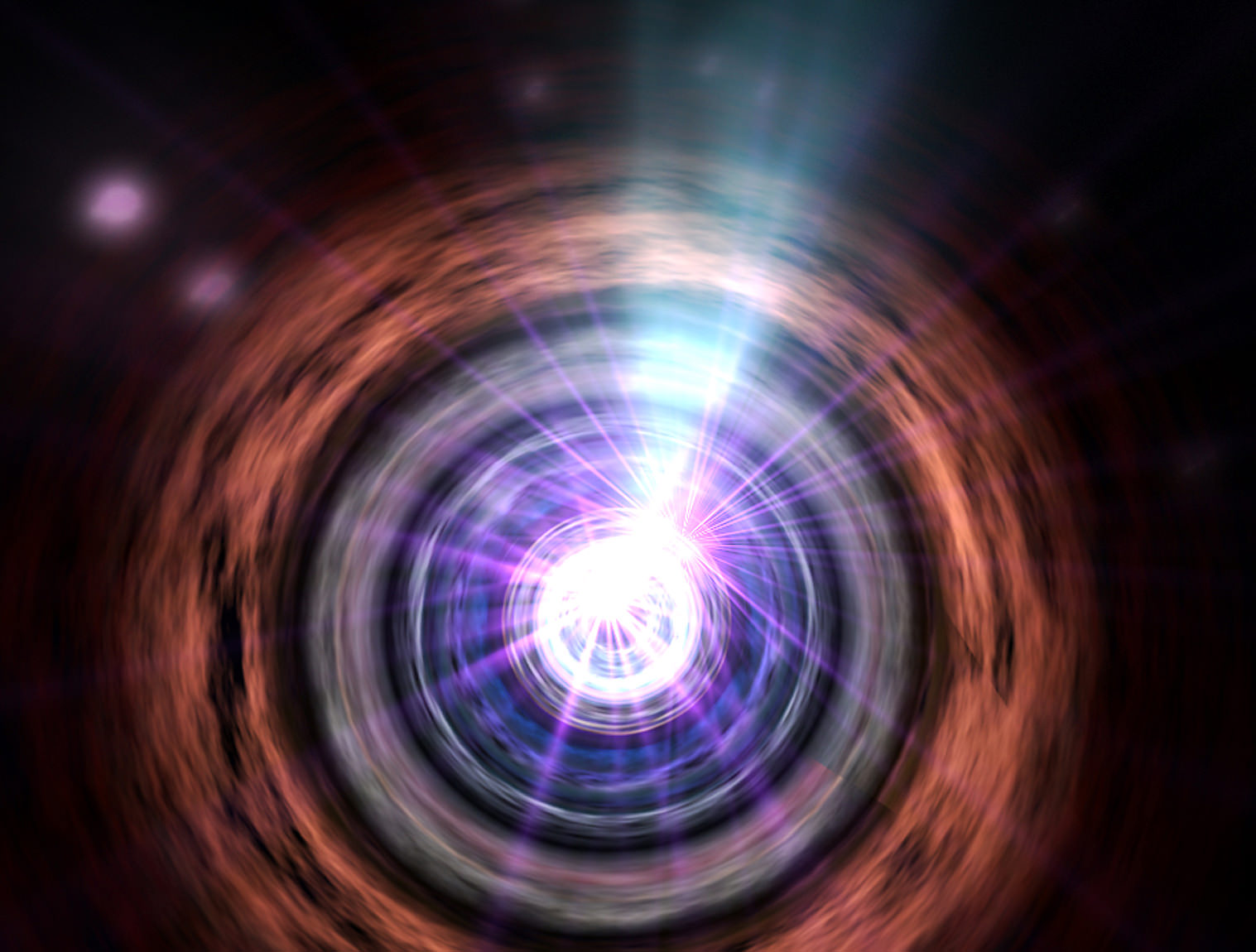
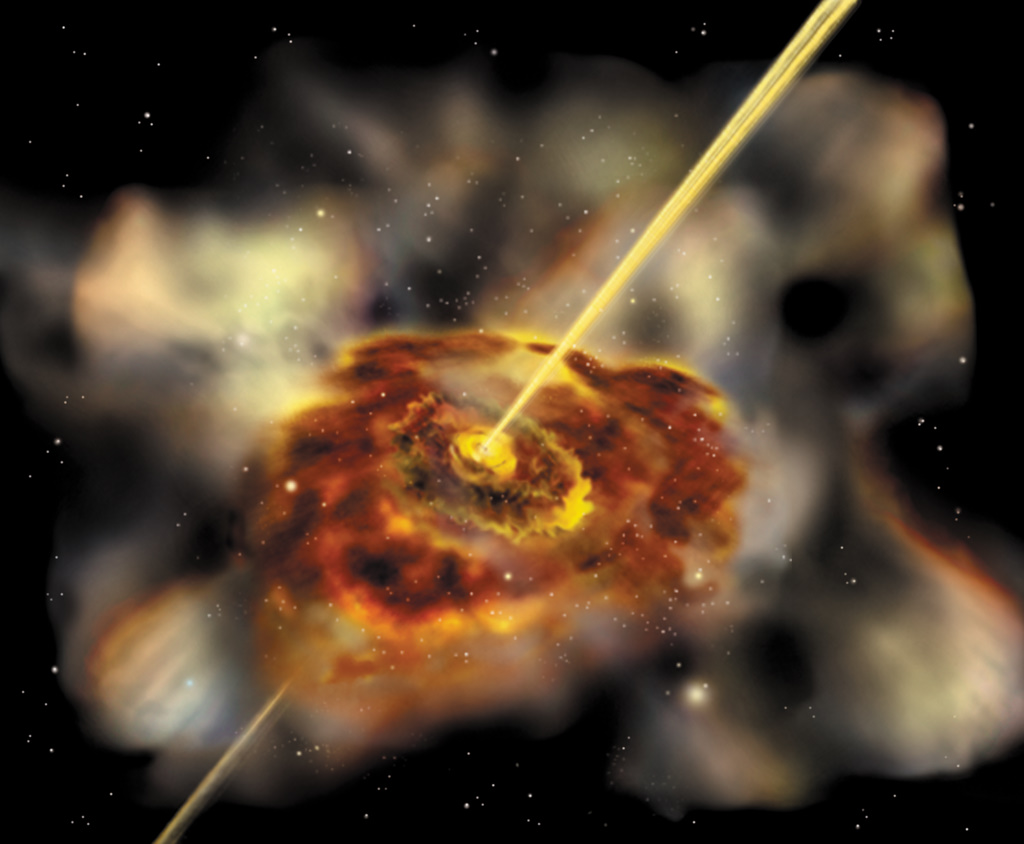
Even the most supermassive of the supermassive black holes aren’t very large, making it extremely difficult to measure their sizes. However, astronomers have recently developed a new technique that can estimate the mass of a black hole based on the movement of hot gas around them – even when the black hole itself it smaller than a single pixel.
Continue reading “Astronomers Have a new way to Measure the Mass of Supermassive Black Holes”Astronomers Might use Pulsars to First Detect Merging Supermassive Black Holes

Astronomers have been using gravitational waves to detect merging black holes for years now, but may have to rely on pulsars – rapidly spinning neutron stars – to observe the mergers of supermassive black holes.
Continue reading “Astronomers Might use Pulsars to First Detect Merging Supermassive Black Holes”Beyond “Fermi’s Paradox” XVII: What is the “SETI-Paradox” Hypothesis?

Welcome back to our Fermi Paradox series, where we take a look at possible resolutions to Enrico Fermi’s famous question, “Where Is Everybody?” Today, we examine the possibility that we haven’t heard from any aliens is because no one is transmitting!
In 1950, Italian-American physicist Enrico Fermi sat down to lunch with some of his colleagues at the Los Alamos National Laboratory, where he had worked five years prior as part of the Manhattan Project. According to various accounts, the conversation turned to aliens and the recent spate of UFOs. Into this, Fermi issued a statement that would go down in the annals of history: “Where is everybody?”
This became the basis of the Fermi Paradox, which refers to the disparity between high probability estimates for the existence of extraterrestrial intelligence (ETI) and the apparent lack of evidence. Since Fermi’s time, there have been several proposed resolutions to his question, including the possibility that everyone is listening, but no one is broadcasting – otherwise known as the “SETI-Paradox.”
Continue reading “Beyond “Fermi’s Paradox” XVII: What is the “SETI-Paradox” Hypothesis?”Arid Meteor Outburst in the Works This Week?
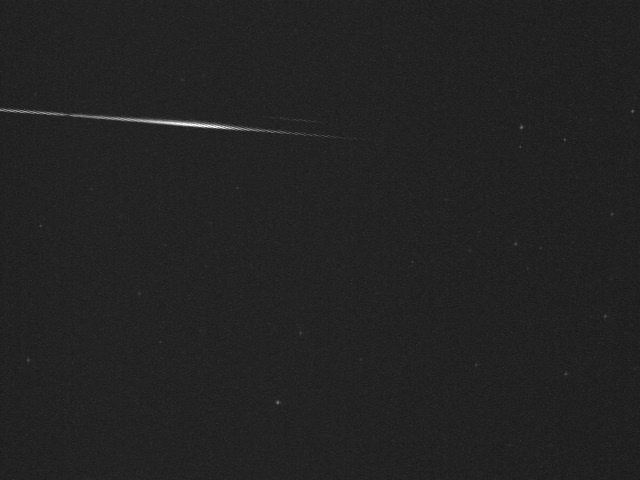
The new Arid meteor shower may be making itself known in early October 2021.
It’s not every day that we witness an outburst from a new meteor shower gracing the skies of the Earth. But that’s just what may be in store this week for fortunate observers deep in the southern hemisphere, with the advent of the Arid meteors.
Continue reading “Arid Meteor Outburst in the Works This Week?”A Technique to Find Oceans on Other Worlds

You could say that the study of extrasolar planets is in a phase of transition of late. To date, 4,525 exoplanets have been confirmed in 3,357 systems, with another 7,761 candidates awaiting confirmation. As a result, exoplanet studies have been moving away from the discovery process and towards characterization, where follow-up observations of exoplanets are conducted to learn more about their atmospheres and environments.
In the process, exoplanet researchers hope to see if any of these planets possess the necessary ingredients for life as we know it. Recently, a pair of researchers from Northern Arizona University, with support from the NASA Astrobiology Institute’s Virtual Planetary Laboratory (VPL), developed a technique for finding oceans on exoplanets. The ability to find water on other planets, a key ingredient in life on Earth, will go a long way towards finding extraterrestrial life.
Continue reading “A Technique to Find Oceans on Other Worlds”Astronomers Look at Super-Earths That had Their Atmospheres Stripped Away by Their Stars

As the planets of our Solar System demonstrate, understanding the solar dynamics of a system is a crucial aspect of determining habitability. Because of its protective magnetic field, Earth has maintained a fluffy atmosphere for billions of years, ensuring a stable climate for life to evolve. In contrast, other rocky planets that orbit our Sun are either airless, have super-dense (Venus), or have very thin atmospheres (Mars) due to their interactions with the Sun.
In recent years, astronomers have been on the lookout for this same process when studying extrasolar planets. For instance, an international team of astronomers led by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) recently conducted follow-up observations of two Super-Earths that orbit very closely to their respective stars. These planets, which have no thick primordial atmospheres, represent a chance to investigate the evolution of atmospheres on hot rocky planets.
Continue reading “Astronomers Look at Super-Earths That had Their Atmospheres Stripped Away by Their Stars”When Did Photosynthesis Begin?
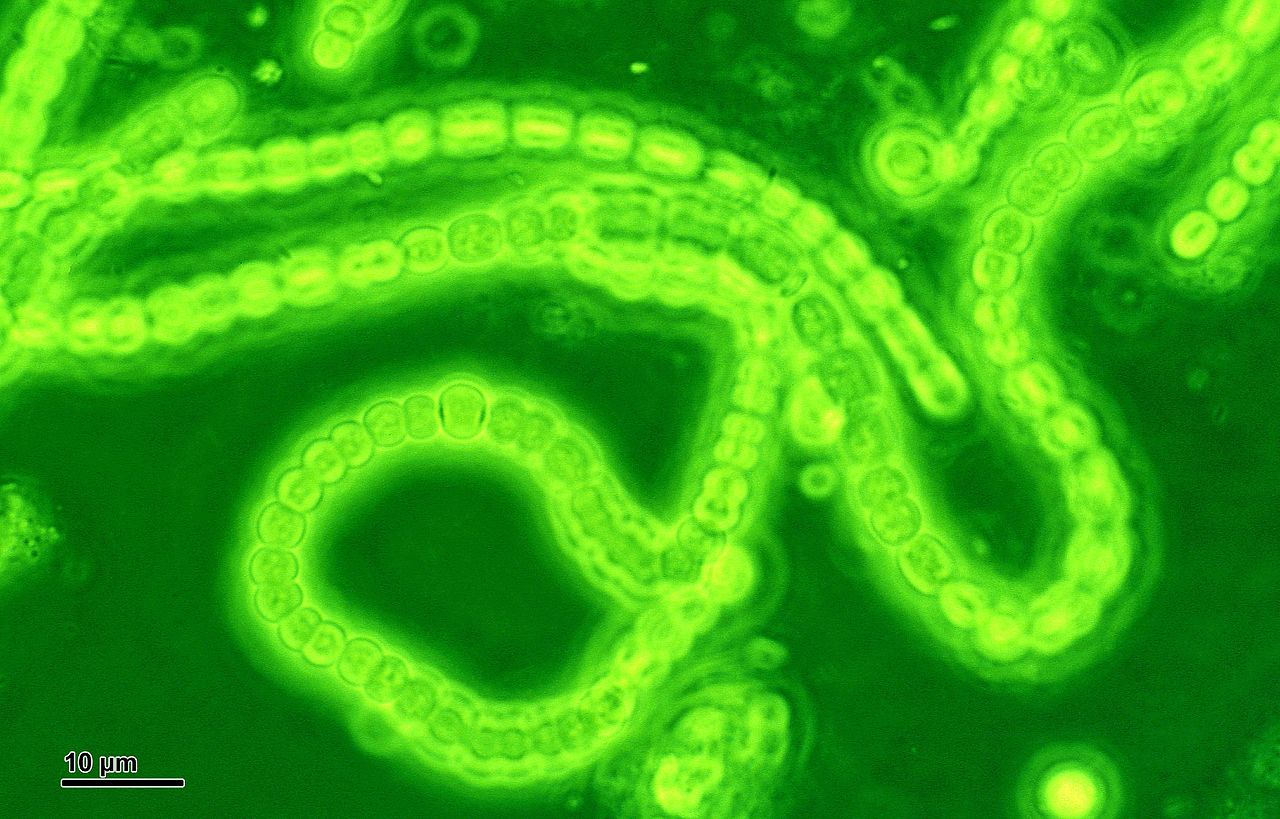
Sometime around 2.4 billion years ago, a nascent planet Earth underwent one of the most dramatic changes in its history. Known as the Great Oxidation Event, this period saw Earth’s atmosphere suddenly bloom with (previously scarce) molecular oxygen. The rapid alteration of the atmosphere’s composition was nothing short of a cataclysm for some early lifeforms (at the time, mostly simple celled prokaryotes). Anaerobic species – those that dwell in oxygen-free environments – experienced a near extinction-level event. But the Great Oxidation was also an opportunity for other forms of life to thrive. Oxygen in the atmosphere tempered the planetary greenhouse effect, turning methane into the less potent carbon dioxide, and ushering in a series of ice ages known as the Huronian Glaciation. But oxygen is an energy-rich molecule, and it also bolstered diversity and activity on the planet, as a powerful new source of fuel for living organisms.
The cause of this dramatic event? The tiniest of creatures: little ocean-dwelling cyanobacteria (sometimes known as blue-green algae) that had developed a new super-power never before seen on planet Earth: photosynthesis. This unique ability – to gain energy from sunlight and release oxygen as a waste product – was a revolutionary step for so small a critter. It quite literally changed the world.
Continue reading “When Did Photosynthesis Begin?”Even the Quiet Supermassive Black Holes are Blasting out Neutrinos and Gamma Rays
Is there anywhere in the Universe where we can escape from radiation? Certainly not here on Earth. And not in space itself, which is filled with diffuse radiation in the form of gamma rays and neutrinos. Scientists have struggled to explain where all those gamma rays and neutrinos come from. A trio of researchers is proposing a source for all that radiation in a new paper: resting black holes.
Continue reading “Even the Quiet Supermassive Black Holes are Blasting out Neutrinos and Gamma Rays”NASA’s Human Space Exploration Division is Being Split in Two
Large government organizations require lots of people to run them. NASA is no exception. America’s space agency has long been under pressure to organizationally support its ongoing Artemis program to return to the moon. Now, it has taken a step in that direction by announcing that its Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate will split into two new ones: the Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate and the Space Operations Missions Directorate.
Continue reading “NASA’s Human Space Exploration Division is Being Split in Two”Vera Rubin Observatory Should Find 5 Interstellar Objects a Year, Many of Which we Could Chase Down With Spacecraft

In a year (perhaps two), the Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile will become operational and commence its 10-year Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST). Using its 8.4-meter (27 foot) mirror and 3.2 gigapixel camera, this observatory is expected to collect 500 petabytes of images and data. It will also address some of the most pressing questions about the structure and evolution of the Universe and everything in it.
One of the highly-anticipated aspects of the LSST is how it will allow astronomers to locate and track interstellar objects (ISOs), which have become of particular interest since `Oumuamua flew through our system in 2017. According to a recent study by a team from the University of Chicago and the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA), the Rubin Observatory will detect around 50 objects during its 10-year mission, many of which we will be able to study up-close using rendezvous missions.
Continue reading “Vera Rubin Observatory Should Find 5 Interstellar Objects a Year, Many of Which we Could Chase Down With Spacecraft”