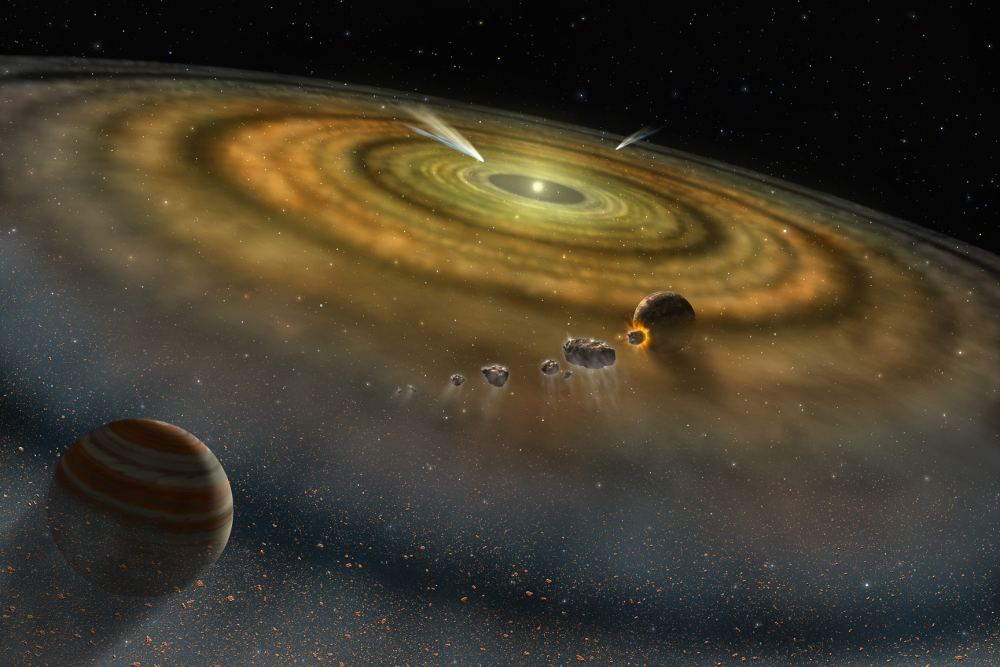
In the past few decades, the number of planets discovered beyond our Solar System has grown into the thousands. At present, 4,389 exoplanets have been confirmed in 3,260 systems, with another 5,941 candidates awaiting confirmation. Thanks to numerous follow-up observations and studies, scientists have learned a great deal about the types of planets that exist in our Universe, how planets form, and how they evolve.
A key consideration in all of this is how planets become (and remain) habitable over time. In general, astrobiologists have operated under the assumption that habitability comes down to where a planet orbits within a system – within its parent star’s habitable zone (HZ). However, new research by a team from Rice University, indicates that where a planet forms in its respective star system could be just as important.
Continue reading “The Elements for Life Depend on Both how and Where a Planet Forms”