Six and a half decades after he passed away, famed theoretical physicist Albert Einstein is still being proven right! In addition to General Relativity (GR) being tested under the most extreme conditions, lesser-known aspects of his theories are still being validated as well. For example, GR predicts that gravity and inertia are often indistinguishable, in what is known as the gravitational Strong Equivalence Principle (SEP).
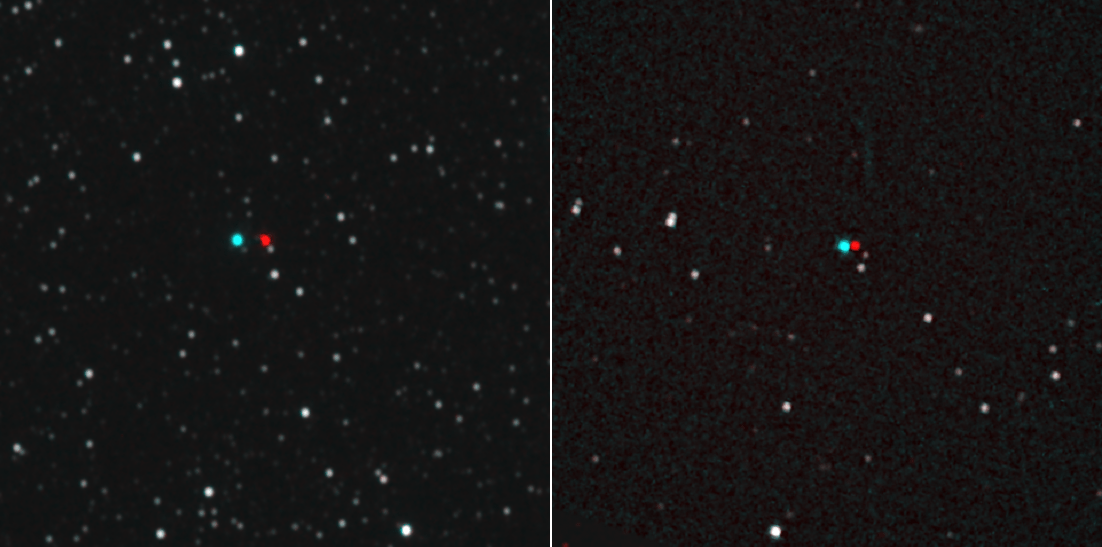
Thanks to an international team of researchers, it has been proven under the strongest conditions to date. By precisely tracking the motion of a pulsar, the team demonstrated that gravity causes neutron stars and white dwarf stars to fall with equal accelerations. This confirms Einstein’s prediction that freefall accurately simulates zero-gravity conditions in all inertial reference frames.
Continue reading “Pulsars Confirm One of Einstein’s Best Ideas, That Freefall Really Feels Like You’re Experiencing a Lack of Gravity”