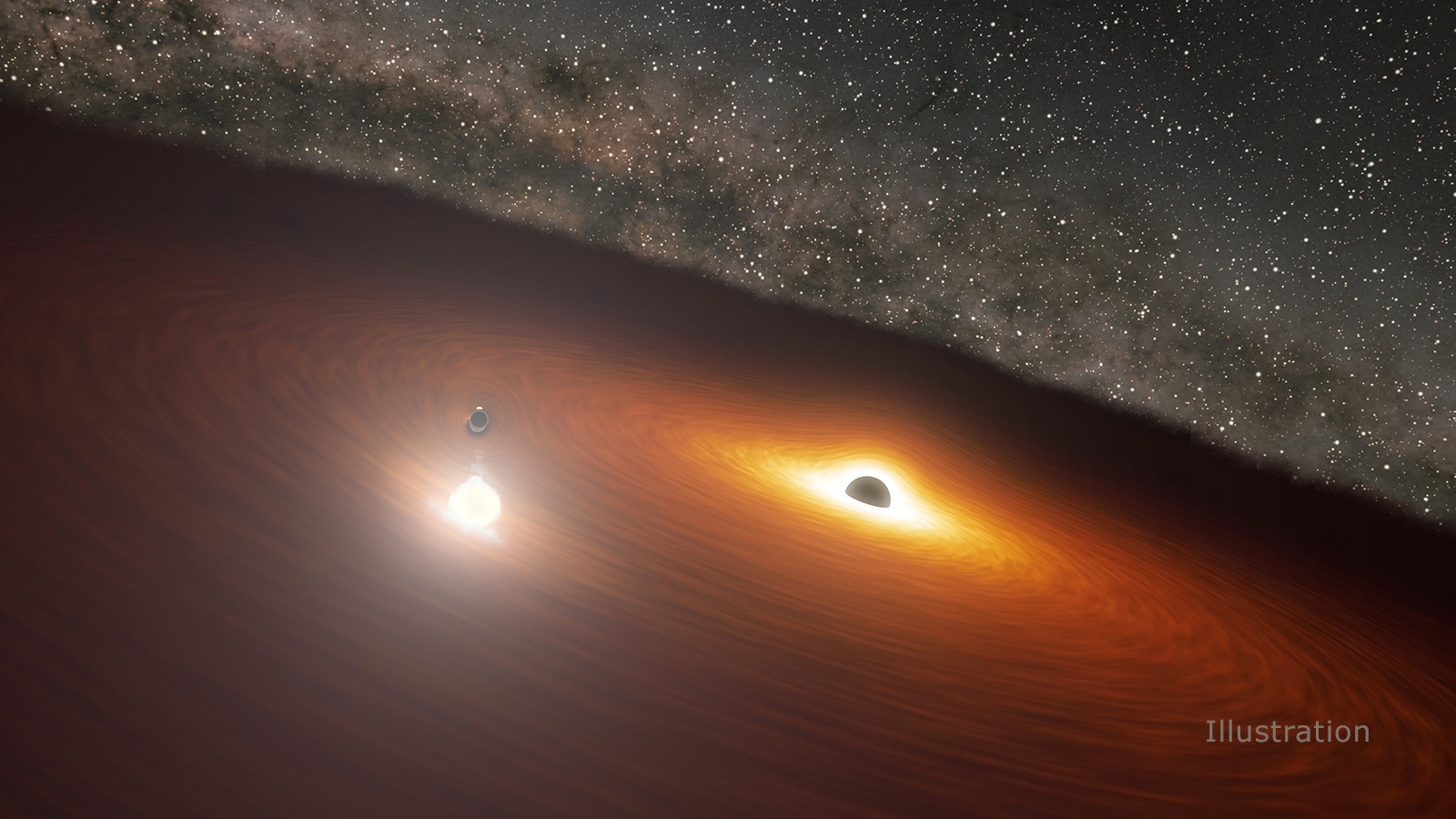
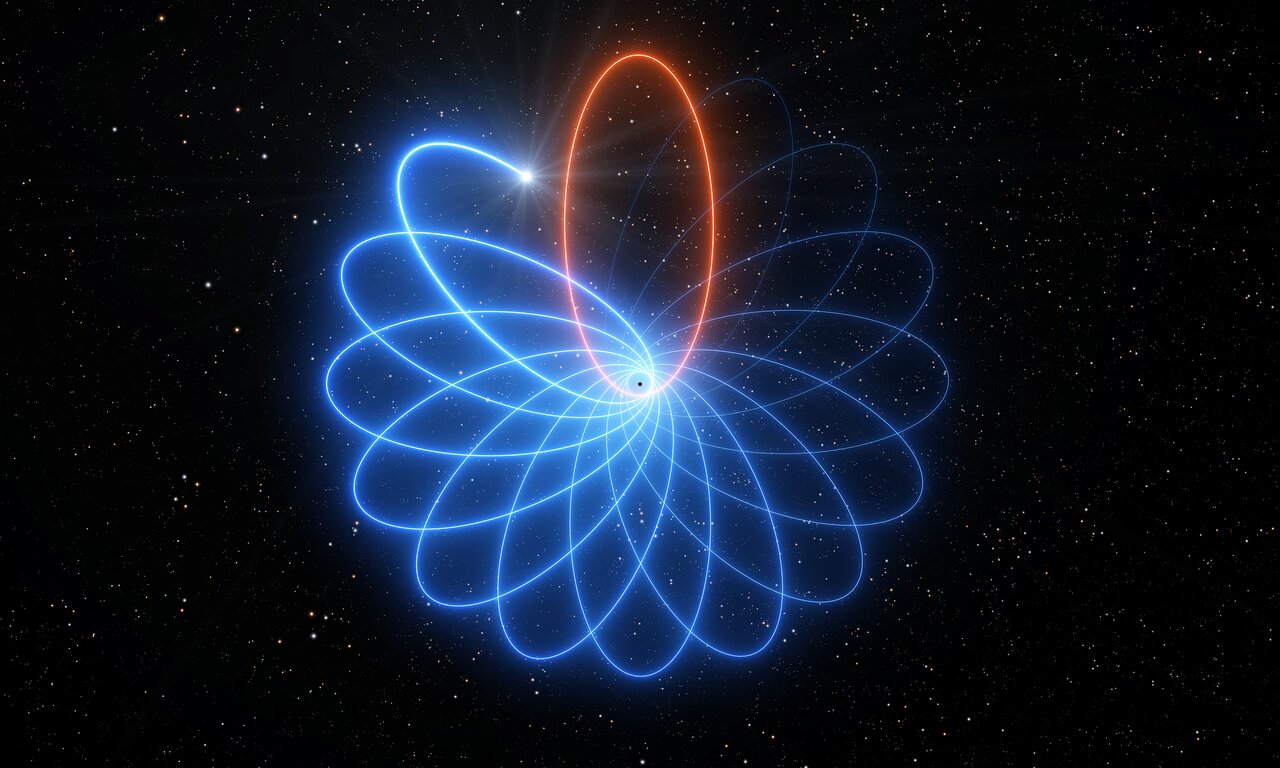
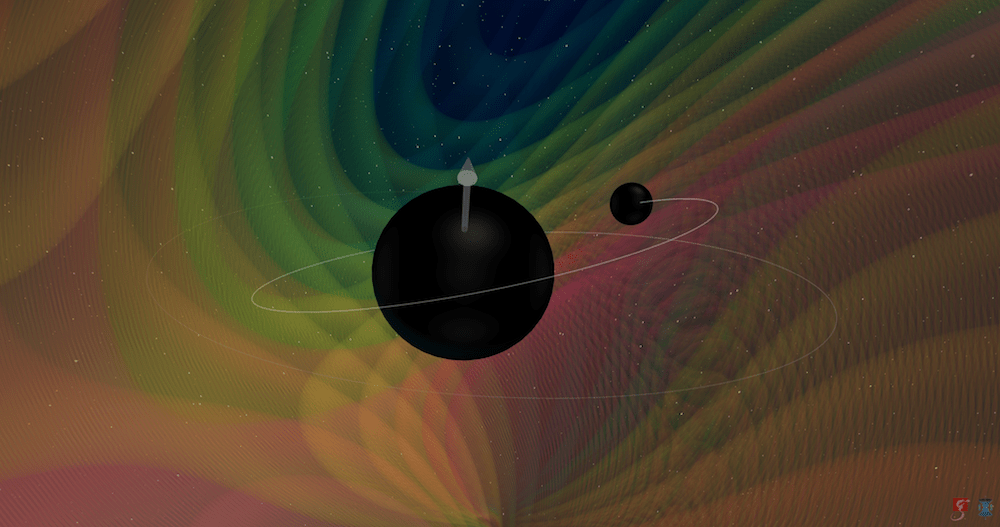
NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope may be retired, but the things it witnessed during its sixteen and a half year mission will be the subject of study for many years to come. For instance, Spitzer is the only telescope to witness something truly astounding occurring at the center of the distant galaxy OJ 287: a supermassive black hole (SMBH) orbited by another black hole that regularly passes through its accretion disk.
Whenever this happens, it causes a flash that is brighter than all the stars in the Milky Way combined. Using Spitzer‘s observations, an international team of astronomers was able to finally create a model that accurately predicts the timing of these flashes and the orbit of the smaller black hole. In addition to demonstrating General Relativity in action, their findings also provide validation to Stephen Hawking‘s “no-hair theorem.”
Continue reading “Supermassive Black Hole Orbits an Even More Massive Black Hole, Crashing Through its Accretion Disk Every 12 Years”