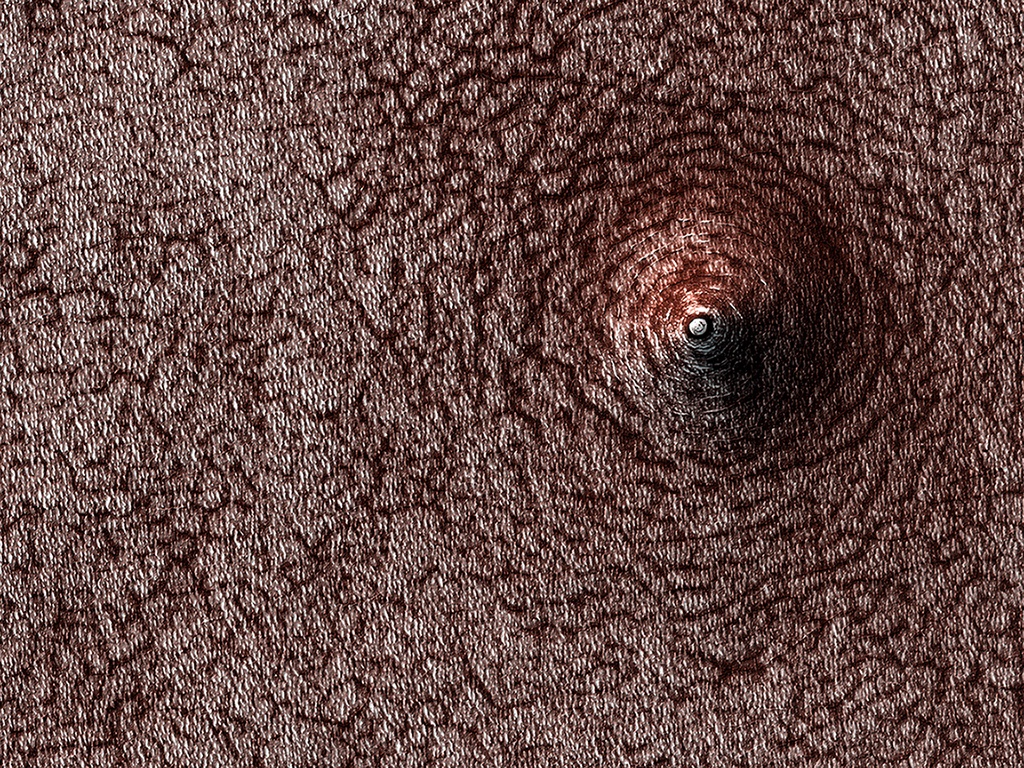
Mars has been in the news a lot lately, and for good reason. With the historic landing of the Perseverance Rover earlier in the year, and the successful flight of Ingenuity, the first-ever aircraft to fly in another atmosphere, earlier this morning (April 19, 2021), there’s no shortage of exciting stories of technical brilliance from the human-built wonders exploring the red planet. High above the plucky helicopter, the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) surveys the Martian landscape on a grand scale. A brain-bending image released by High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE), a powerful camera aboard MRO, shows a sunken pit in the planet’s polar region. From the high-altitude perspective of the orbiter, it’s easy for the mind to warp the concave depression into a convex, acne-esque Martian polar zit!
Continue reading “This Is a Collapsed Pit on Mars, Not a Pimple”This Is a Collapsed Pit on Mars, Not a Pimple