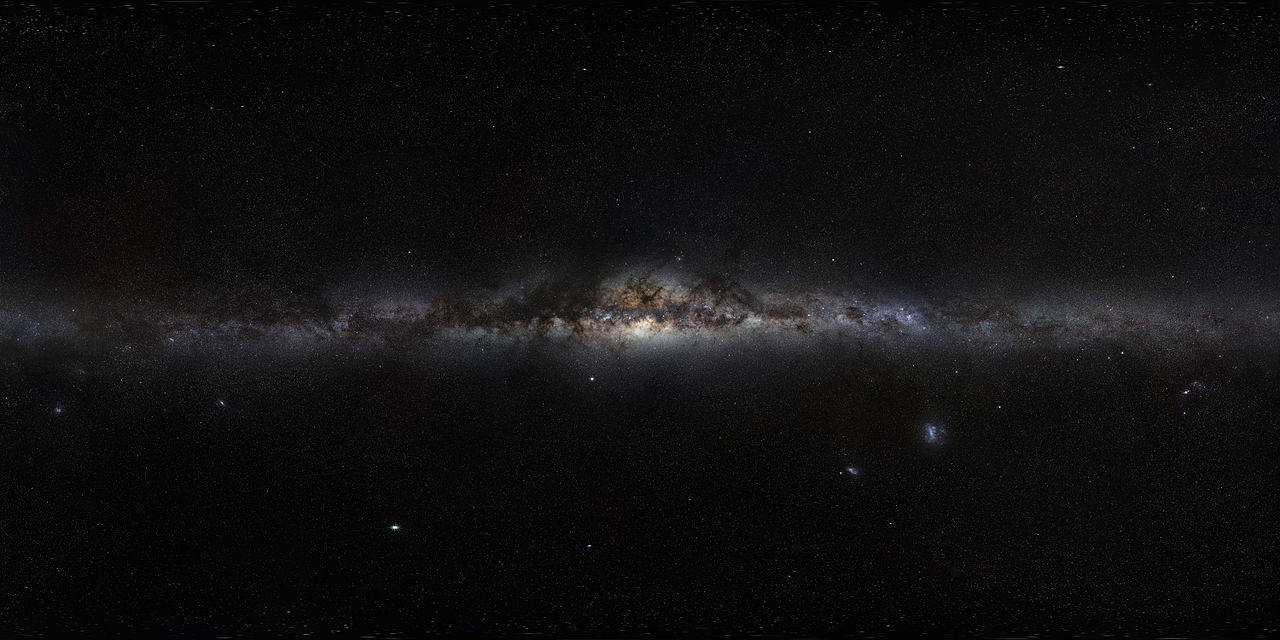
According to the most widely-accepted cosmological models, the first galaxies began to form between 13 and 14 billion years ago. Over the course of the next billion years, the cosmic structures we’ve all come to know emerged. These include things like galaxy clusters, superclusters, and filaments, but also galactic features like globular clusters, galactic bulges, and Supermassive Black Holes (SMBHs).
However, like living organisms, galaxies have continued to evolve ever since. In fact, over the course of their lifetimes, galaxies accrete and eject mass all the time. In a recent study, an international team of astronomers calculated the rate of inflow and outflow of material for the Milky Way. Then the good folks at astrobites gave it a good breakdown and showed just how relevant it is to our understanding of galactic formation and evolution.
Continue reading “Earth, Solar System, Milky Way. Are they Getting More or Less Massive Over Time?”