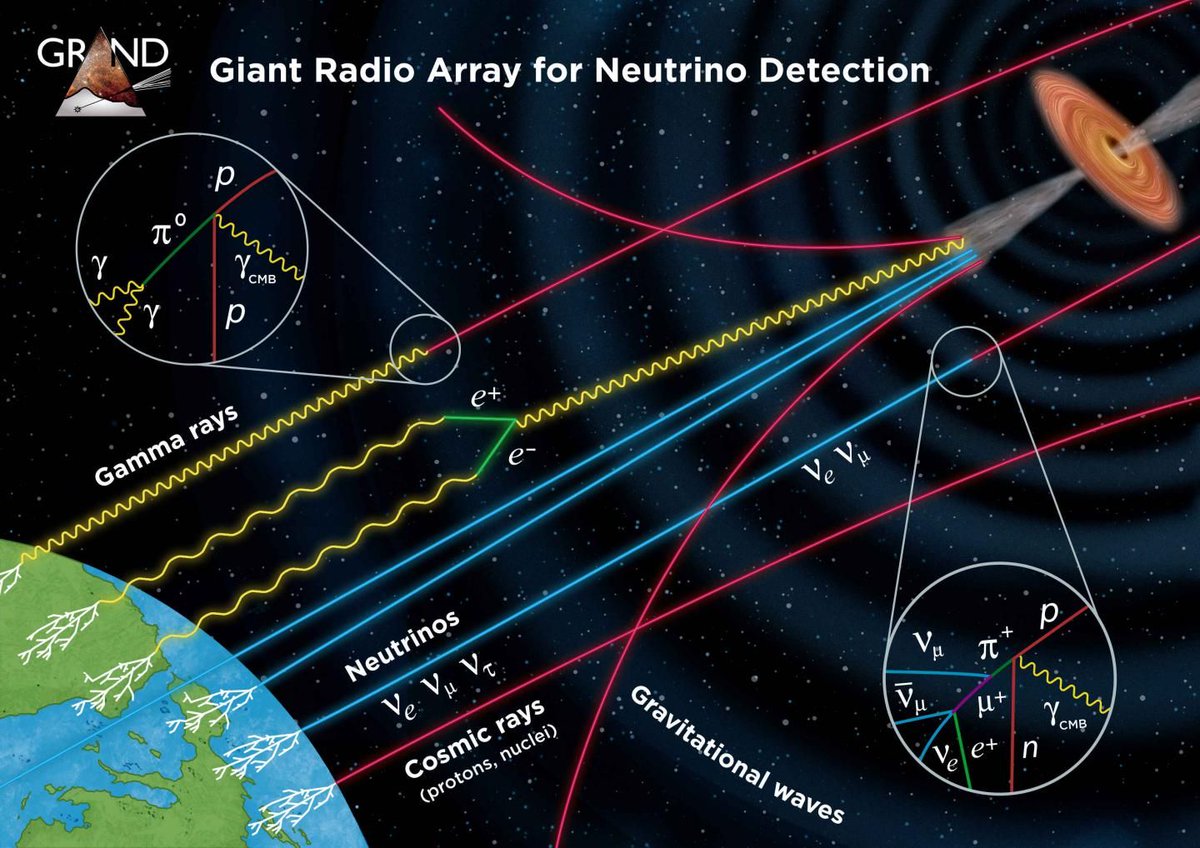
Sometimes in astronomy the acronym for a project fits it particularly well. That would absolutely be the case for the Giant Radio Array for Neutrino Detection, who hopes to scale up to a size of 200,000 sq km in an effort to measure ultra-high-energy tau-neutrinos. Is it ambitious? Yes, but that doesn’t really stop humanity from exploring when it wants to.
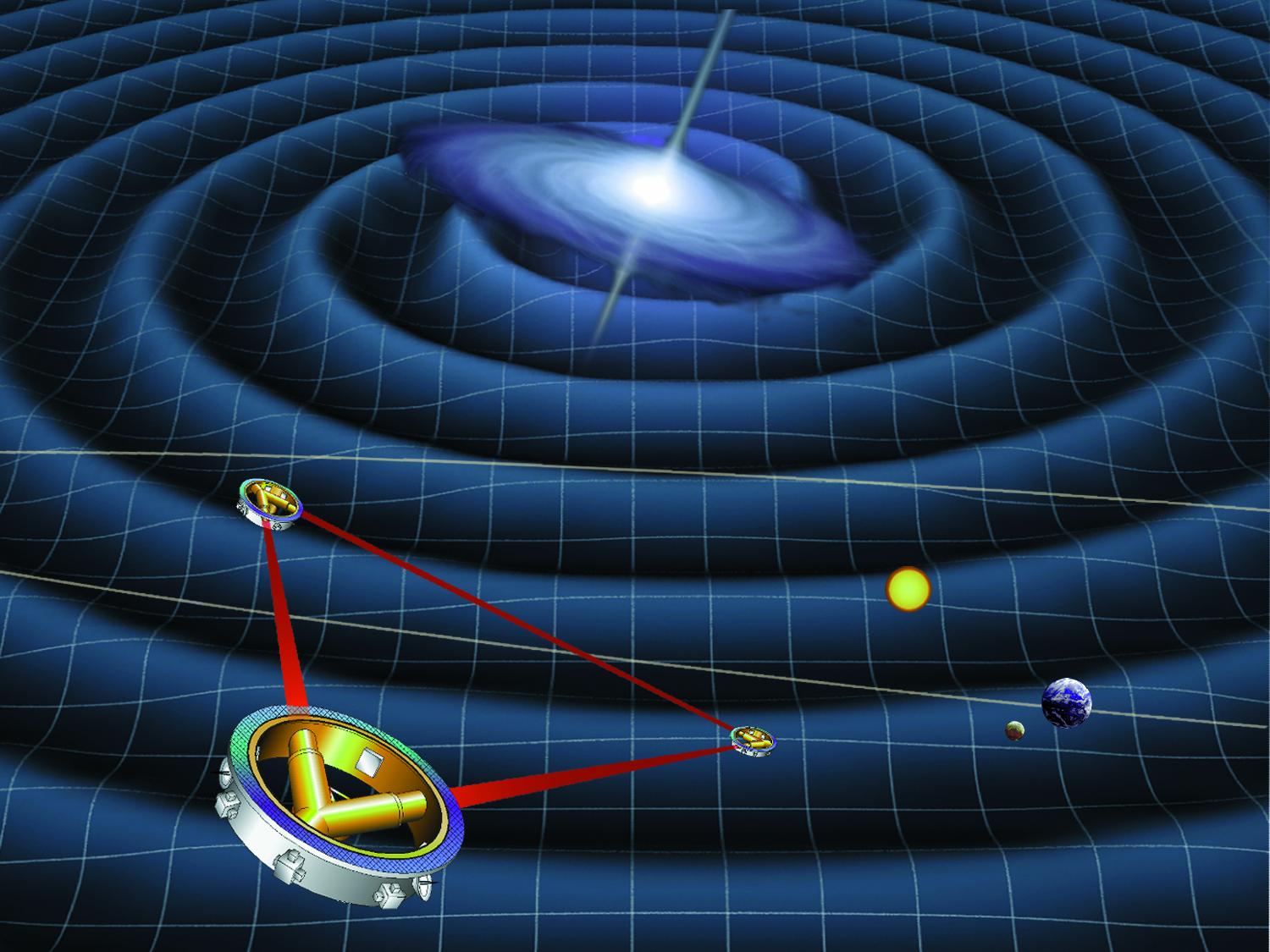
Continue reading “A Proposal for a Neutrino Detection Array Spanning 200,000 Square Kilometers”China’s Planning to Launch a Space-Based Gravitational Wave Observatory in the 2030s: TianQin. Here’s how it’ll Stack up Against LISA
The successful detection of gravitational waves has been a game-changer for astronomy. And now the new frontier is in space, with satellite-based detection systems currently in development that will uncover some of the universe’s biggest mysteries. And while the team behind LISA is now developing that observatory in space, it just may be outclassed by a rival, TianQin, developed by the Chinese.
Continue reading “China’s Planning to Launch a Space-Based Gravitational Wave Observatory in the 2030s: TianQin. Here’s how it’ll Stack up Against LISA”This galaxy took only 500 million years to form
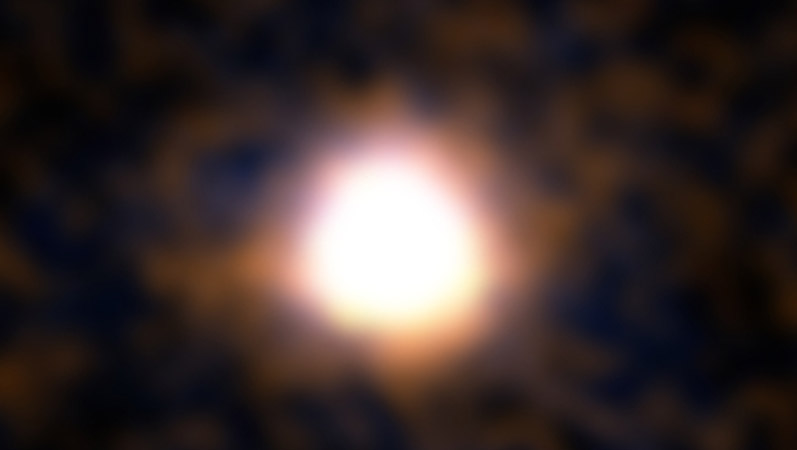
Galaxies are supposed to build up a very slowly, taking billions of years to acquire their vast bulk. But a newfound galaxy, appearing in the universe when it was only 1.8 billion years old, tells a different tale. It formed stars at a rate hundreds of times greater than the Milky Way, and was able to build itself up to host 200 billion stars in less than 500 million years – perhaps the universe’s greatest speed run.
Continue reading “This galaxy took only 500 million years to form”Beyond “Fermi’s Paradox” XIV: What is the Aurora Hypothesis?
Welcome back to our Fermi Paradox series, where we take a look at possible resolutions to Enrico Fermi’s famous question, “Where Is Everybody?” Today, we examine the possibility that the reason for the Great Silence is that colonizing other star systems is hazardous to our health!
In 1950, Italian-American physicist Enrico Fermi sat down to lunch with some of his colleagues at the Los Alamos National Laboratory, where he had worked five years prior as part of the Manhattan Project. According to various accounts, the conversation turned to aliens and the recent spate of UFOs. Into this, Fermi issued a statement that would go down in the annals of history: “Where is everybody?“
This became the basis of the Fermi Paradox, which refers to the disparity between high probability estimates for the existence of extraterrestrial intelligence (ETI) and the apparent lack of evidence. Since Fermi’s time, there have been several proposed resolutions to his question, which includes the Aurora Hypothesis that states that just because planets are habitable doesn’t mean that intelligent life can colonize there.
Continue reading “Beyond “Fermi’s Paradox” XIV: What is the Aurora Hypothesis?”The European Extremely Large Telescope Just Got a 10% Budget Boost, Now Costing $1.5 Billion
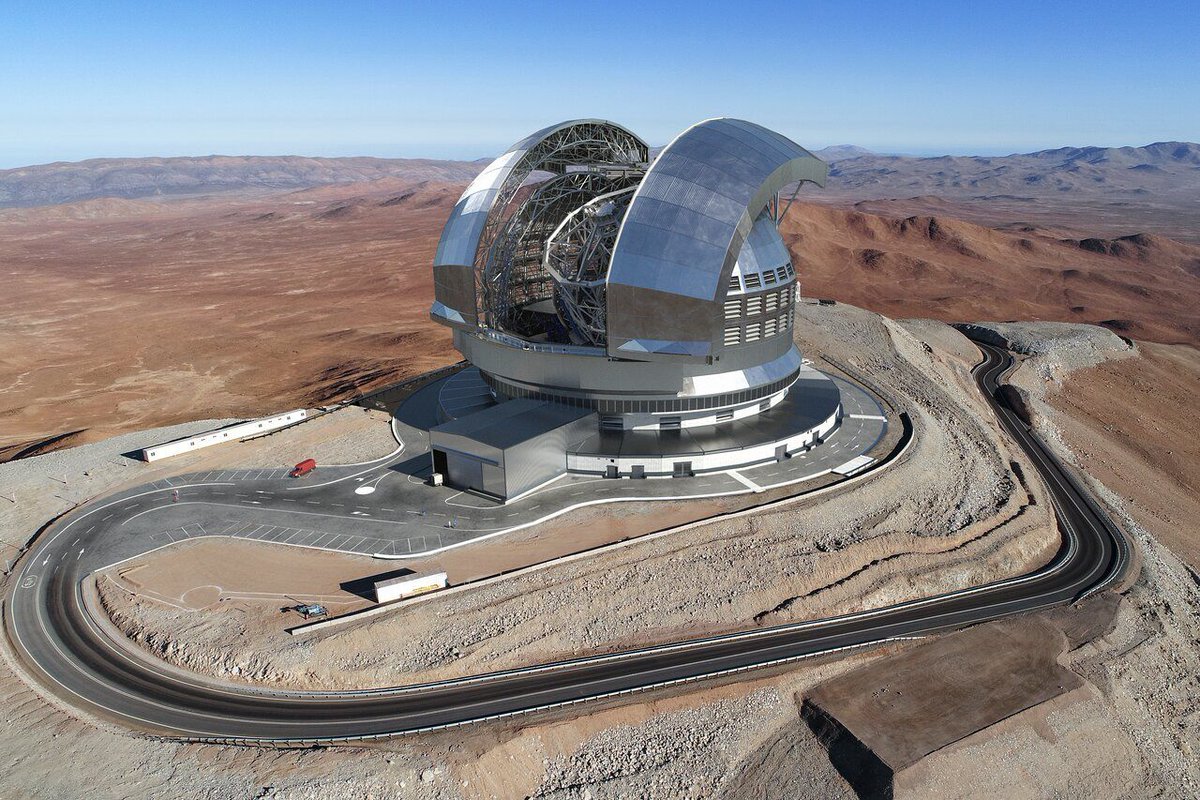
Funding is an extremely important aspect of any large-scale science project. The whims of financial controllers can greatly expand or completely sink the efforts of hundred or thousands of other workers. Many times, funding announcements for large scientific projects focus on cuts or “cost-savings” which hobble the eventual end system they are trying to build. But recently the European Southern Observatory (ESO) announced it had actually increased the budget for the under-construction Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) by 10%.
Continue reading “The European Extremely Large Telescope Just Got a 10% Budget Boost, Now Costing $1.5 Billion”Here are NASA’s Science Priorities for the Artemis Missions
In October of 2024, NASA will send astronauts to the Moon for the first time since the Apollo Era. After establishing orbit with their Orion spacecraft, a team of two astronauts (“the first woman and the next man”) will land in the Moon’s southern polar region. Over the course of a week, these astronauts will explore and investigate one of the region’s many permanently-shadowed craters.
As the first crewed lunar mission in over fifty years, this mission and those that follow will have a robust series of science objectives. These objectives were laid out in the Artemis III Science Definition Team Report, which was released to the public earlier this month. This report is a summary of the science plan prepared at the behest of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate (SMD) for the Artemis III mission.
Continue reading “Here are NASA’s Science Priorities for the Artemis Missions”Here’s Chang’e-5, Seen From Lunar Orbit
On Tuesday, December 1st, at 10:11 EST (07:00 PST) the Chang’e-5 sample return spacecraft landed safely on the Moon. This mission is the latest in China’s lunar exploration program, which is paving the way for the creation of a lunar outpost and a crewed mission by the 2030s. The day after it landed, the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) passed over the site and acquired an image of the lander.
Continue reading “Here’s Chang’e-5, Seen From Lunar Orbit”The Kilonova-Chasing Gravitational-Wave Optical Transient Observer is About to be Watching the Whole Sky
Lately there has been a flood of interest in gravitational waves. After the first official detection at LIGO / Virgo in 2015, data has been coming in showing how common these once theoretical phenomena actually are. Usually they are caused by unimaginably violent events, such as a merging pair of black holes. Such events also have a tendency to emit another type of phenomena – light. So far it has been difficult to observe any optical associated with these gravitational-wave emitting events. But a team of researchers hope to change that with the full implementation of the Gravitation-wave Optical Transient Observer (GOTO) telescope.
Continue reading “The Kilonova-Chasing Gravitational-Wave Optical Transient Observer is About to be Watching the Whole Sky”A Real River Valley on Mars, Filled With Virtual Water by @Kevinmgill
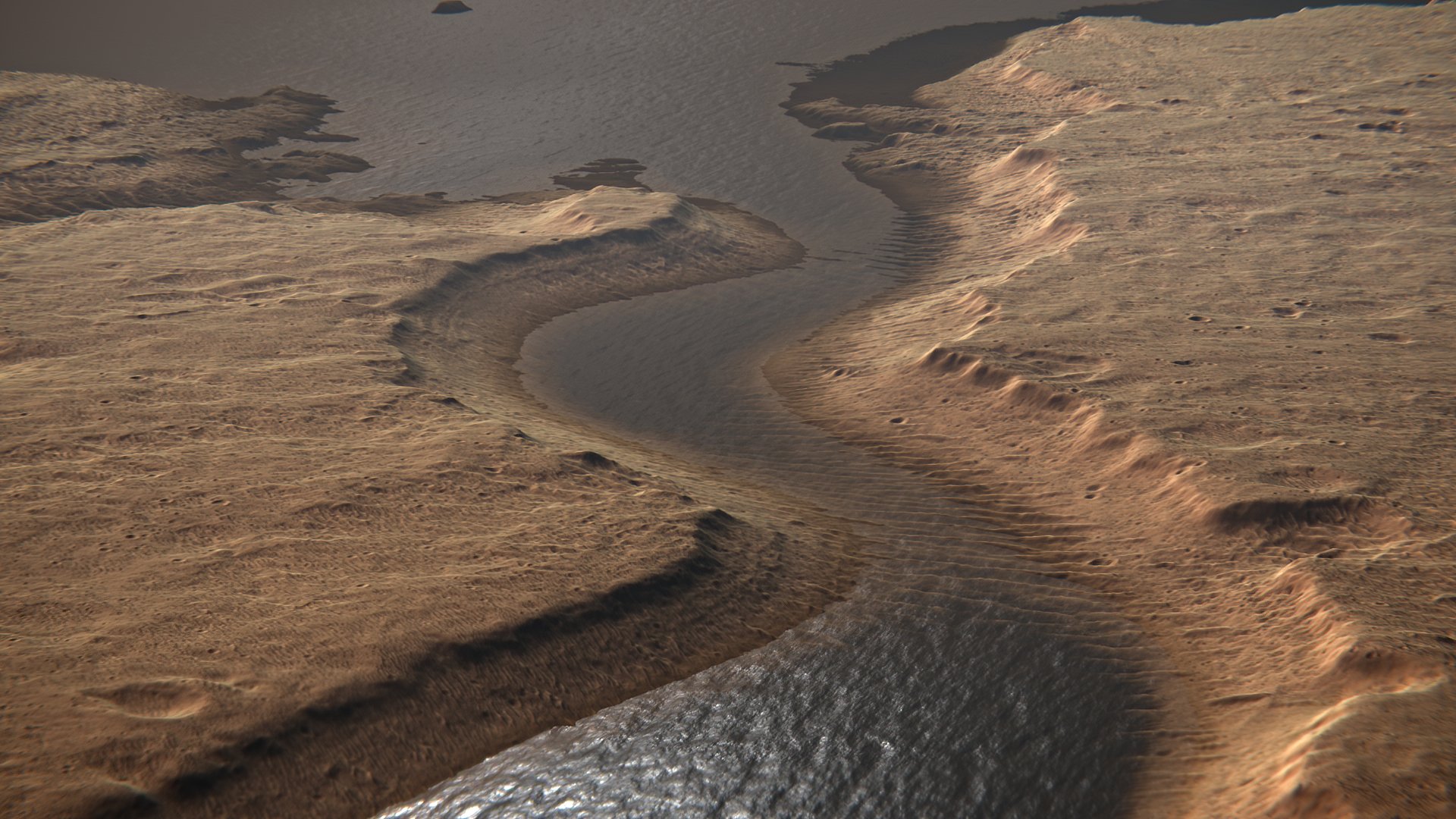
We are once again indebted to Kevin M. Gill, a science data visualization artist with a flair for the cosmos, for this beautiful rendering! The image first popped up on Kevin’s Twitter feed last week and can also be found (and downloaded) on his Flickr account. As he explained, the visual is his rendition of what the Hypanis Valles on Mars may have looked like back when water still flowed in the region. As he described it:
Continue reading “A Real River Valley on Mars, Filled With Virtual Water by @Kevinmgill”“A meandering river? Obvious and bad CGI? Based on a real place on Mars? All Three! Outflow location at Hypanis Valles With Flowing Water, via @HiRISE DTM data.”
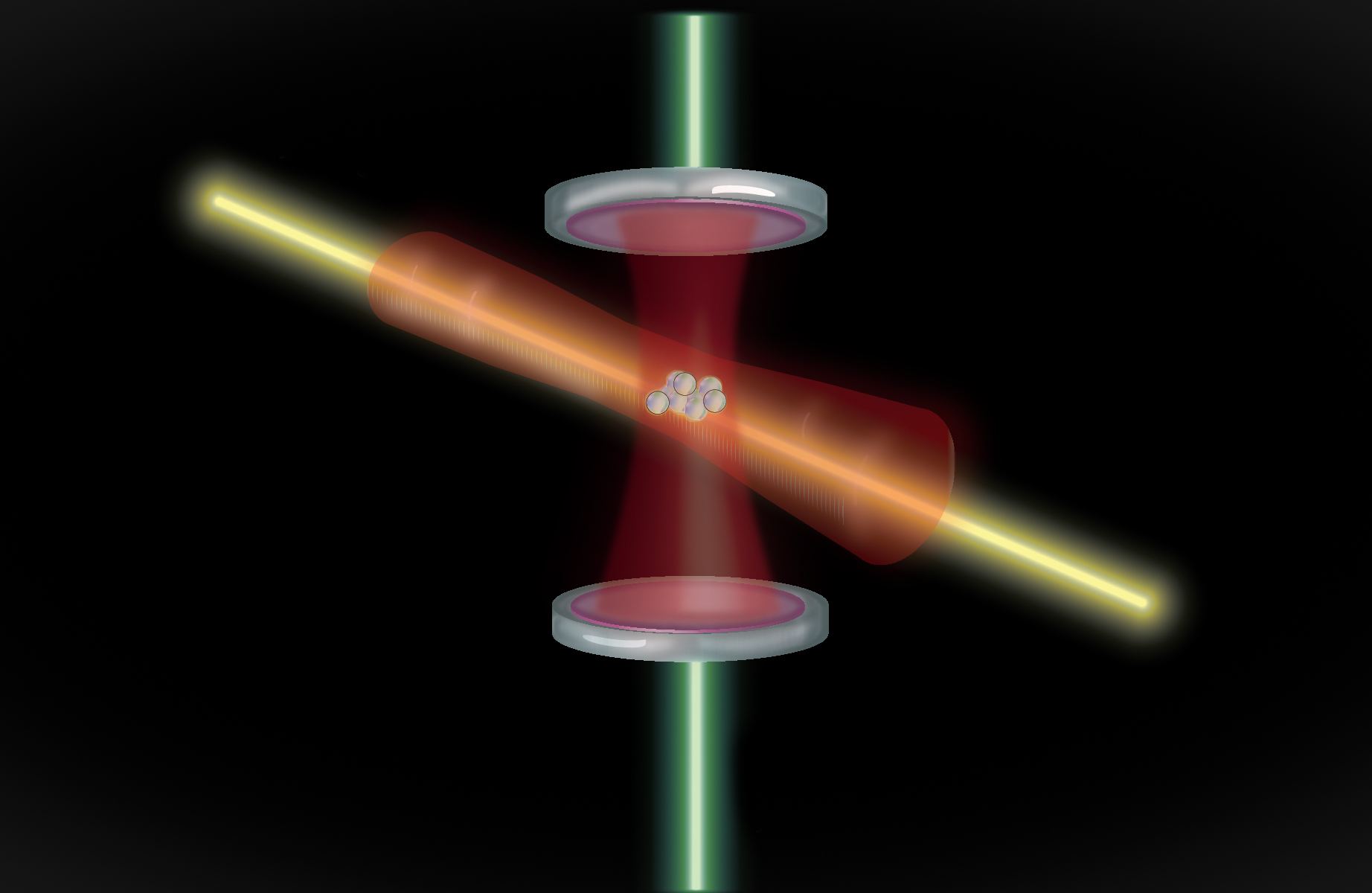
A new Type of Atomic Clock Uses Entangled Atoms. At Most, it Would be off by 100 Milliseconds Since the Beginning of the Universe
Measuring time is about counting steps. Whether it’s the drip-drip of a water clock, the tic-toc of a mechanical clock, or the oscillating crystal of a quartz watch. Any accurate timepiece is built around counting the steps of something regular and periodic. Nothing is perfectly regular, so no clock keeps perfect time, but our timepieces are getting very, very accurate.
Continue reading “A new Type of Atomic Clock Uses Entangled Atoms. At Most, it Would be off by 100 Milliseconds Since the Beginning of the Universe”