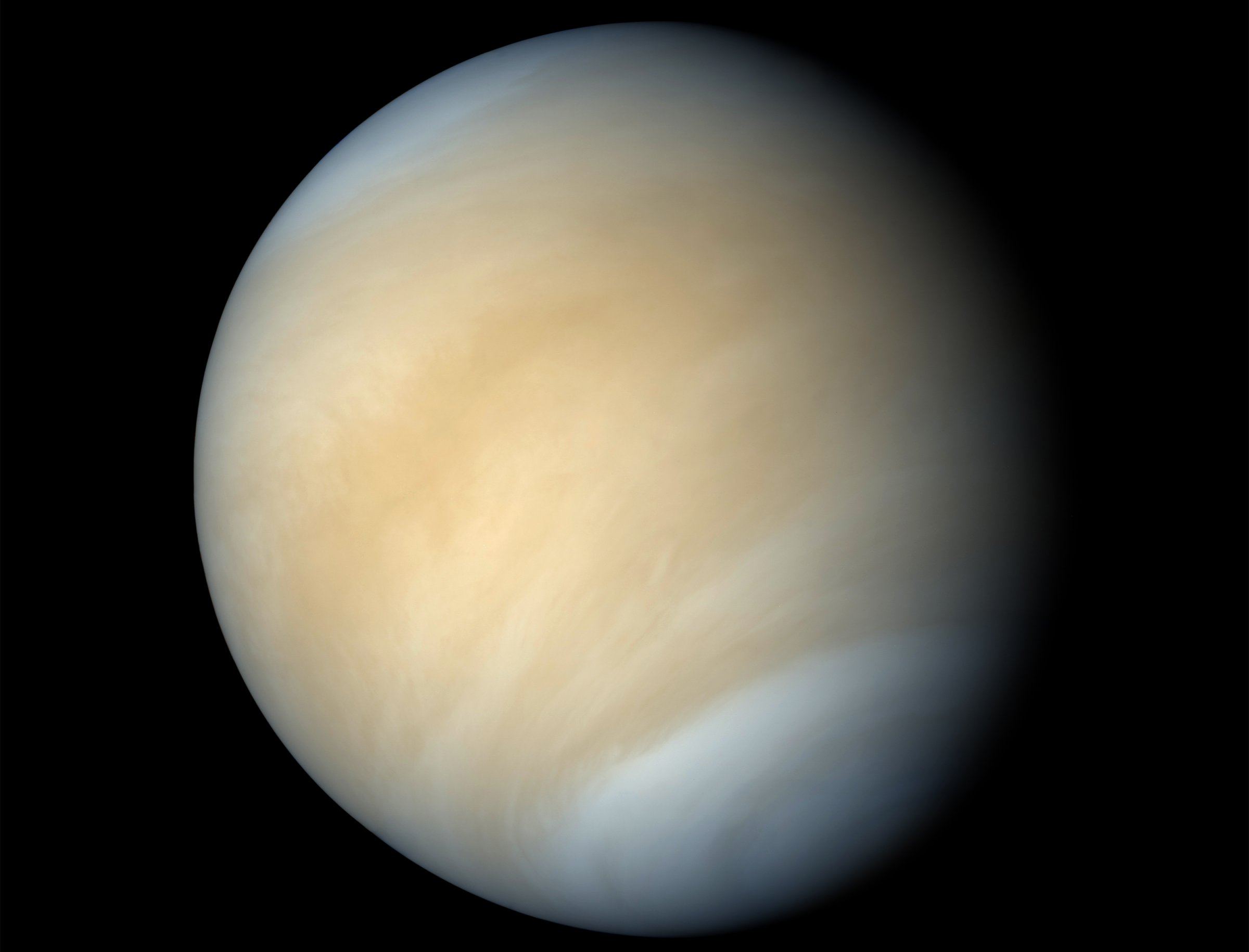
Venus, aka. Earth’s “Sister Planet,” has always been shrouded in mystery for astronomers. Despite being planet Earth’s closest neighbor, scientists remained ignorant of what Venus’ surface even looked like for well into the 20th century, thanks to its incredibly dense and opaque atmosphere. Even in the age of robotic space exploration, its surface has been all but inaccessible to probes and landers.
And so the mysteries of Venus have endured, not the least of which has to do with some of its most basic characteristics – like its internal mass distribution and variations in the length of a day. Thanks to observations conducted by a team led from UCLA, who repeatedly bounced radar off the planet’s surface for the past 15 years, scientists now know the precise length of a day on Venus, the tilt of its axis, and the size of its core.
Continue reading “How Long is a Day on Venus? We Finally Know the Exact Answer”