Are you hanging out at home this week, and looking to observe some naked eye planets? As we mentioned last week, while Venus is shining bright in the dusk sky, all of the other four naked eye planets of Mars, Saturn, Jupiter and Mercury are skulking in the early dawn.
Continue reading “Dawn Patrol: Following this Month’s ‘March of the Planets’”A Star Has Been Found That Pulsates, But Only on One Side
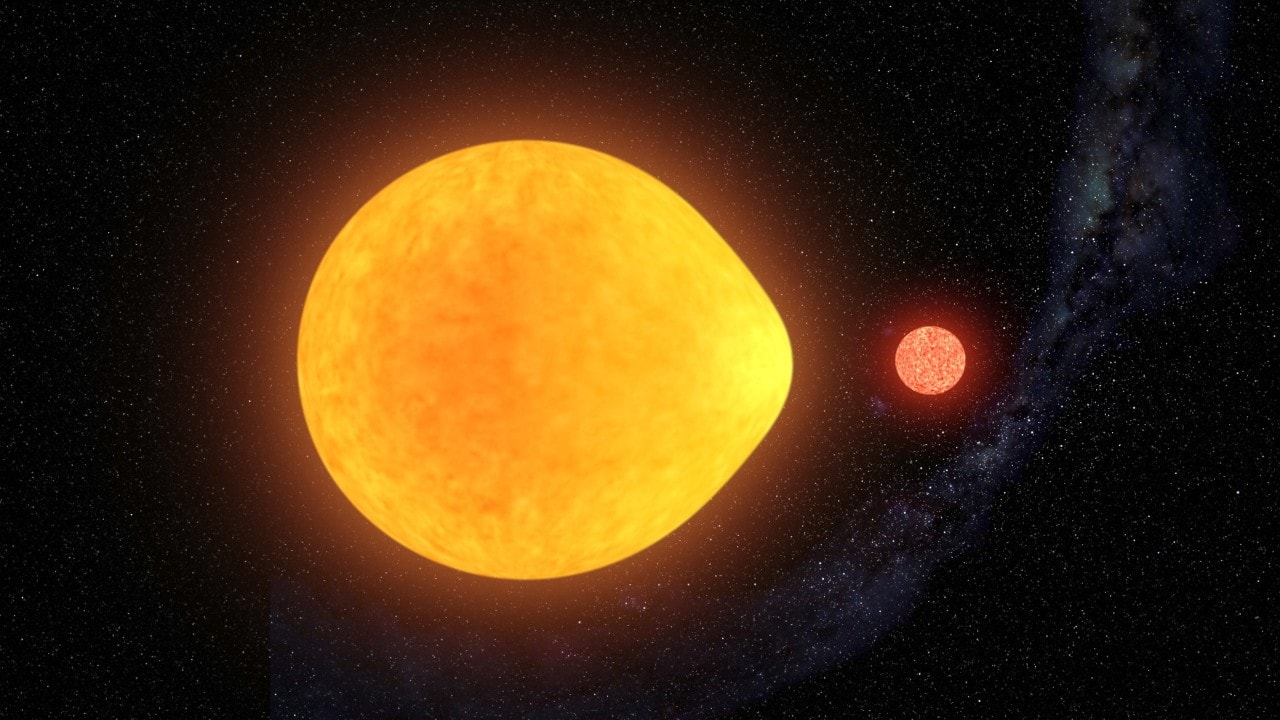
In the 17th century, astronomers witnessed many stellar events that proved that the starry sky was not “fixed and eternal.” This included stars whose brightness varied over time – aka. “variable stars.” By the 20th century, many variable stars had been cataloged and astronomers have discerned subclasses of them as well – notably, stars that swell and shrink, known as pulsating variables.
In all cases, these variable stars were found to have rhythmic pulsations that were visible from all sides. But a recent discovery by an international team has confirmed that there are variable stars that can pulse from only one side. This pulsating star, part of a system known as HD 74423, is located about 1,500 light-years from Earth and is the first of its kind to be found.
Read moreYour Umbrella is Insufficient on a Planet Where it Rains Iron

Imagine a planet where it rained iron. Sounds impossible. But on one distant exoplanet, which is tidally locked to its star, the nightside has to contend with a ferrous downpour.
Continue reading “Your Umbrella is Insufficient on a Planet Where it Rains Iron”Astronomers Spot Rare Brown Dwarf Pair

Sometimes, the strangest stellar finds are right in our own cosmic neighborhood. Astronomers recently made an interesting discovery while putting a new set of telescopes through their paces: an eclipsing pair of sub-stellar brown dwarfs.
Continue reading “Astronomers Spot Rare Brown Dwarf Pair”Gas and Dust Stop Planets From Eating Their Moons
Beyond Earth’s only satellite (the Moon), the Solar System is packed full of moons. In fact, Jupiter alone has 79 known natural satellites while Saturn has the most know moons of any astronomical body – a robust 82. For the longest time, astronomers have theorized that moons form from circumplanetary disks around a parent planet and that the moons and planet form alongside each other.
However, scientists have conducted multiple numerical simulations that have shown this theory to be flawed. What’s more, the results of these simulations are inconsistent with what we see throughout the Solar System. Thankfully, a team of Japanese researchers recently conducted a series of simulations that yielded a better model of how disks of gas and dust can form the kinds of moon systems that we see today.
Continue reading “Gas and Dust Stop Planets From Eating Their Moons”Following the Inner Worlds: Mercury and Venus in 2020
Where have all the planets gone in early 2020? While most of the naked eye planets are hiding in the early dawn sky, one world dominates the evening: brilliant Venus.
Continue reading “Following the Inner Worlds: Mercury and Venus in 2020”Seti@home is on Pause. Unfortunately, it’s not Because They’ve Discovered Aliens
In May of 1999, the Berkeley SETI Research Center launched a citizen-science program that would make the Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence (SETI) open to the public. The brainchild of computer scientist David Gedye, this program would rely on large numbers of internet-connected computers to sort through the volumes of data collected by institutions participating in SETI efforts.
The program was appropriately named SETI@home and would rely on the computers of volunteers to process radio signals for signs of transmissions. And after twenty years, the program recently announced that it has gone into hibernation. The reason, they claim, is that the program’s network has become too big for its own britches and the scientists behind it need time to process and share all the results they’ve obtained so far.
Continue reading “Seti@home is on Pause. Unfortunately, it’s not Because They’ve Discovered Aliens”Life Could be Common Across the Universe, Just Not in Our Region
The building blocks of life can, and did, spontaneously assemble under the right conditions. That’s called spontaneous generation, or abiogenesis. Of course, many of the details remain hidden to us, and we just don’t know exactly how it all happened. Or how frequently it could happen.
Continue reading “Life Could be Common Across the Universe, Just Not in Our Region”Europe’s Mission to Jupiter’s Moons Just Got its First Instrument
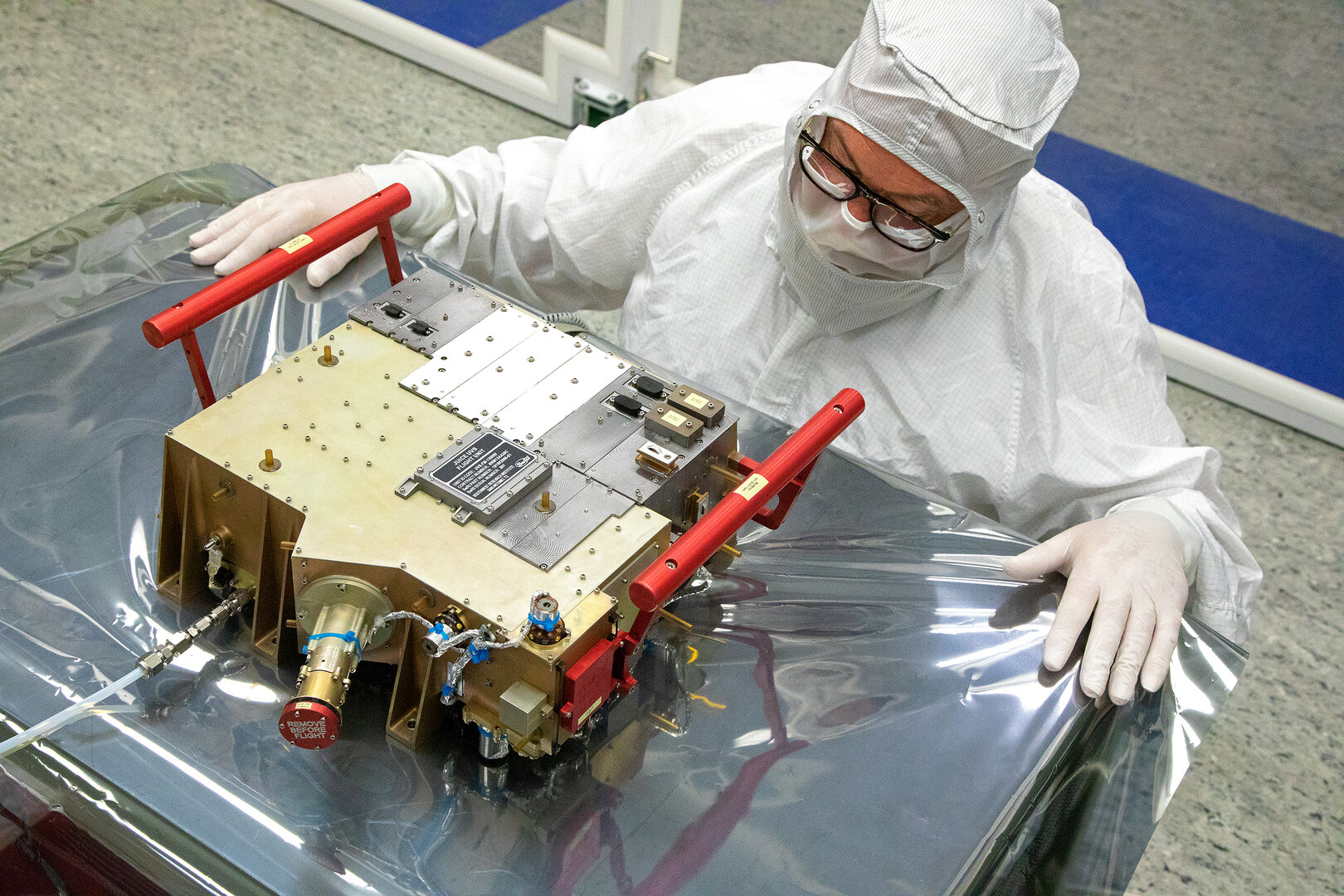

The space agencies of the world have some truly ambitious plans in mind for the coming decade. Alongside missions that will search for evidence for past (and maybe present) life on Mars, next-generation space telescopes, and the “return to the Moon”, there are missions will which will explore Jupiter’s moons for signs of extra-terrestrial life. These include the ESA’s JUpiter Icy Moon Explorer (JUICE), which will launch in 2022.
As part of the agency’s Cosmic Vision 2015-2025 program, this spacecraft will conduct detailed observations of Jupiter and three of its large moons – Ganymede, Callisto, and Europa – to see if they could indeed harbor life in their interiors. Late last month (Feb. 25th), the first instrument that will fly aboard JUICE and aid in these efforts was delivered and began the process of integration with the spacecraft.
Continue reading “Europe’s Mission to Jupiter’s Moons Just Got its First Instrument”XMM Newton Catches a Tiny Flare Star in Action
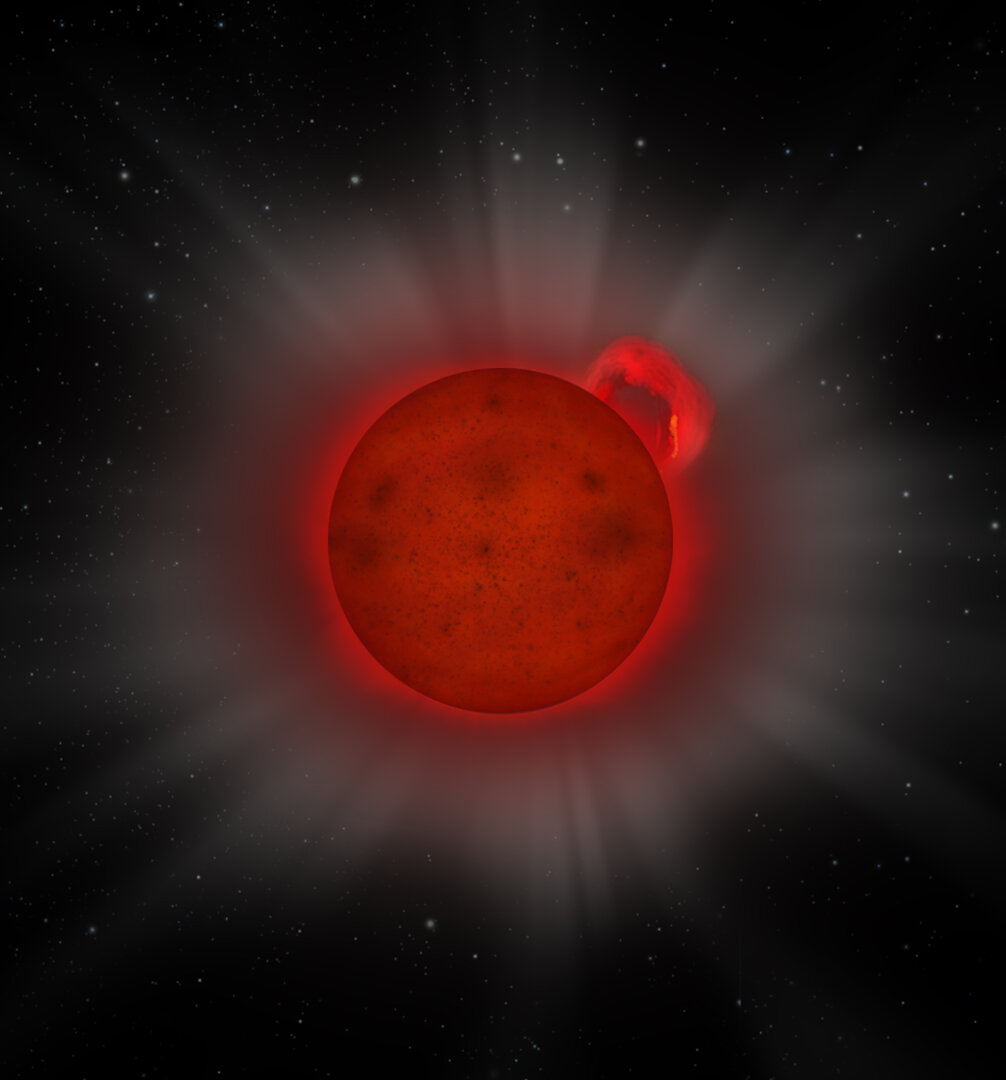
Sometimes, even small stars can pack a mighty punch. And in the case of a flare star, the results can be awesome. Very awesome.
Astronomers uncovered just such an anomaly recently, culling through data from the European Space Agency’s XMM-Newton orbiting X-ray observatory: the first X-ray flare from a distant cool L-dwarf type star.
Continue reading “XMM Newton Catches a Tiny Flare Star in Action”





