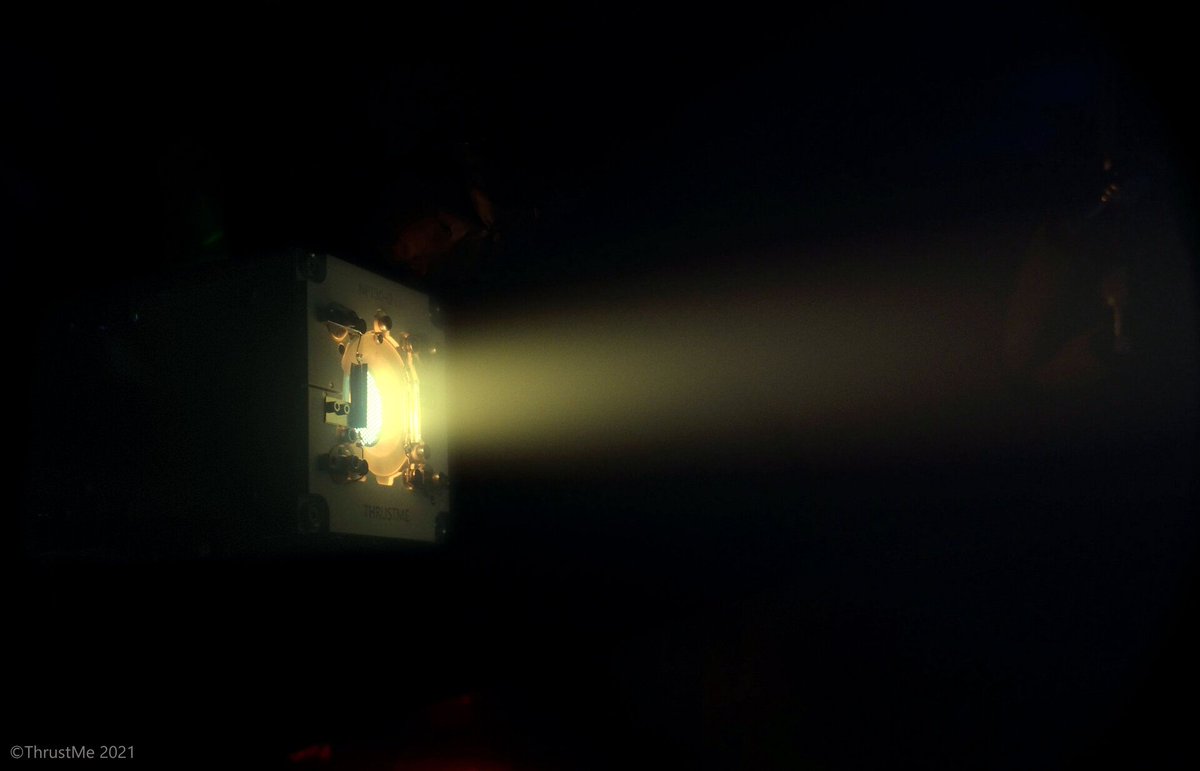
Rocket fuel is one of the most important components of any maneuverable spacecraft. That is also true for ion thrusters – while they don’t use traditional chemical fuel, they do still need a feed source for their ion engines. Now, a team from ThrustMe, a spinoff of the École Polytechnique and CNRS, has designed a type of ion thruster using a completely novel propellant – iodine.
Continue reading “Lightweight Iodine Thruster Could Help Solve Space Junk Problem”A New Idea to Harness Energy From Black Holes
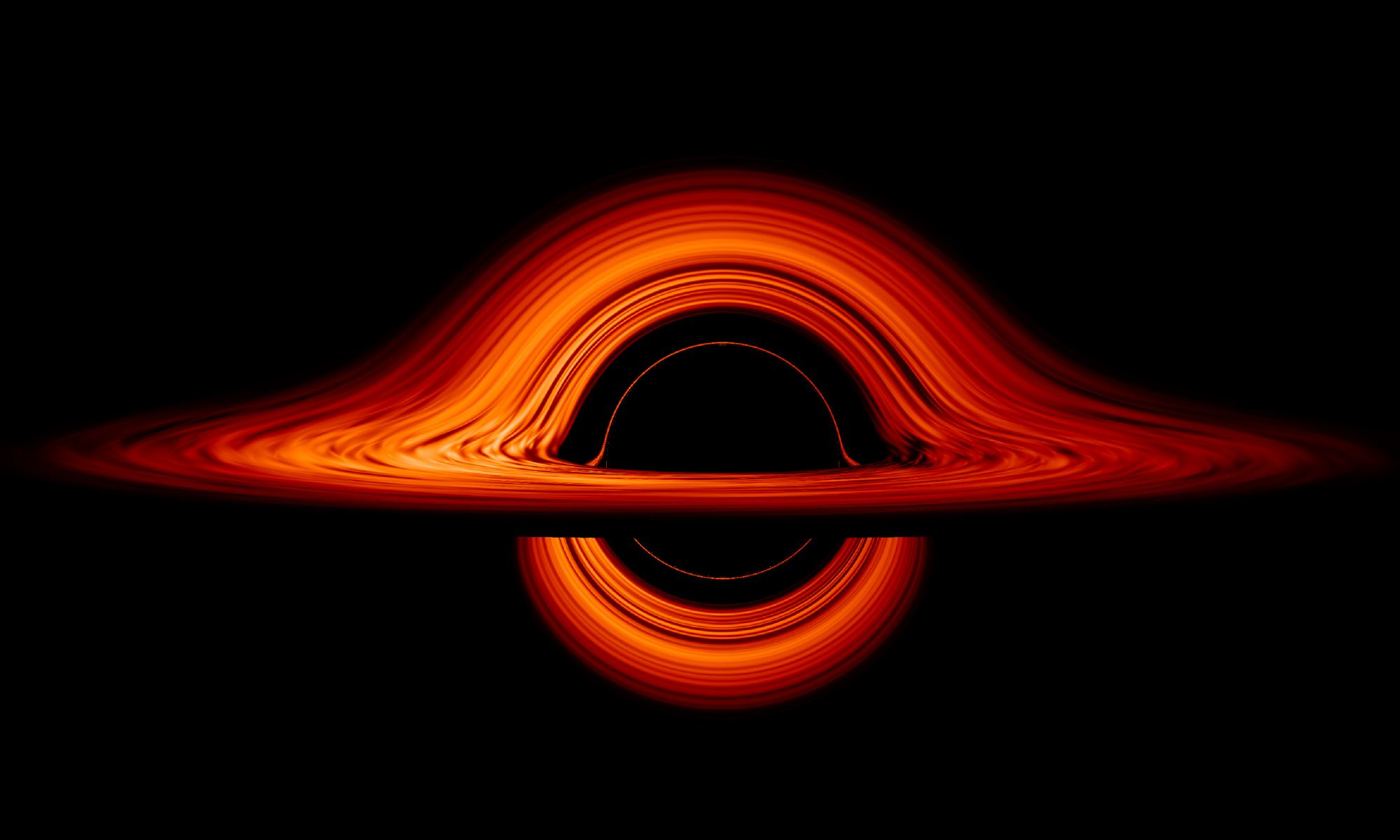
Fifty years ago, English mathematical physicist and Nobel-prize winner Roger Penrose proposed that energy could be extracted from the space around a rotating black hole. Known as the ergosphere, this region lies just outside an event horizon, the boundary within which nothing can escape a black hole’s gravitational pull (even light). It is also here where infalling matter is accelerated to incredible speeds and emits all kinds of energy.
This became known as the Penrose Process, which many theorists have since expanded on. The latest comes from a study conducted by researchers from Columbia University and the Universidad Adolfo Ibáñez in Chile. With support from organizations like NASA, they demonstrated how a better understanding of the physics at work around spinning black holes could allow us to harness their energy someday.
Continue reading “A New Idea to Harness Energy From Black Holes”3-D Printing on the Moon. From Regolith to Paste to Useful Objects and Structures
In the academic literature, review papers are widespread, and can help ground discussion on a specific topic by bringing new researchers up to speed as well as allowing experienced hands to catch up on some topics they might have otherwise missed. Anytime a new one on a topic of space exploration is published, it helps move understanding of the entire discipline forward, even if it might not directly contribute to furthering research itself. With that in mind, it can also be interesting for laymen to read them as well, as they are an excellent way to be quickly brought up to speed on a certain topic.
So if you happen to be interested in lunar exploration, or additive manufacturing more generally, you might be interested in a new review paper from a team at the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology. It reviews the current state of the art in additive manufacturing (AM) technology and how it might be applied to building useful tools and structures on the lunar surface.
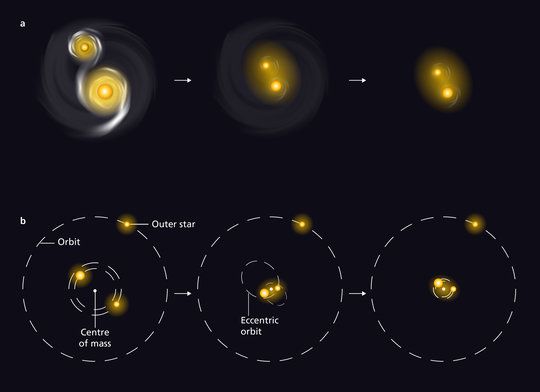
Continue reading “3-D Printing on the Moon. From Regolith to Paste to Useful Objects and Structures”Massive Binary Stars Huddle Up Surprisingly Quickly
Dancing is a favorite pastime of many couples. Swinging around a dance floor, using the laws of physics to twirl at just the right moment, and hopefully not step on any toes, is an art unto itself. The same laws of physics that govern couples on a dance floor also govern (to some extent) the much larger dance of stellar objects. And recently astronomers have started to understand the intricacies of how binary stars dance with each other – turns out it’s not quite as simple as doing the tango.
Continue reading “Massive Binary Stars Huddle Up Surprisingly Quickly”In Theory, Supermassive Black Holes Could get Even More Supermassive
Our universe contains some enormous black holes. The supermassive black hole in the center of our galaxy has a mass of 4 million Suns, but it’s rather small as galactic black holes go. Many galactic black holes have a billion solar masses, and the most massive known black hole is estimated to have a mass of nearly 70 billion Suns. But just how big can a black hole get?
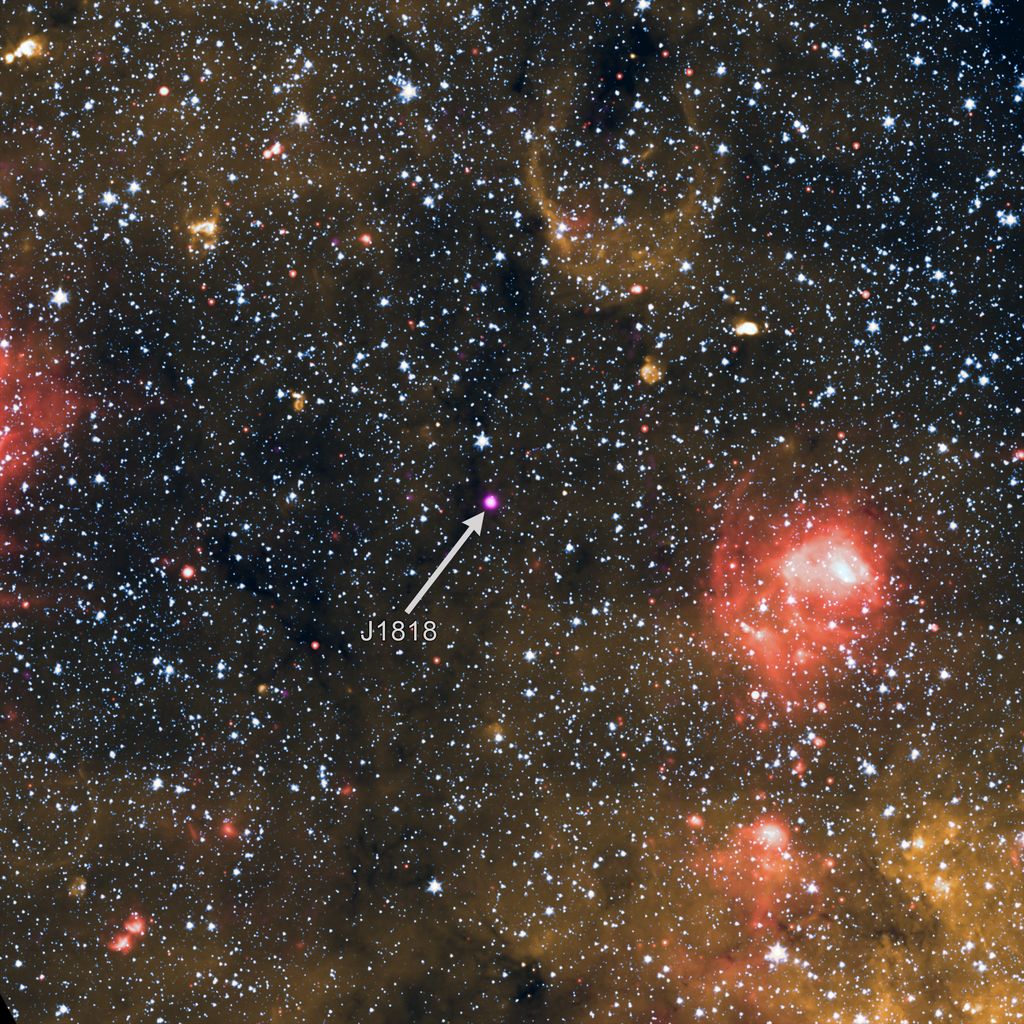
Continue reading “In Theory, Supermassive Black Holes Could get Even More Supermassive”Only 31 Magnetars Have Ever Been Discovered. This one is Extra Strange. It’s Also a Pulsar
Some of the most stunningly powerful objects in the sky aren’t necessarily the prettiest to look at. But their secrets can allow humanity to glimpse some of the more intricate details of the universe that are exposed in their extreme environs. Any time we find one of these unique objects it’s a cause for celebration, and recently astronomers have found an extremely unique object that is both a magnetar and a pulsar, making it one of only 5 ever found.
Continue reading “Only 31 Magnetars Have Ever Been Discovered. This one is Extra Strange. It’s Also a Pulsar”Astronomers Confirm That Darksat is About Half as Bright as an Unpainted Starlink
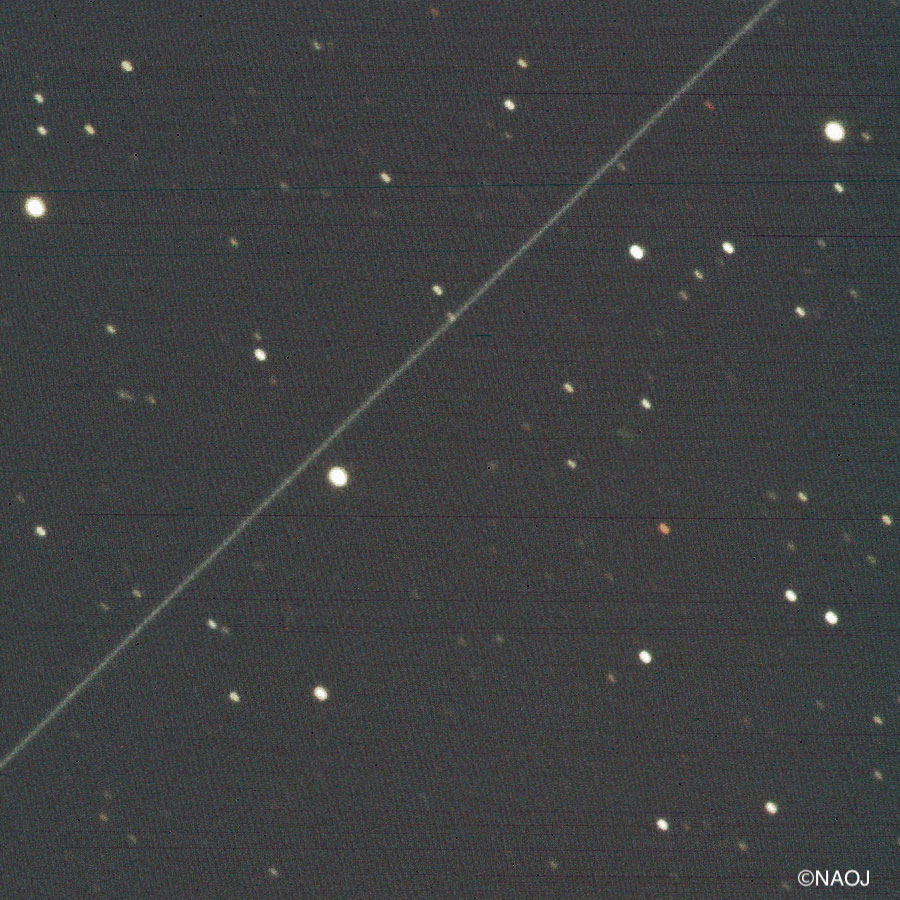
Space-based internet service is poised to revolutionize the internet and bring high-speed connectivity to countless communities worldwide. Programs like SpaceX’s Starlink paint a picture of a bright future for the citizens of the world. Like many revolutionary technological advances, there is a dark side to Starlink.
The constellation of hundreds (and eventually thousands) of satellites reflect light back to the Earth, impinging on the darkness of the skies for professional astronomers and stargazers alike. Astronomers report images and data being disrupted by bright streaks left from the satellites passing through their observational fields of view. One potential solution to this issue is applying a dark coating to the reflective antennae on the satellites’ ground-facing side. In January of 2020, SpaceX launched the experimental DarkSat to test the effectiveness of such a coating. Astronomers around the world observed the new satellite. In December of 2020, a team from the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) released a paper in The Astrophysical Journal showing detailed measurements of the efficacy of DarkSat.
Continue reading “Astronomers Confirm That Darksat is About Half as Bright as an Unpainted Starlink”This is a Simulation of the Interstellar Medium Flowing Like Smoke Throughout the Milky Way
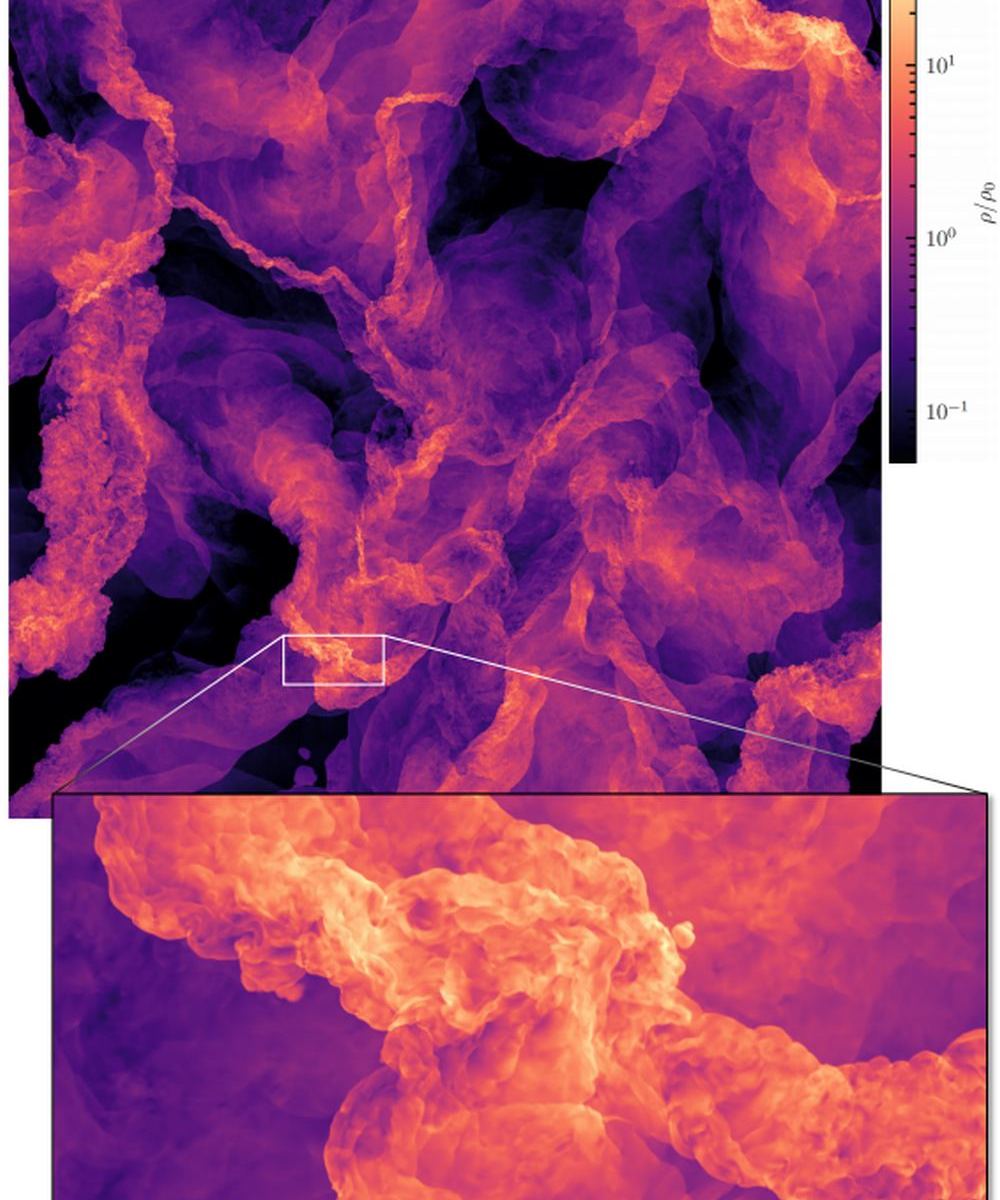
How do stars form?
We know they form from massive structures called molecular clouds, which themselves form from the Interstellar Medium (ISM). But how and why do certain types of stars form? Why, in some situations, does a star like our Sun form, versus a red dwarf or a blue giant?
That’s one of the central questions in astronomy. It’s also a very complex one.
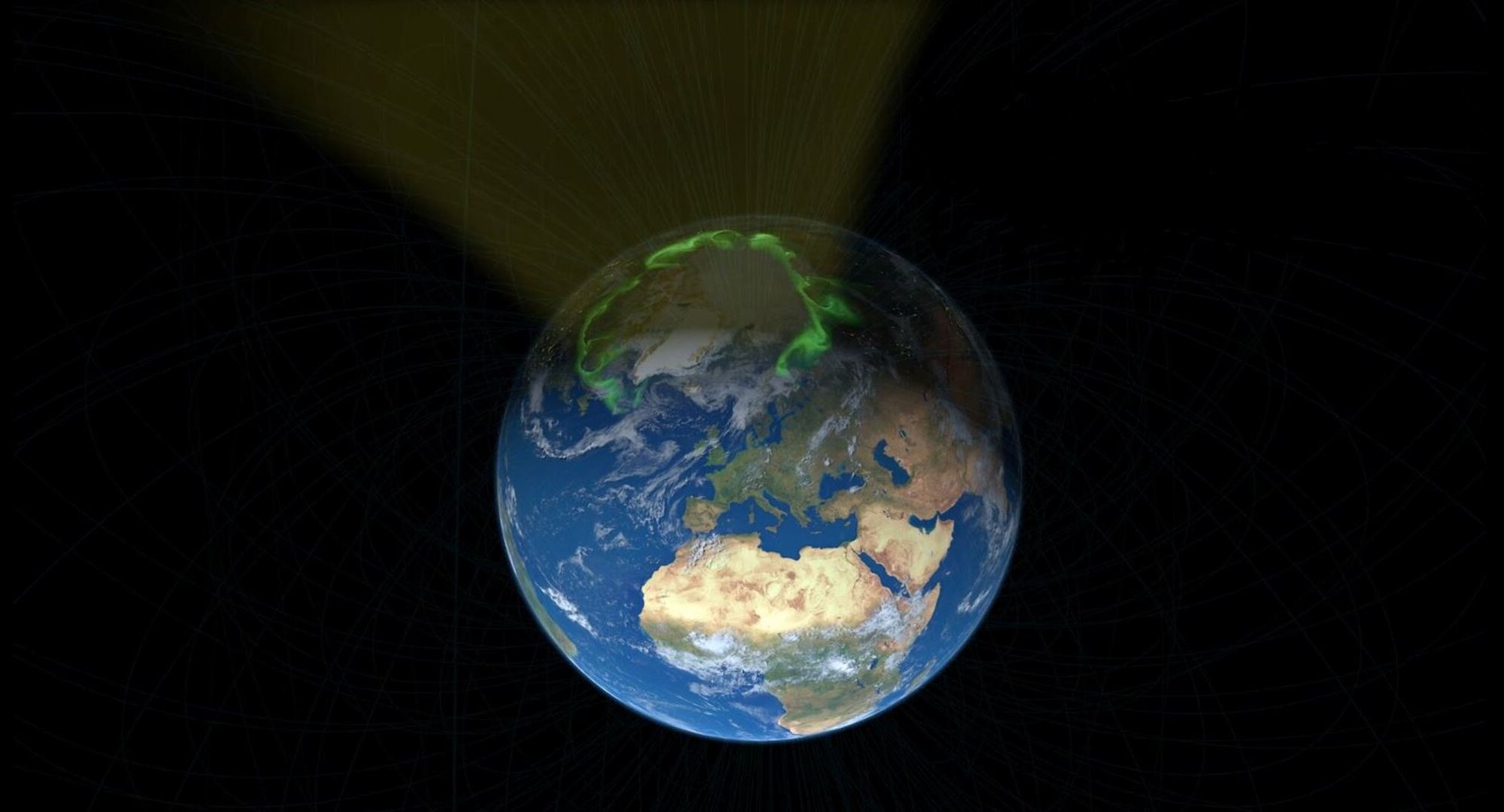
Continue reading “This is a Simulation of the Interstellar Medium Flowing Like Smoke Throughout the Milky Way”The Solar Wind is More Attracted to the Earth’s North Pole Than the South. Why?
Likely the most well-known result of the Earth’s magnetic field are the Aurora Borealis and Australis (Northern and Southern Lights). When chargers particles from the solar wind run into the Earth’s magnetic field, they can occasionally elicit spectacular light displays. For years now, scientists have thought that the charged particles that cause those displays were sent in equal numbers toward the north and south pole. However, recent research from a team led by scientists from the University of Alberta, have shown that there are actually more charged particles heading north rather than south. The question now is why?
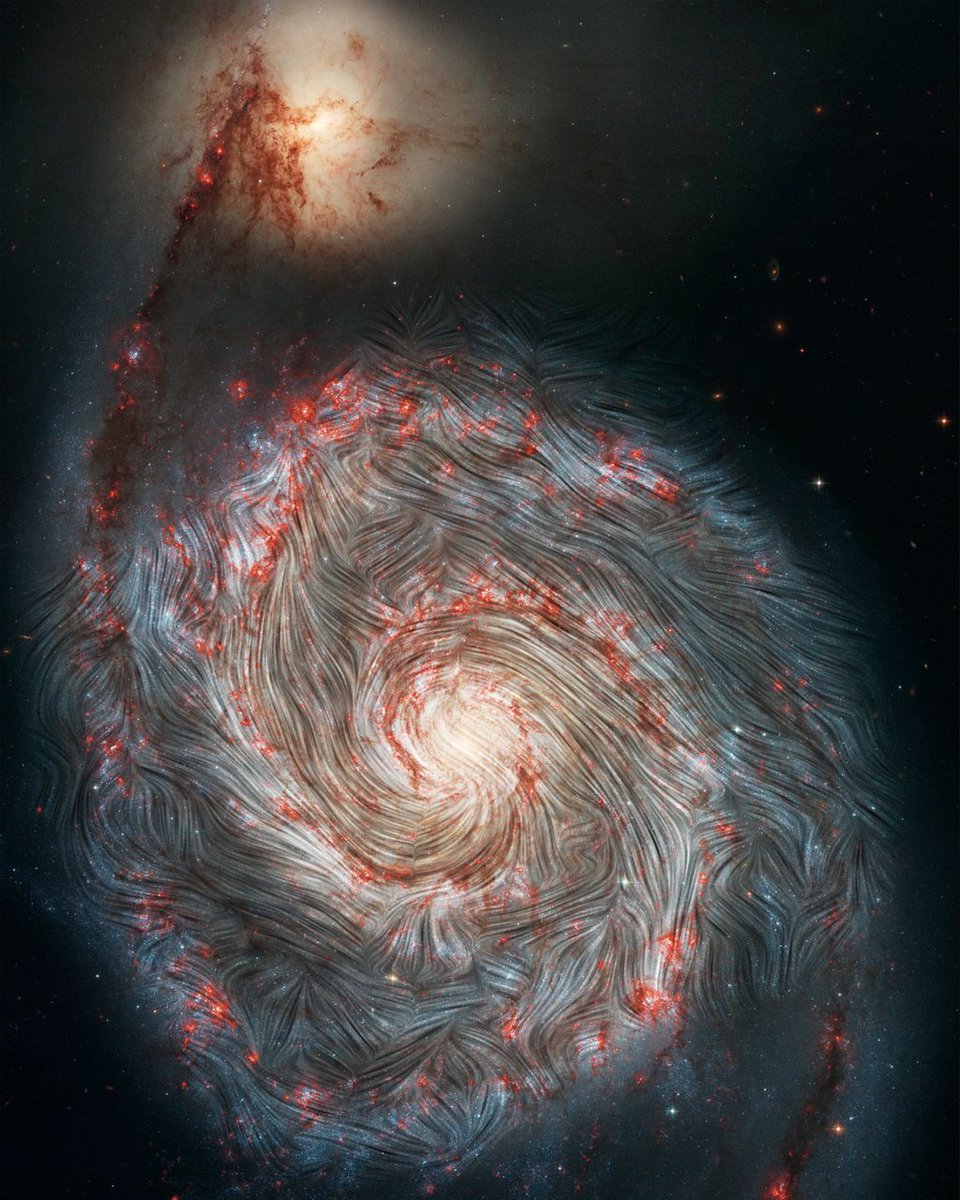
Continue reading “The Solar Wind is More Attracted to the Earth’s North Pole Than the South. Why?”The Magnetic Fields Swirling Within the Whirlpool Galaxy
Messier objects are some of the most imaged objects in the universe. In part that’s because many of them are so visibly appealing. A good example of that is the Whirlpool galaxy, M51, which recently received an even more dramatic visual representation with a new photo released by NASA. In it, the magnetic fields that are holding the galaxy together and tearing it apart at the same time are clearly visible. And it is even more stunning to look at.
Continue reading “The Magnetic Fields Swirling Within the Whirlpool Galaxy”