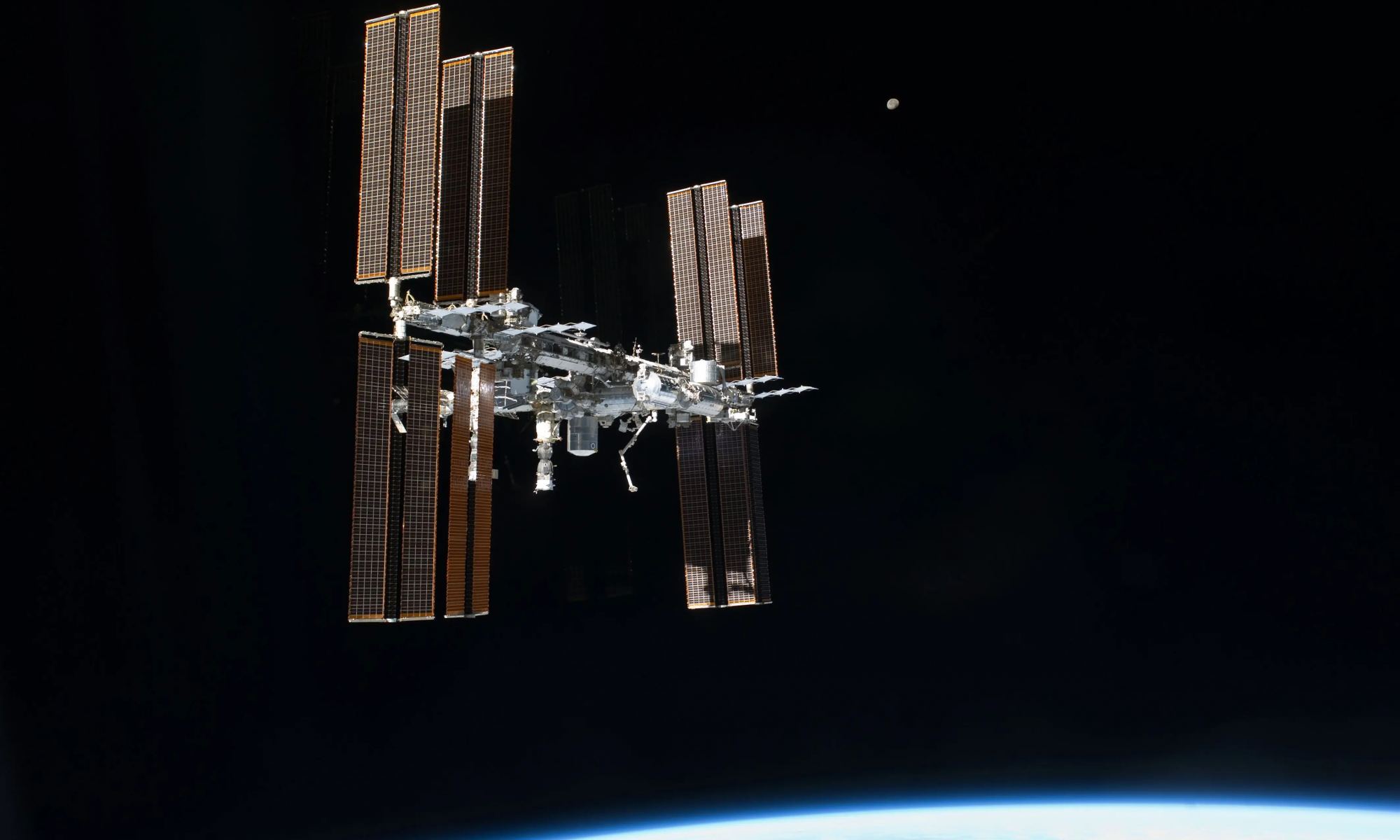
It’s no secret that the International Space Station (ISS) has had a problem with leaks for more than a year. While pressure loss is a perpetual issue, officials noticed an increase last September, which became more serious over the past summer. As of August, the crew began a hard-target search for the source of the leak, eventually narrowing it down to the Zvezda module in the Russian section.
Thanks to an ongoing search over the past two months, the crew has finally pinpointed the leak using a novel detection method. Simply put, they released tea leaves into the Zvezda module and followed them to the source! According to a statement by Roscosmos, the crew of Expedition 63/64 has patched the hole with some heavy-duty tape they had aboard the station. Talk about DIY repairs!
Continue reading “The Crew of the ISS has Found the Source of the Station’s Air Leak”