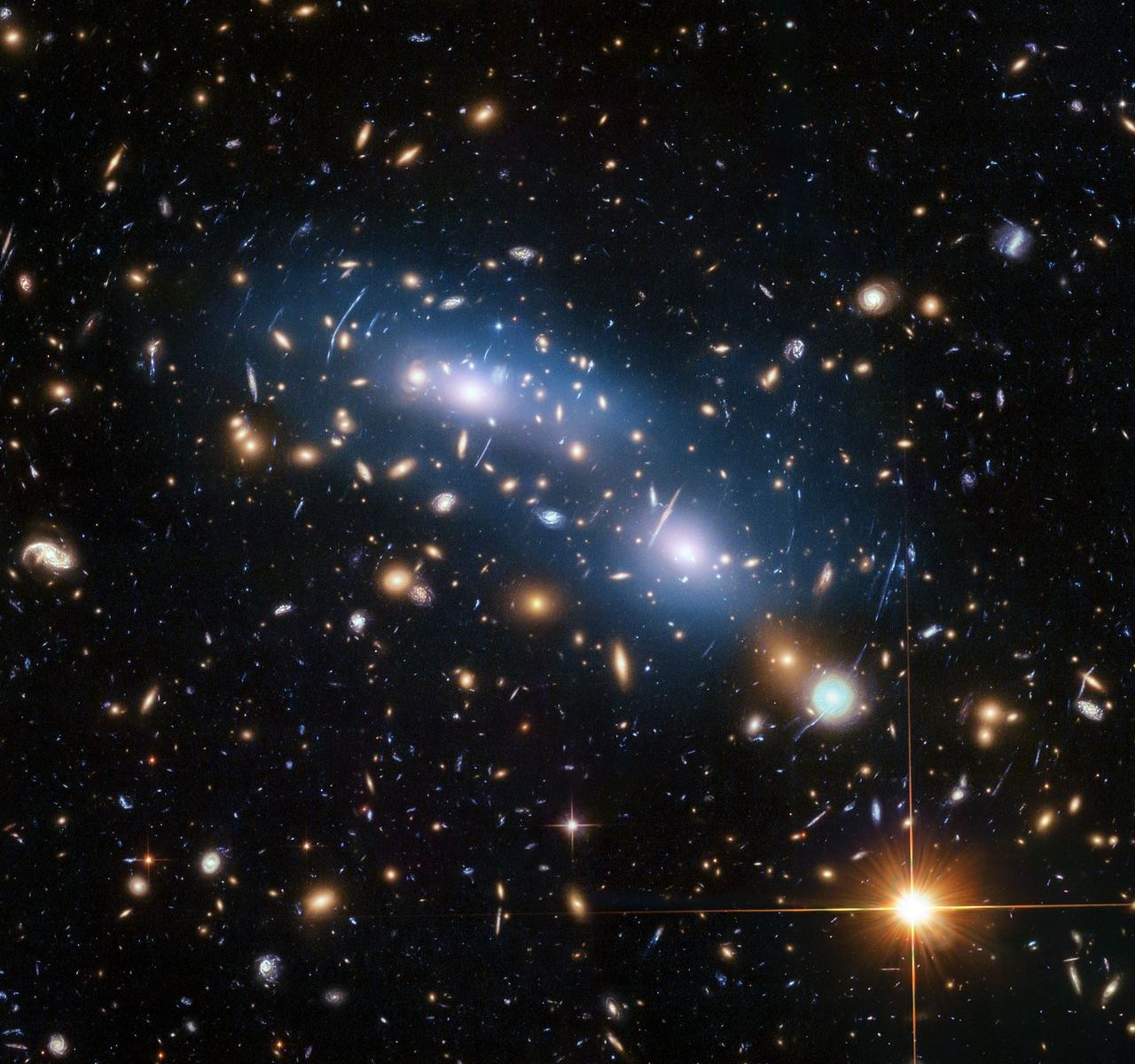
Weighing the universe is a tricky task, but a team of astronomers have used a clever technique to measure how many galaxy clusters are in the cosmos, and from there come up with a total amount of matter. The answer: 31.5±1.3% of all the energy in the universe.
Continue reading “Matter makes up exactly 31.5±1.3% of the Universe”Matter makes up exactly 31.5±1.3% of the Universe