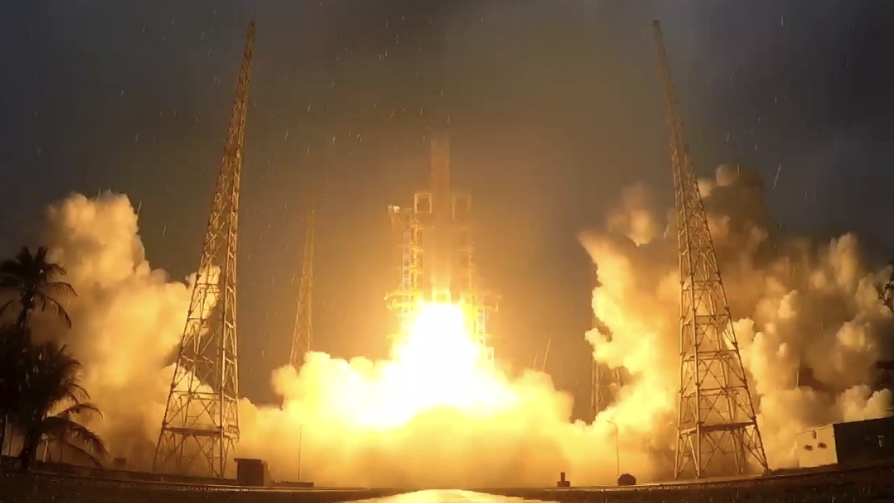
On Friday, May 3rd, the sixth mission in the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program (Chang’e-6) launched from the Wenchang Spacecraft Launch Site in southern China. Shortly after, China announced that the spacecraft separated successfully from its Long March 5 Y8 rocket. The mission, consisting of an orbiter and lander element, is now on its way to the Moon and will arrive there in a few weeks. By June, the lander element will touch down on the far side of the Moon, where it will gather about 2 kg (4.4 lbs) of rock and soil samples for return to Earth.
Continue reading “China is Going Back to the Moon Again With Chang'e-6”China Creates a High-Resolution Atlas of the Moon
Multiple space agencies are looking to send crewed missions to the Moon’s southern polar region in this decade and the next. Moreover, they intend to create the infrastructure that will allow for a sustained human presence, exploration, and economic development. This requires that the local geography, resources, and potential hazards be scouted in advance and navigation strategies that do not rely on a Global Positioning System (GPS) developed. On Sunday, April 21st, the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) released the first complete high-definition geologic atlas of the Moon.
This 1:2.5 million scale geological set of maps provides basic geographical data for future lunar research and exploration. According to the Institute of Geochemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), the volume includes data on 12,341 craters, 81 impact basins, 17 types of lithologies, 14 types of structures, and other geological information about the lunar surface. This data will be foundational to China’s efforts in selecting a site for their International Lunar Research Station (ILRS) and could also prove useful for NASA planners as they select a location for the Artemis Base Camp.
Continue reading “China Creates a High-Resolution Atlas of the Moon”Dinkinesh's Moonlet is Only 2-3 Million Years Old
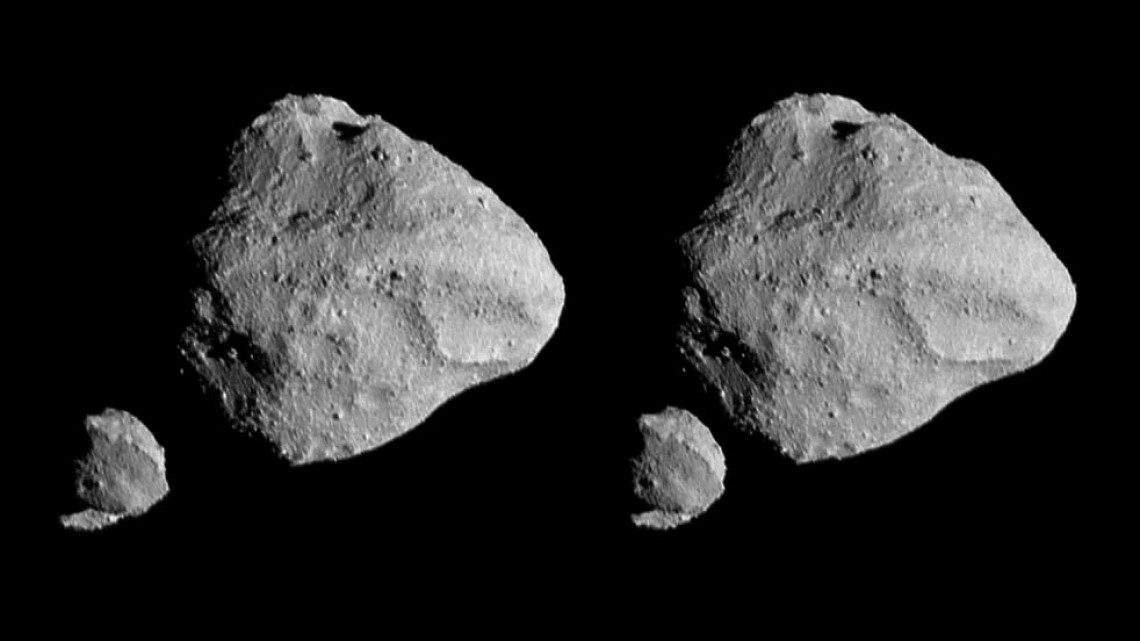

Last November, NASA’s Lucy mission conducted a flyby of the asteroid Dinkinish, one of the Main Belt asteroids it will investigate as it makes its way to Jupiter. In the process, the spacecraft spotted a small moonlet orbiting the larger asteroid, now named Selam (aka. “Lucy’s baby”). The moonlet’s name, an Ethiopian name that means “peace,” pays homage to the ancient human remains dubbed “Lucy” (or Dinkinish) that were unearthed in Ethiopia in 1974. Using novel statistical calculations based on how the two bodies orbit each other, a Cornell-led research team estimates that the moonlet is only 2-3 million years old.
Continue reading “Dinkinesh's Moonlet is Only 2-3 Million Years Old”Vera Rubin’s Primary Mirror Gets its First Reflective Coating
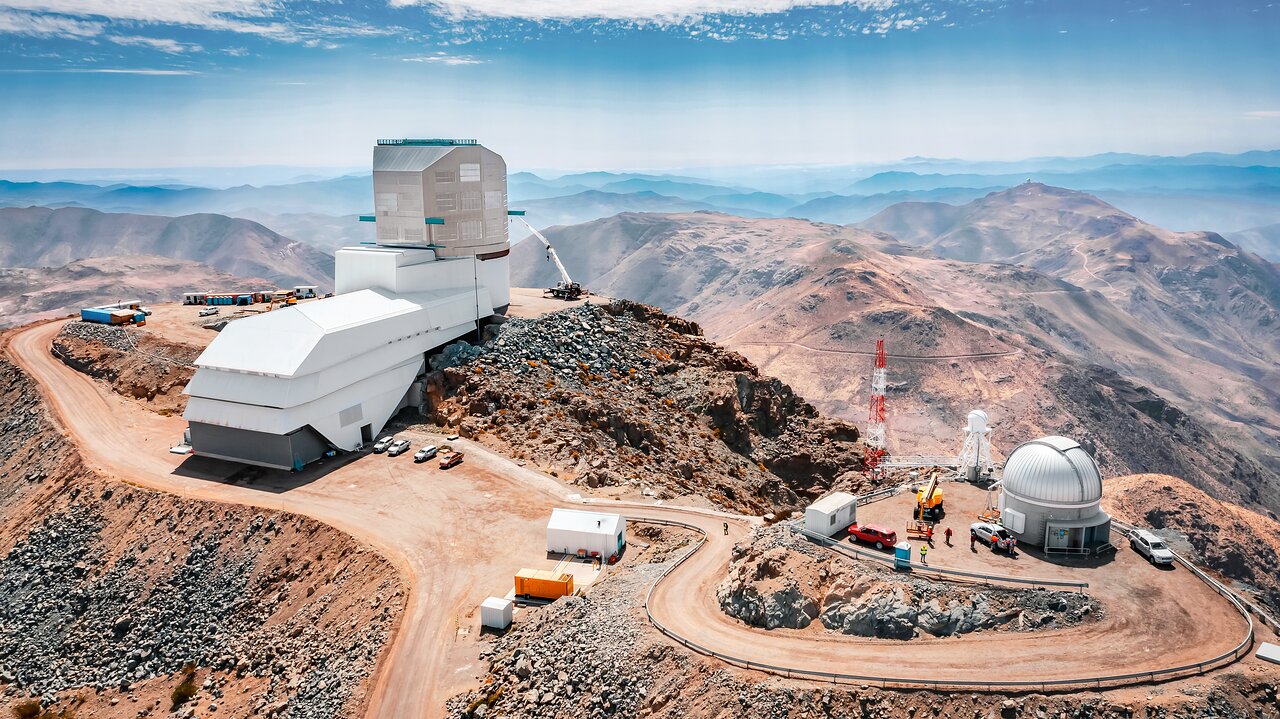

First light for the Vera Rubin Observatory (VRO) is quickly approaching and the telescope is reaching milestone after milestone. A few weeks ago, the observatory announced that its digital camera, the largest one ever made, is complete.
Now the observatory has announced that its unique primary/tertiary mirror has its first reflective coating.
Continue reading “Vera Rubin’s Primary Mirror Gets its First Reflective Coating”Two Stars in a Binary System are Very Different. It's Because There Used to be Three
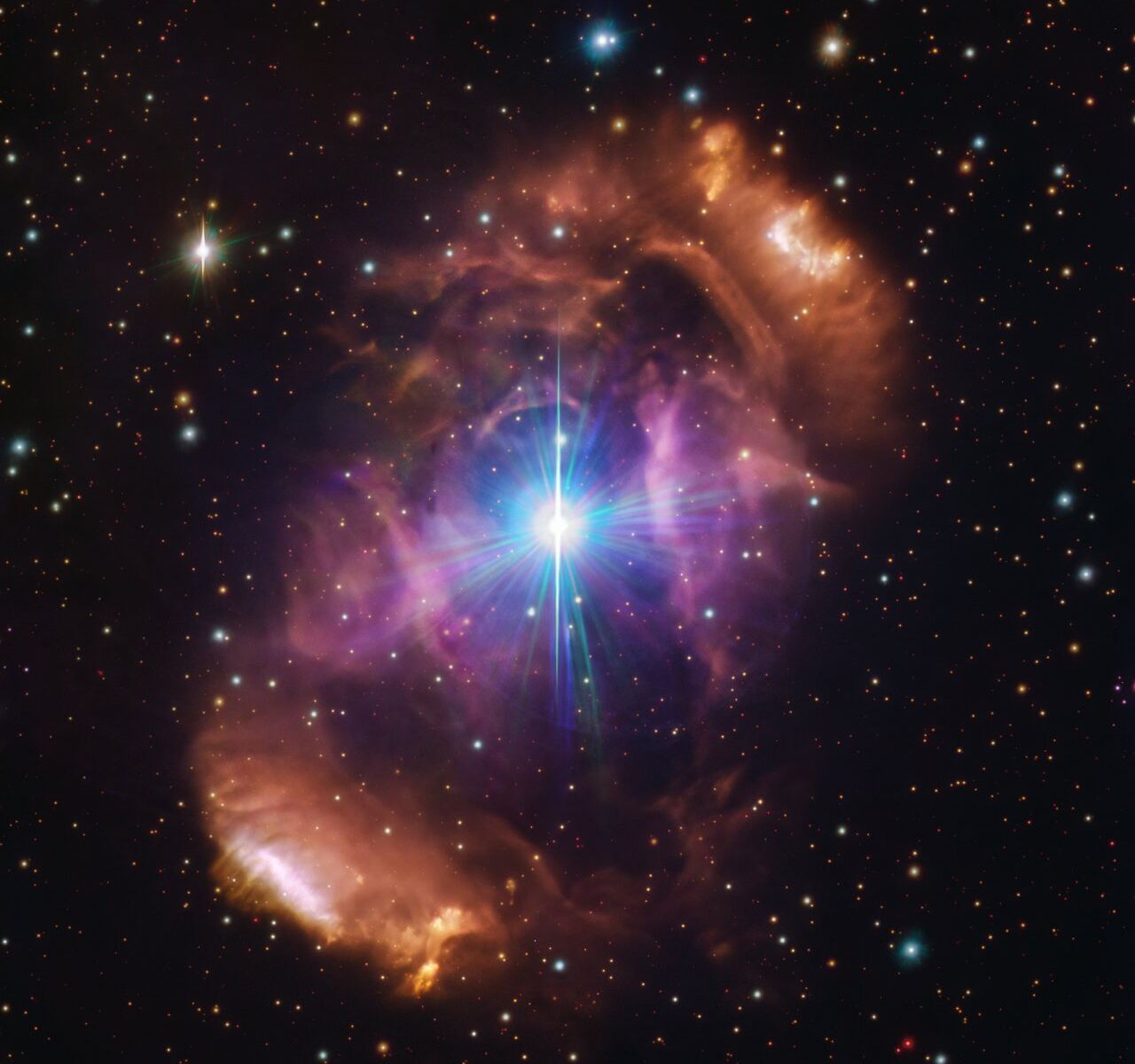

A beautiful nebula in the southern hemisphere with a binary star at it’s center seems to break our standard models of stellar evolution. But new data from the European Southern Observatory (ESO) suggests that there may once have been three stars, and that one was destroyed in a catastrophic collision.
Continue reading “Two Stars in a Binary System are Very Different. It's Because There Used to be Three”The Highest Observatory in the World Comes Online
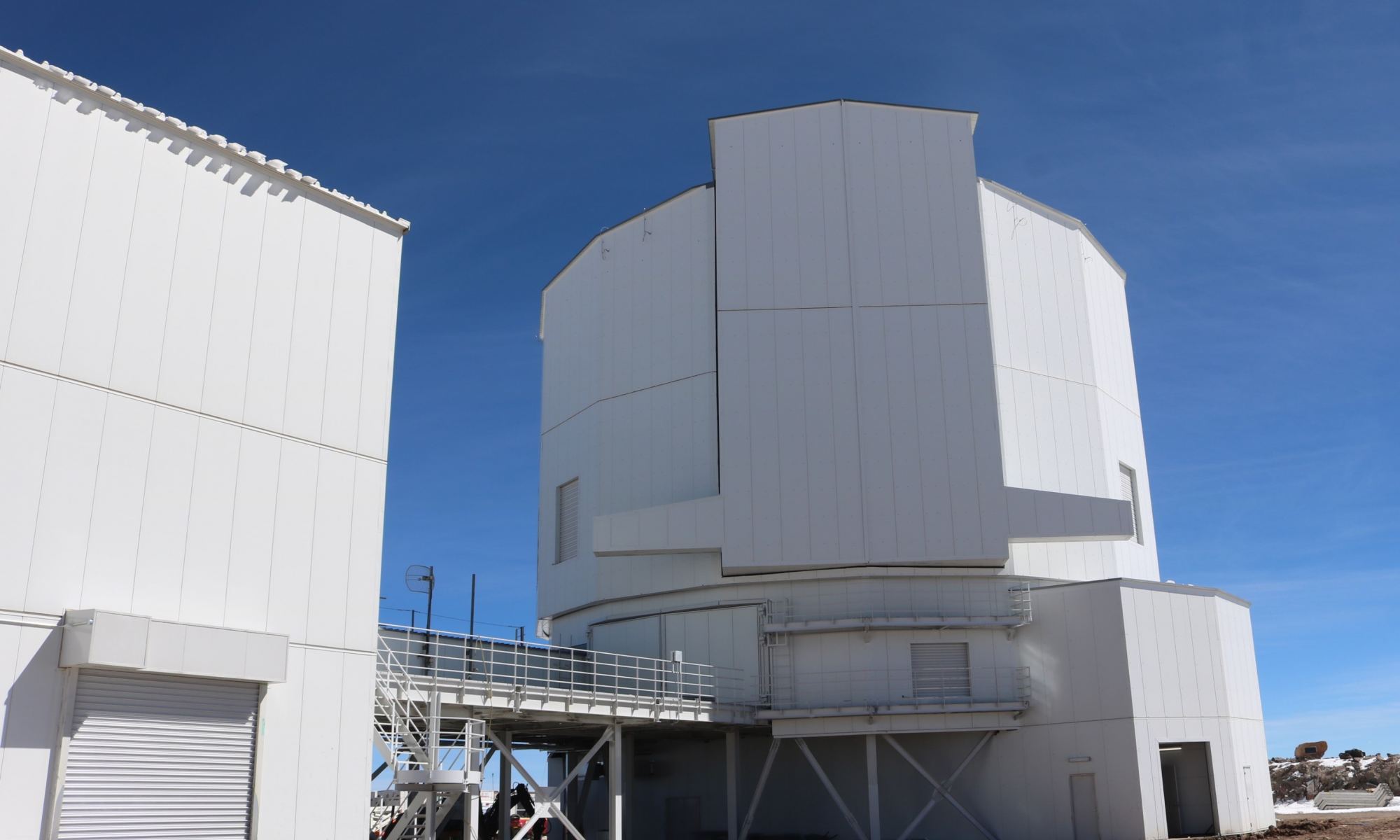

The history of astronomy and observatories is full of stories about astronomers going higher and higher to get better views of the Universe. On Earth, the best locations are at places such as the Atacama Desert in Chile. So, that’s where the University of Tokyo Atacama Observatory just opened its high-altitude eye on the sky, atop Cerro Chajnantor.
Continue reading “The Highest Observatory in the World Comes Online”What Can AI Learn About the Universe?
Artificial intelligence and machine learning have become ubiquitous, with applications ranging from data analysis, cybersecurity, pharmaceutical development, music composition, and artistic renderings. In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have also emerged, adding human interaction and writing to the long list of applications. This includes ChatGPT, an LLM that has had a profound impact since it was introduced less than two years ago. This application has sparked considerable debate (and controversy) about AI’s potential uses and implications.
Astronomy has also benefitted immensely, where machine learning is used to sort through massive volumes of data to look for signs of planetary transits, correct for atmospheric interference, and find patterns in the noise. According to an international team of astrophysicists, this may just be the beginning of what AI could do for astronomy. In a recent study, the team fine-tuned a Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) model using observations of astronomical objects. In the process, they successfully demonstrated that GPT models can effectively assist with scientific research.
Continue reading “What Can AI Learn About the Universe?”Insanely Detailed Webb Image of the Horsehead Nebula
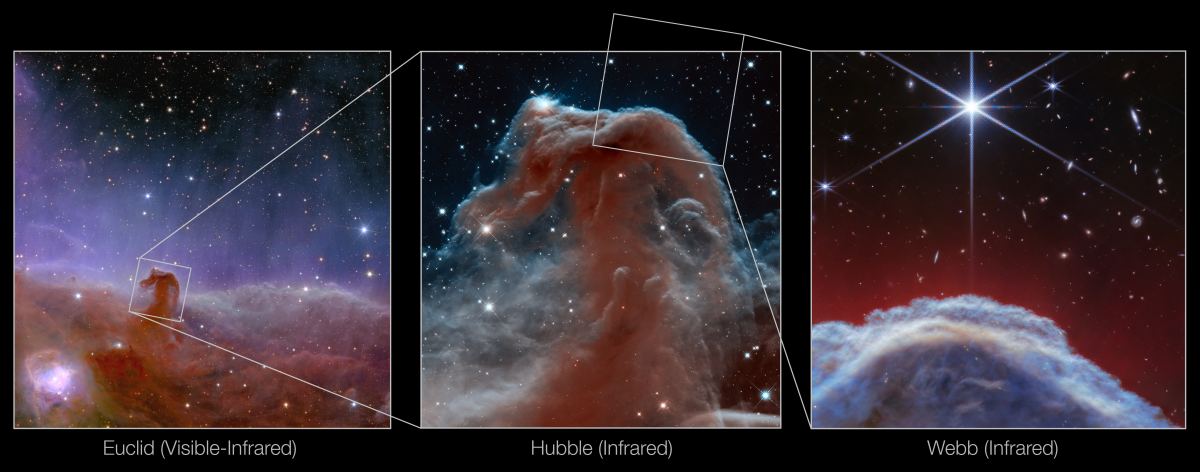

Few space images are as iconic as those of the Horsehead Nebula. Its shape makes it instantly recognizable. Over the decades, a number of telescopes have captured its image, turning it into a sort of test case for a telescope’s power.
The JWST has them all beat.
Continue reading “Insanely Detailed Webb Image of the Horsehead Nebula”Astronomers Think They’ve Found Examples of the First Stars in the Universe
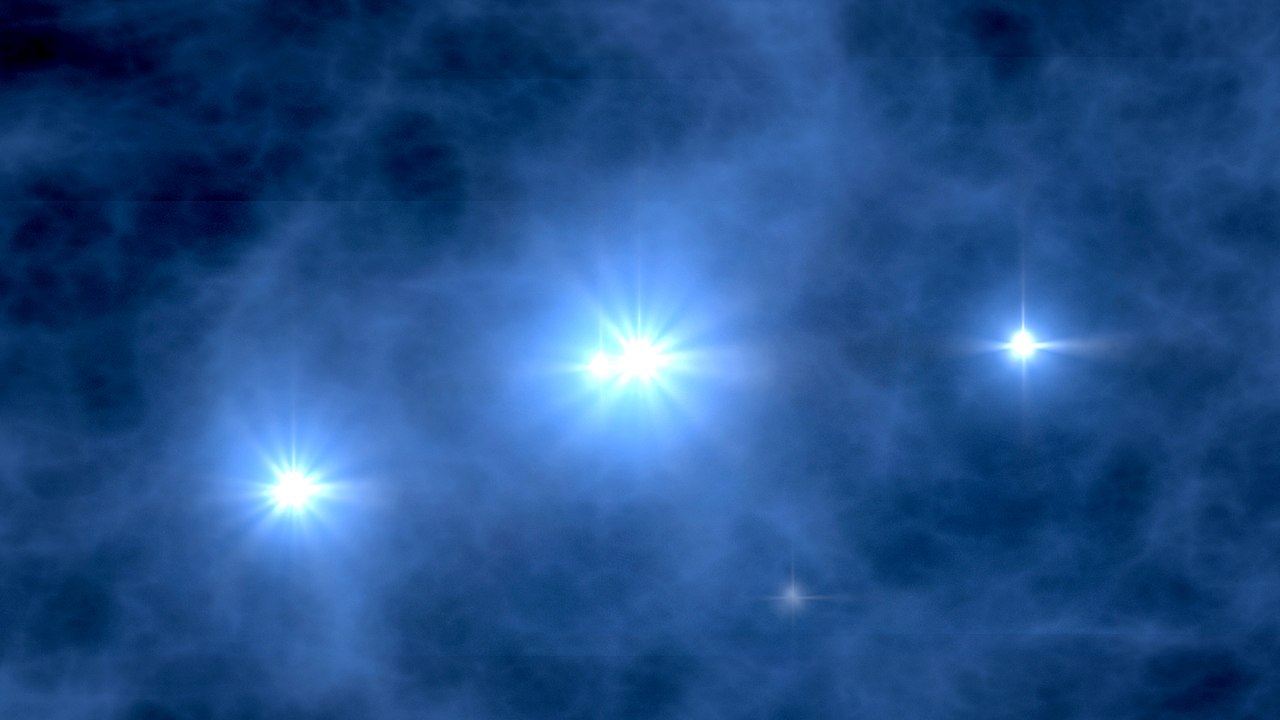

When the first stars in the Universe formed, the only material available was primordial hydrogen and helium from the Big Bang. Astronomers call these original stars Population Three stars, and they were extremely massive, luminous, and hot stars. They’re gone now, and in fact, their existence is hypothetical.
But if they did exist, they should’ve left their fingerprints on nearby gas, and astrophysicists are looking for it.
Continue reading “Astronomers Think They’ve Found Examples of the First Stars in the Universe”Another New Molecule Discovered Forming in Space
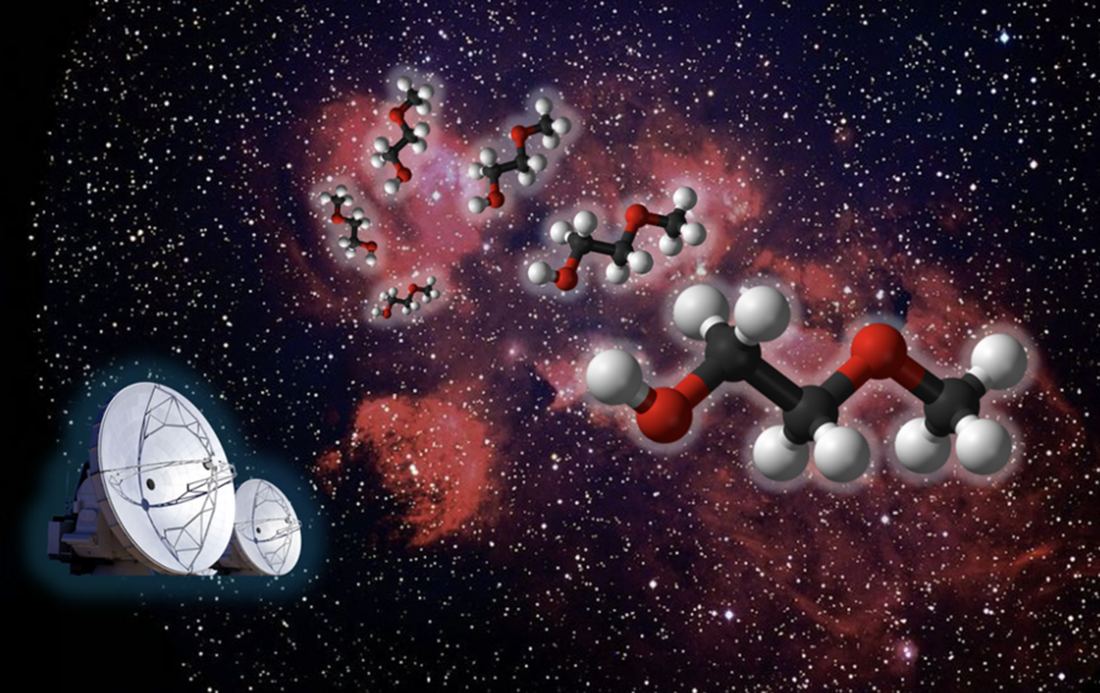
The list of chemicals found in space is growing longer and longer. Astronomers have found amino acids and other building blocks of life on comets, asteroids, and even floating freely in space. Now, researchers have found another complex chemical to add to the list.
Continue reading “Another New Molecule Discovered Forming in Space”


