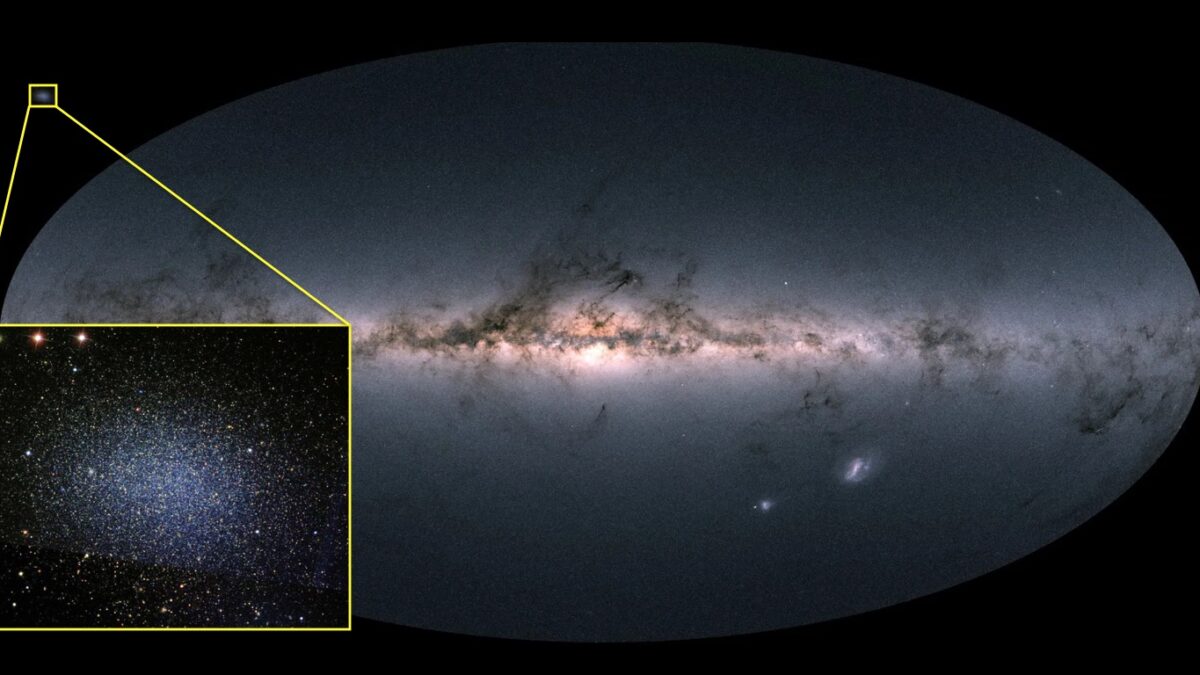
Since the 1970s, scientists have known that within the cores of most massive galaxies in the Universe, there beats the heart of a Supermassive Black Hole (SMBH). The presence of these giant black holes causes these galaxies to be particularly energetic, to the point where their central regions outshine all the stars in their disks combined – aka. Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN). The Milky Way galaxy has its own SMBH, known as Sagittarius A*, which has a mass of over 4 million Suns.
For decades, scientists have studied these objects in the hopes of learning more about their role in galactic formation and evolution. However, current research has shown that SMBHs may not be restricted to massive galaxies. In fact, a team of astronomers from the University of Texas at Austin’s McDonald Observatory recently discovered a massive black hole at the heart of a dwarf galaxy that orbits the Milky Way (Leo I). This finding could redefine our understanding of how black holes and galaxies evolve together.
Continue reading “A Nearby Dwarf Galaxy has a Surprisingly Massive Black Hole in its Heart”