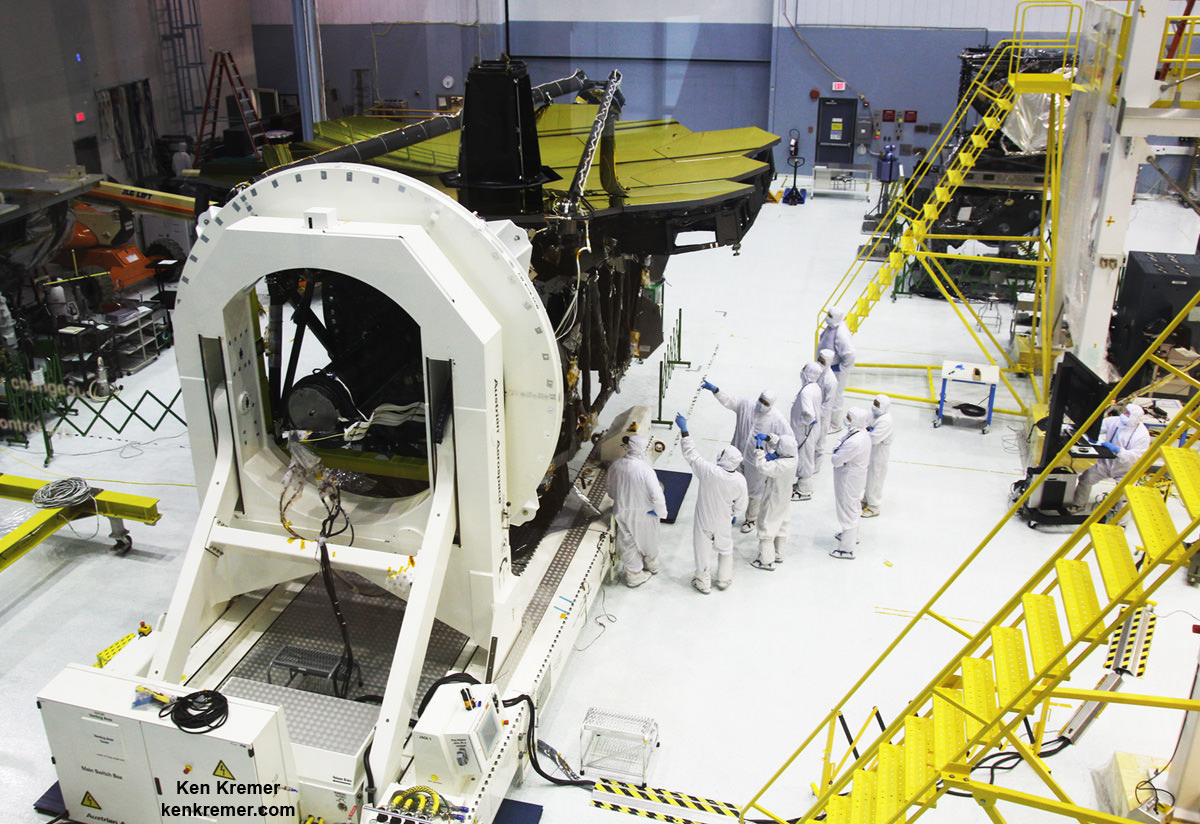
NASA GODDARD SPACE FLIGHT CENTER, MD – It’s Mesmerizing ! That’s the overwhelming feeling expressed among the fortunate few setting their own eyeballs on the newly exposed golden primary mirror at the heart of NASA’s mammoth James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) – a sentiment shared by the team building the one-of-its-kind observatory and myself during a visit this week by Universe Today.
“The telescope is cup up now [concave]. So you see it in all its glory!” said John Durning, Webb Telescope Deputy Project Manager, in an exclusive interview with Universe Today at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center on Tuesday, May 3, after the covers were carefully removed just days ago from all 18 primary mirror segments and the structure was temporarily pointed face up.
“The entire mirror system is checked out, integrated and the alignment has been checked.”
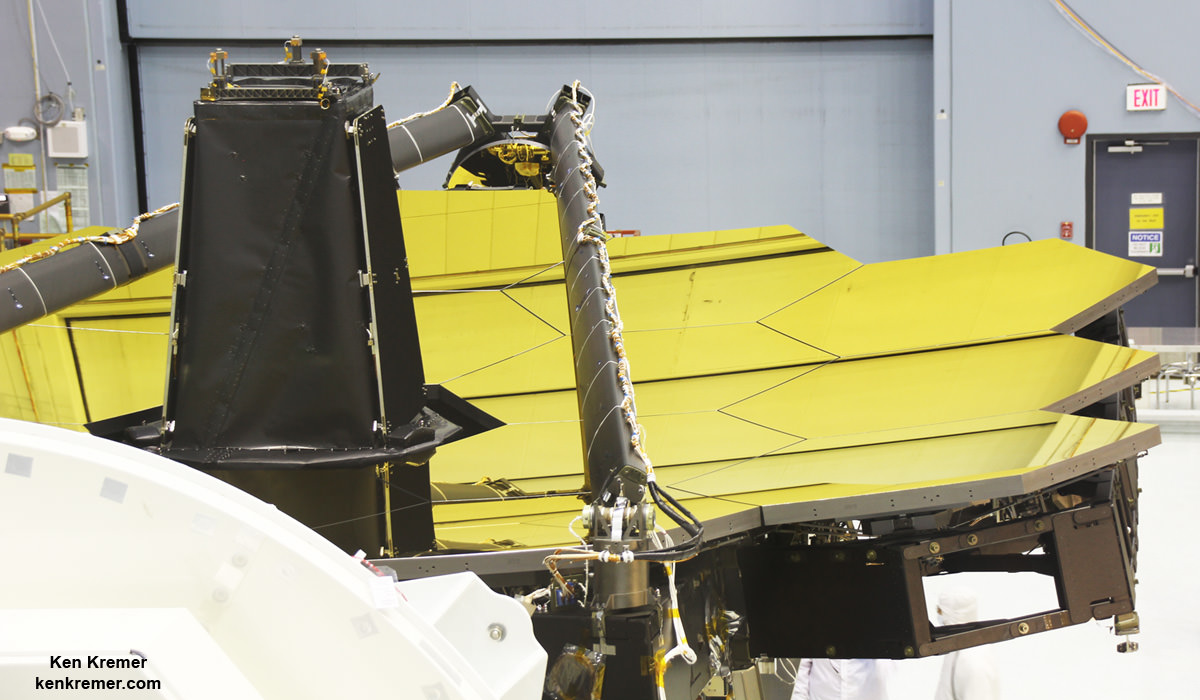

It’s a banner year for JWST at Goddard where the engineers and technicians are well into the final assembly and integration phase of the optical and science instrument portion of the colossal observatory that will revolutionize our understanding of the cosmos and our place it in. And they are moving along at a rapid pace.
JWST is the scientific successor to NASA’s 25 year old Hubble Space Telescope. It will become the biggest and most powerful space telescope ever built by humankind after it launches 30 months from now.
The flight structure for the backplane assembly truss that holds the mirrors and science instruments arrived at Goddard last August from Webb prime contractor Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems in Redondo Beach, California.
The painstaking assembly work to piece together the 6.5 meter diameter primary mirror began just before the Thanksgiving 2015 holiday, when the first unit was successfully installed onto the central segment of the mirror holding backplane assembly.
Technicians from Goddard and Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York then methodically populated the backplane assembly one-by-one, sequentially installing the last primary mirror segment in February followed by the single secondary mirror at the top of the massive trio of mirror mount booms and the tertiary and steering mirrors inside the Aft Optics System (AOS).
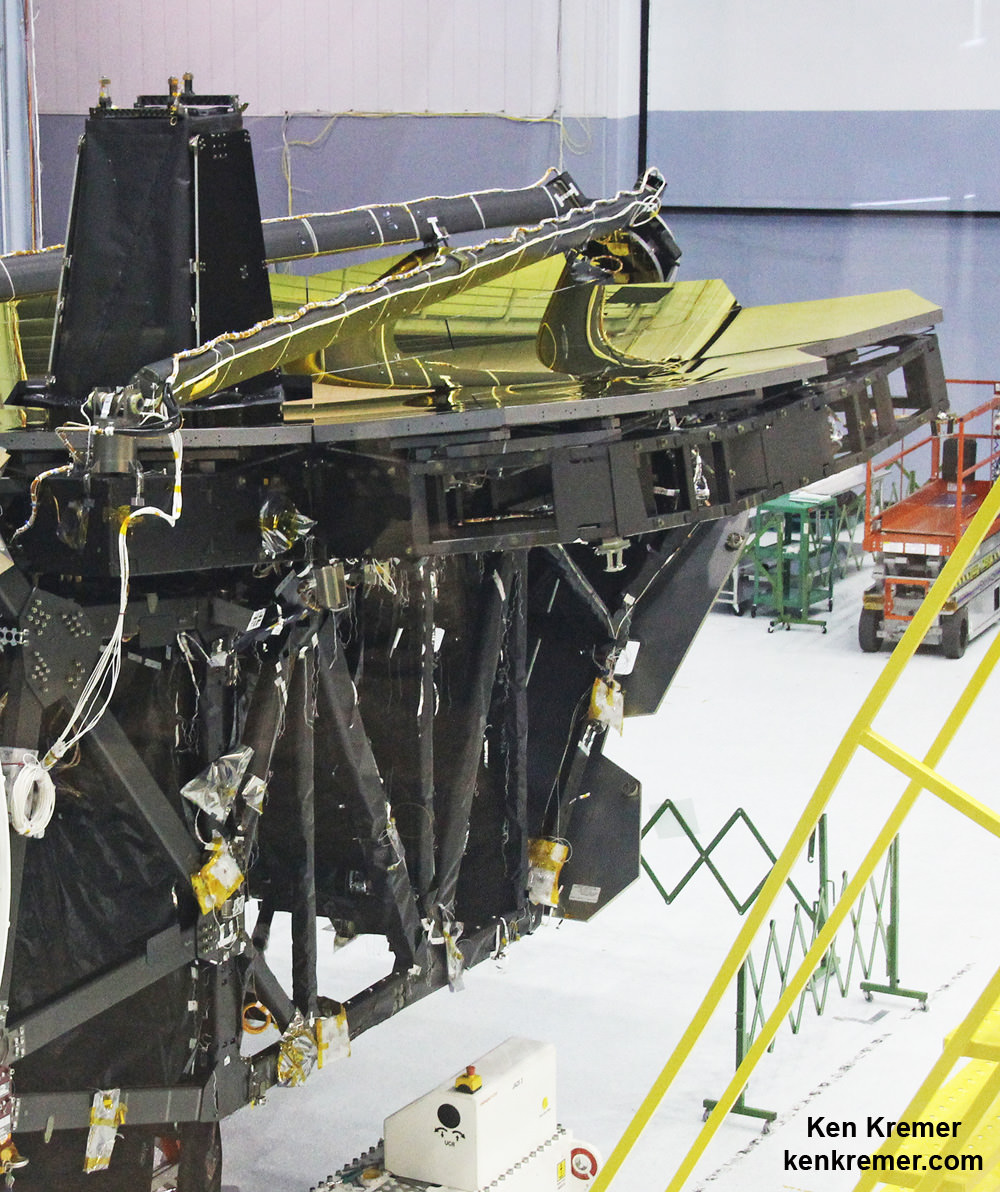

Everything proceeded according to the meticulously choreographed schedule.
“The mirror installation went exceeding well,” Durning told Universe Today.
“We have maintained our schedule the entire time for installing all 18 primary mirror segments. Then the center section, which is the cone in the center, comprising the Aft Optics System (AOS). We installed that two months ago. It went exceedingly well.”
The flight structure and backplane assembly serve as the $8.6 Billion Webb telescopes backbone.
The next step is to install the observatory’s quartet of state-of-the-art research instruments, a package known as the ISIM (Integrated Science Instrument Module), in the truss structure over the next few weeks.
“The telescope is fully integrated and we are now doing the final touches to get prepared to accept the instrument pack which will start happening later this week,” Durning explained.
The integrated optical mirror system and ISIM form Webb’s optical train.
“So we are just now creating the new integration entity called OTIS – which is a combination of the OTE (Optical Telescope Assembly) and the ISIM (Integrated Science Instrument Module) together.”
“That’s essentially the entire optical train of the observatory!” Durning stated.
“It’s the critical photon path for the system. So we will have that integrated over the next few weeks.”
The combined OTIS entity of mirrors, science module and backplane truss weighs 8786 lbs (3940 kg) and measures 28’3” (8.6m) x 8”5” (2.6 m) x 7”10“ (2.4 m).
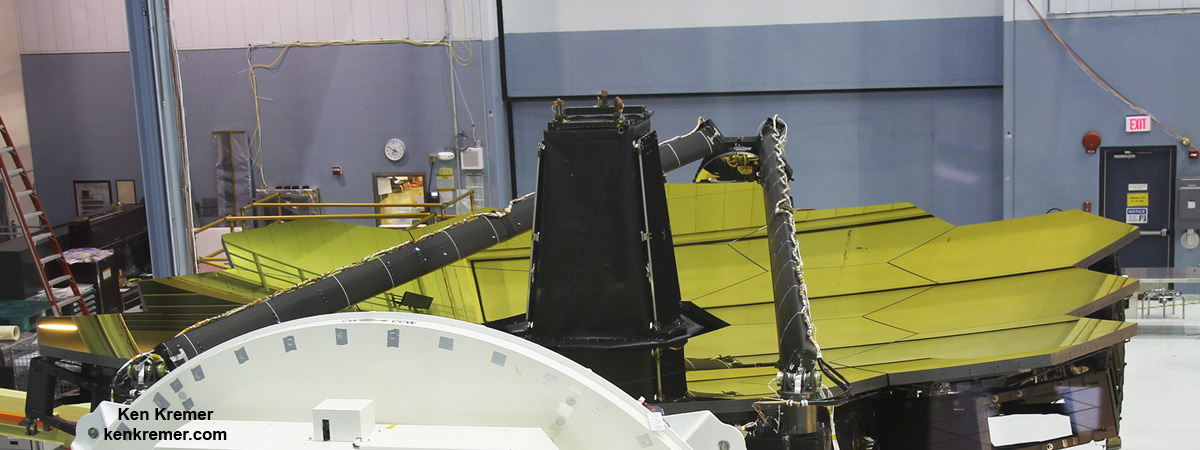

After OTIS is fully integrated, engineers and technicians will spend the rest of the year exposing it to environmental testing, adding the thermal blanketry and testing the optical train – before shipping the huge structure to NASA’s Johnson Space Center.
“Then we will send it to NASA’s Johnson Space Center (JSC) early next year to do some cryovac testing, and the post environmental test verification of the optical system,” During elaborated.
“In the meantime Northrup Grumman is finishing the fabrication of the sunshield and finishing the integration of the spacecraft components into their pieces.”
“Then late in 2017 is when the two pieces – the OTIS configuration and the sunshield configuration – come together for the first time as a full observatory. That happens at Northrup Grumman in Redondo Beach.”
Webb’s optical train is comprised of four different mirrors. We discussed the details of the mirrors, their installation, and testing.
“There are four mirror surfaces,” Durning said.
“We have the large primary mirror of 18 segments, the secondary mirror sitting on the tripod above it, and the center section looking like a pyramid structure [AOS] contains the tertiary mirror and the fine steering mirror.”
“The AOS comes as a complete package. That got inserted down the middle [of the primary mirror].”
Each of the 18 hexagonal-shaped primary mirror segments measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). They are made of beryllium, gold coated and about the size of a coffee table.
In space, the folded mirror structure will unfold into side by side sections and work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror, unprecedented in size and light gathering capability.
The lone rounded secondary mirror sits at the top of the tripod boom over the primary.
The tertiary mirror and fine steering mirror sit in the Aft Optics System (AOS), a cone shaped unit located at the center of the primary mirror.
“So how it works is the light from the primary mirror bounces up to the secondary, and the secondary bounces down to the tertiary,” Durning explained.
“And then the tertiary – which is within that AOS structure – bounces down to the steering mirror. And then that steering mirror steers the beams of photons to the pick off mirrors that sit below in the ISIM structure.”
“So the photons go through that AOS cone. There is a mask at the top that cuts off the path so we have a fixed shape of the beam coming through.”
“It’s the tertiary mirror that directs the photons to the fine steering mirror. The fine steering mirror then directs it [the photons] to the pick off mirrors that sit below in the ISIM structure.”
So the alignment between the AOS system and the telescopes primary and secondary mirrors is incredibly critical.
“The AOS tertiary mirror catches the light [from the secondary mirror] and directs the light to the steering mirror. The requirements for alignment were just what we needed. So that was excellent progress.”
“So the entire mirror system is checked out. The system has been integrated and the alignment has been checked.”
Webb’s golden mirror structure was tilted up for a very brief period this week on May 4 as seen in this NASA time-lapse video:
The 18-segment primary mirror of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope was raised into vertical alignment in the largest clean room at the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, on May 4, 2016. Credit: NASA
The gargantuan observatory will significantly exceed the light gathering power of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope (HST) – currently the most powerful space telescope ever sent to space.
With the mirror structure complete, the next step is ISIM science module installation.
To accomplish that, technicians carefully moved the Webb mirror structure this week into the clean room gantry structure.
As shown in this time-lapse video we created from Webbcam images, they tilted the structure vertically, flipped it around, lowered it back down horizontally and then transported it via an overhead crane into the work platform.
Time-lapse showing the uncovered 18-segment primary mirror of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope being raised into vertical position, flipped and lowered upside down to horizontal position and then moved to processing gantry in the largest clean room at the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, on May 4/5, 2016. Images: NASA Webbcam. Time-lapse by Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com/Alex Polimeni
The telescope will launch on an Ariane V booster from the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana in 2018.
The Webb Telescope is a joint international collaborative project between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
Webb is designed to look at the first light of the Universe and will be able to peer back in time to when the first stars and first galaxies were forming. It will also study the history of our universe and the formation of our solar system as well as other solar systems and exoplanets, some of which may be capable of supporting life on planets similar to Earth.
More about ISIM in the next story.
Watch this space for my ongoing reports on JWST mirrors, science, construction and testing.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
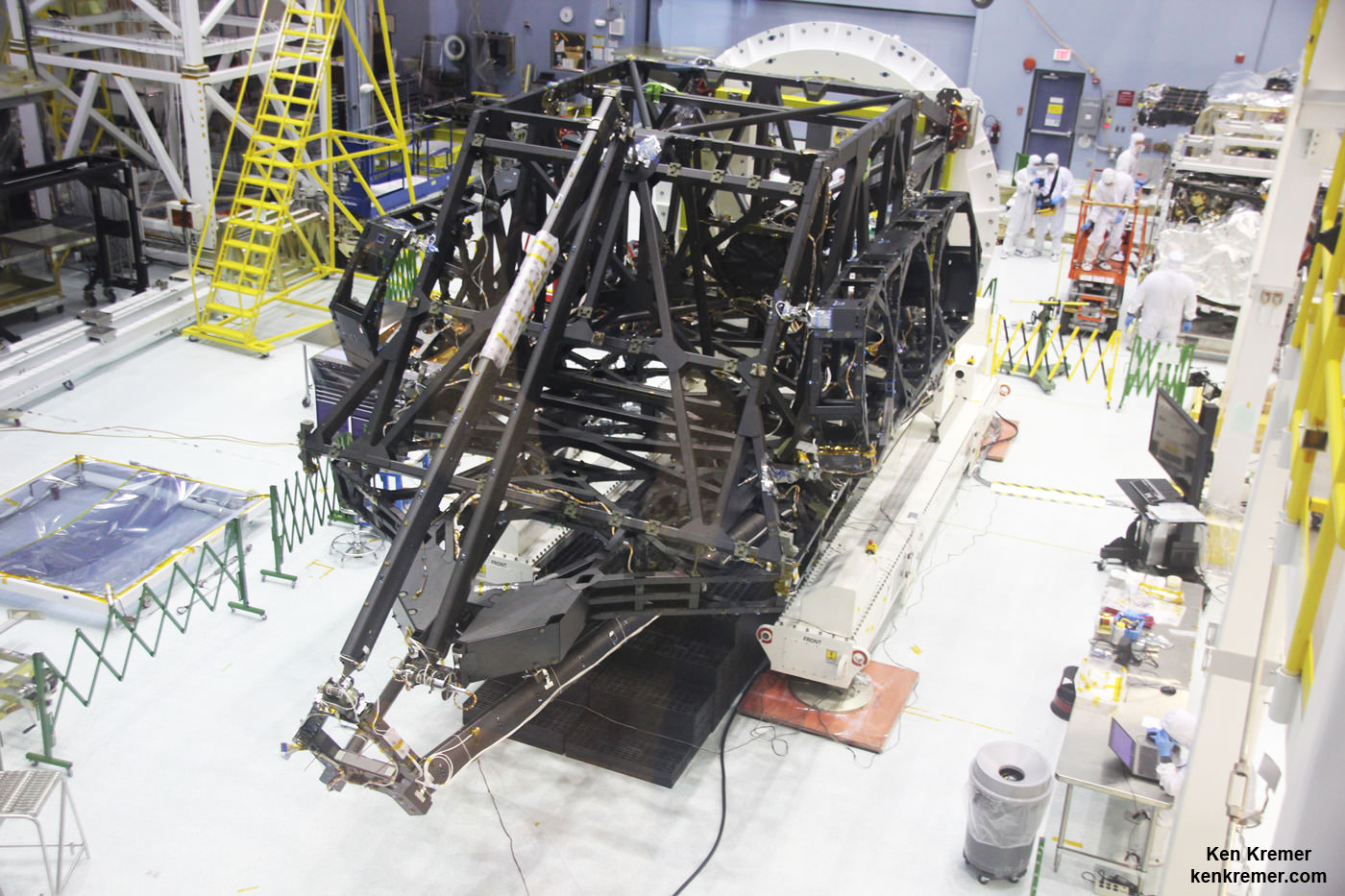
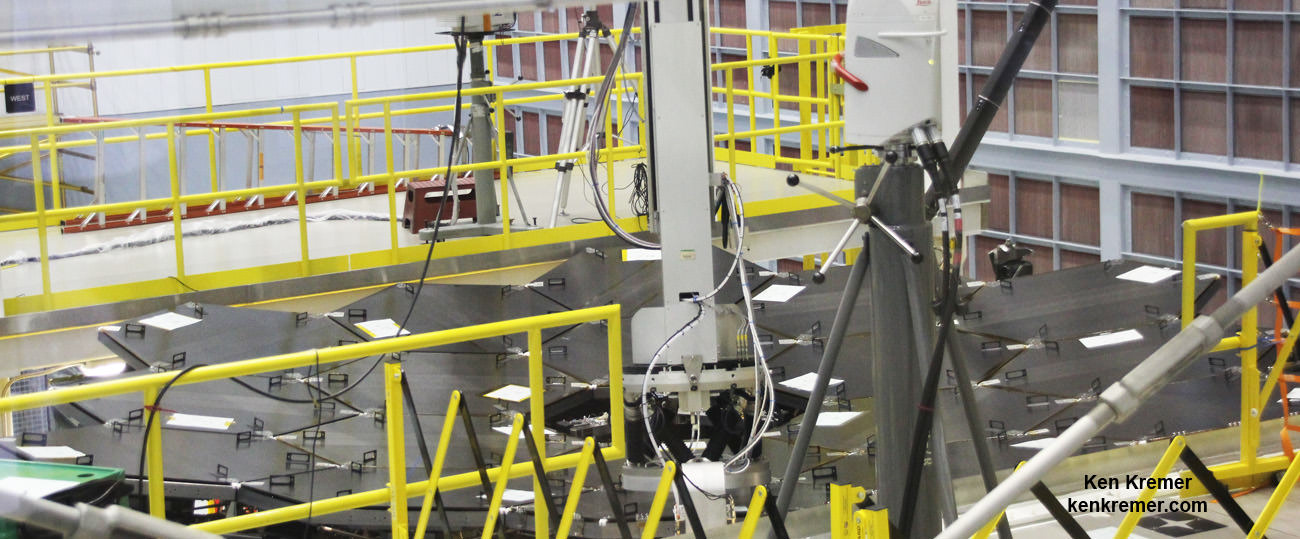



Image Credit: NASA/JPL