NASA’s planetary science program is making a big bet on Venus, after decades of putting its chips on Mars in the search for hints of past or present life out there in the solar system.
The bet comes in the form of a double dose of development funding for Discovery Program missions, amounting to as much as $1 billion. Both DAVINCI+ and VERITAS were selected from a field of four finalists in a competitive process — leaving behind missions aimed at studying Jupiter’s moon Io and Neptune’s moon Triton.
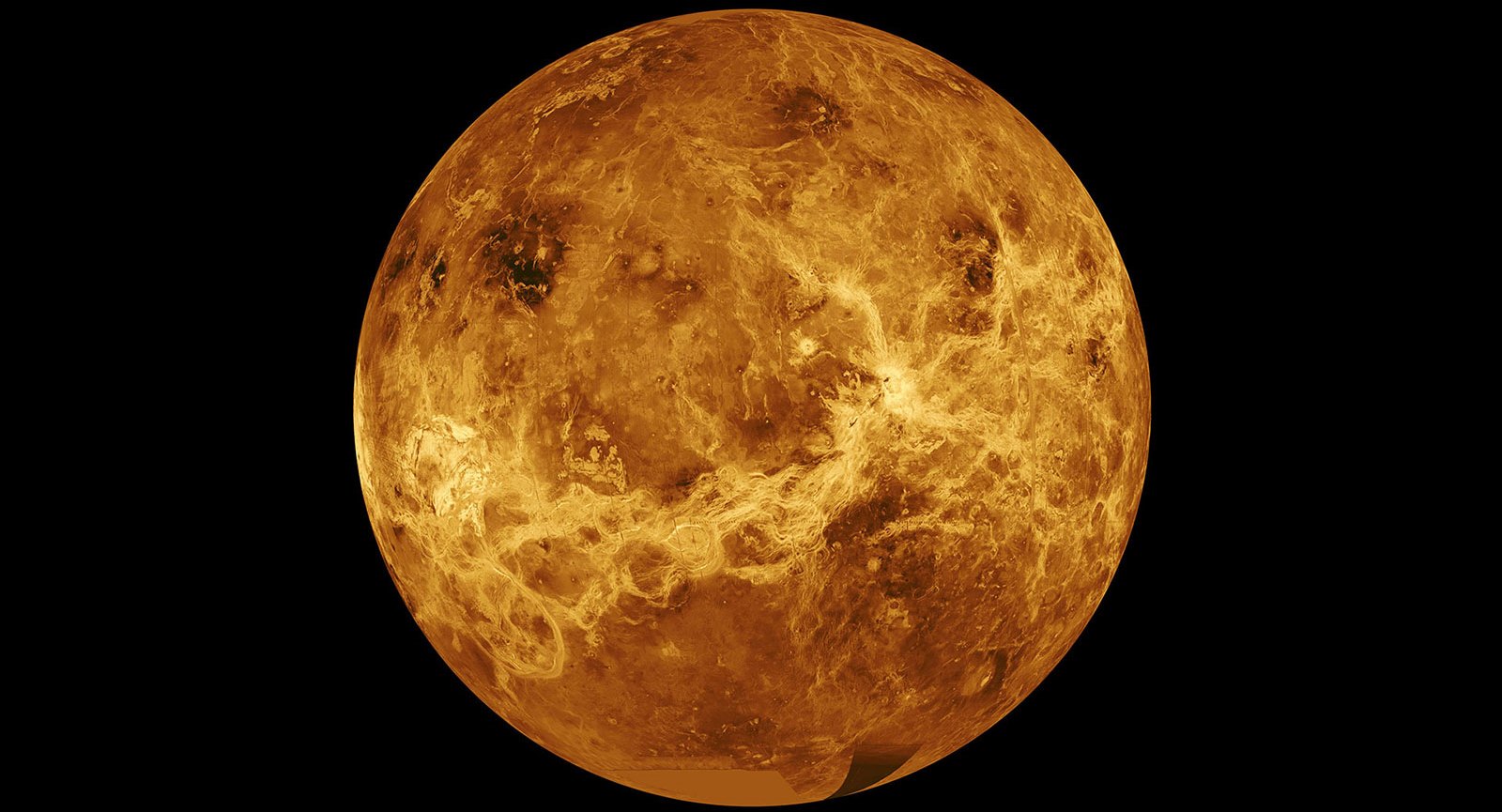
“These two sister missions are both aimed to understand how Venus became an inferno-like world capable of melting lead at the surface,” NASA Administrator Bill Nelson said June 2 in his first “State of NASA” address. “They will offer the entire science community the chance to investigate a planet we haven’t been to in more than 30 years.”
Lessons from Venus, which underwent a runaway greenhouse effect early in its existence, could improve scientists’ understanding of our own planet’s changing climate. The missions could also address one of the biggest questions about the second rock from the Sun: whether life could exist in the upper reaches of its cloud layer.
Continue reading “NASA Orders Up a Double Shot of Venus Missions Amid Questions About Life”