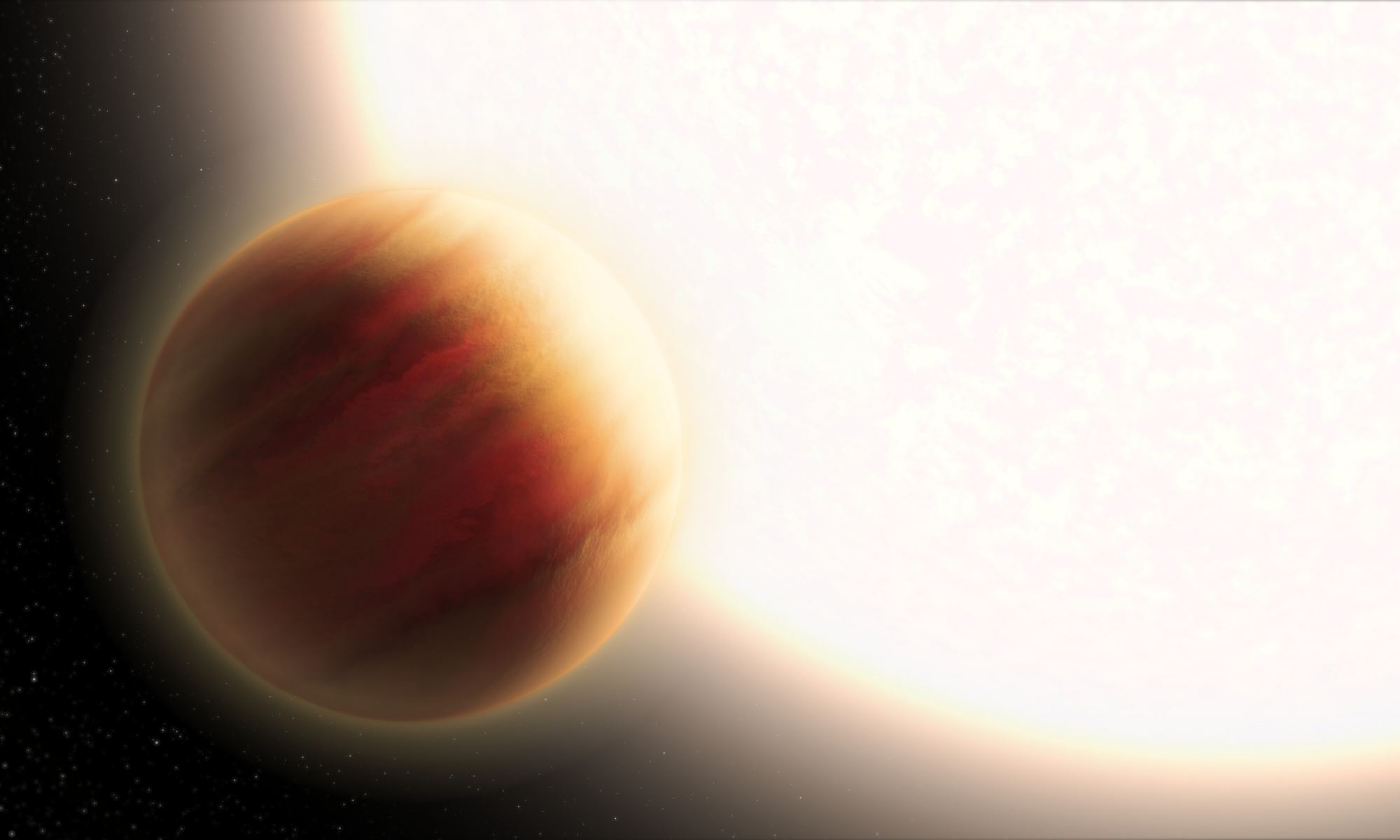
Continue reading “Astronomy Jargon 101: Gravitational Lens”Astronomers Measure the Layers of an Exoplanet's Atmosphere
The number of planets discovered beyond our Solar System has grown exponentially in the past twenty years, with 4,919 confirmed exoplanets (and another 8,493 awaiting confirmation)! Combined with improved instruments and data analysis, the field of study is entering into an exciting new phase. In short, the focus is shifting from discovery to characterization, where astronomers can place greater constraints on potential habitability.
In particular, the characterization of exoplanet atmospheres will allow astronomers to determine their chemical makeup and whether they have the right characteristics to support life. In a new study led by the University of Lund, an international team of researchers characterized the atmosphere of one of the most extreme exoplanets yet discovered. This included discerning what could be several distinct layers that have particular characteristics.
Continue reading “Astronomers Measure the Layers of an Exoplanet's Atmosphere”UAE’s Mars Hope Team Publishes ‘Mars Atlas’
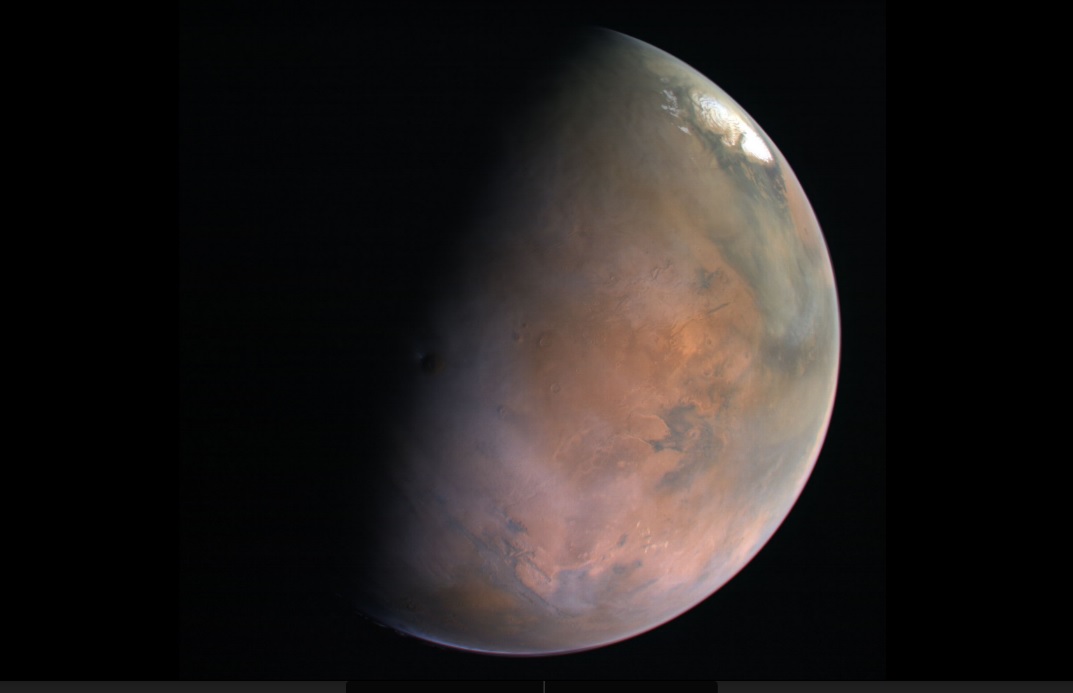
The United Arab Emirates Space Agency releases a unique comprehensive Mars Atlas of the Red Planet.
You have never seen Mars like this. Recently, the New York University of Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) released an 88-page look at Red Planet, dubbed The Atlas of Mars. The Atlas is free online, and uses spectacular imagery taken from the United Arab Emirates Space Agency’s ambitious Mars Hope mission.
Continue reading “UAE’s Mars Hope Team Publishes ‘Mars Atlas’”Astronomy Jargon 101: Neutrinos
In this series we are exploring the weird and wonderful world of astronomy jargon! You’ll barely be able to see today’s topic: neutrinos!
Continue reading “Astronomy Jargon 101: Neutrinos”