[/caption]
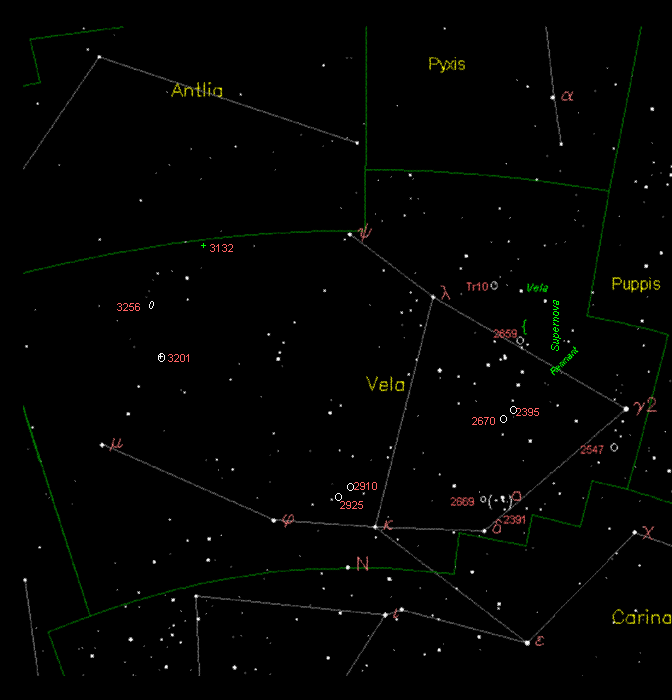
The constellation of Vela is located south of the ecliptic plane and was once part of the much larger constellation of Argo Navis – now divided into three parts. It is now abbreviated and Vela represents the “sails”. Vela encompasses 500 square degrees of sky, ranking 32nd in constellation size. It has 5 main stars in its asterism and 50 Bayer Flamsteed designated stars within its confines. Vela is bordered by the constellations of Antlia, Pyxis, Puppis, Carina and Centaurus. It is visible to all observers located at latitudes between +30° and ?90° and is best seen at culmination during the month of March.
There are three annual meteor showers associated with Vela. The first is the Gamma Velids which peak on or about the night of January 6/7 of each year. At maximum, this stream produces about 8 meteors per hour average. The second is the Delta Velids, which peak on or about February 15 of each year. This is a weak stream with the radiant near Delta and viewers can expect to only see about one meteor per hour on the average. The last is the Puppid-Velid meteor shower, which begins activity on or about December 1 and lasts through around December 15 of each year. The expected date of maximum activity usually occurs on or about December 6 and the complex meteoroid stream can produce up to 10 faint meteors per hour on the average. Most Puppid-Velid meteors are quite faint, but occasionally produce bright fireballs. This particular shower is best viewed just before dawn.
While Vela has no real mythology associate with it since it wasn’t visible to the ancient Greeks and Romans, it does have some very lovely tales and a fascinating history. Argo Navis (or simply Argo) was a large southern constellation representing the Argo, the ship used by Jason and the Argonauts in Greek mythology. The Argo was built by the shipwright Argus, and its crew were specially protected by the goddess Hera. The best source for the myth is the Argonautica by Apollonius Rhodius. According to a variety of sources of the legend, the Argo was said to have been planned or constructed with the help of Athena. According to other legends it contained in its prow a magical piece of timber from the sacred forest of Dodona, which could speak and render prophecies. After the successful journey, the Argo was consecrated to Poseidon in the Isthmus of Corinth. It was then translated into the sky and turned into the constellation of Argo Navis. The name “Vela” is Latin for the sails of a ship!
Now, let us set sail on a binocular tour of Vela as we begin with its largest object, the Vela Supernova Remnant. Located some 800 light years away from Earth and formed about 11,000-12,300 years ago, this shredded curtain of interstellar medium is the result of a gigantic explosion of a star in a supernova – and explosion so massive it covers a full 8 degrees of sky! When it comes to this area, though, the spherical, expanding shock wave is most visible only in X-rays – but don’t stop scanning around. Spanning over distance of 100 light years of space, you’ll find threads of nebulosity, filamentary structure and gigantic shock formations in visible light, too.
Take a look with your binoculars on the northern edge for open cluster Trumpler 10 (RA 08: 47 42 Dec -42: 27 00). Chances are this magnitude 4, widely scattered stellar beauty was first discovered by Nicholas Lacaille in 1751 when he was first cataloging the southern skies. At around 47 million years old and about 1100 light-years distant, this region has been studied for galactic fountains and their connection with high and intermediate velocity clouds, as well as isolated cooling neutron stars and blue straggler stars in open star clusters!
Further along the Vela Supernove Remnant on the central eastern edge is galactic star cluster NGC 2659 (RA 8 : 42.6 Dec -44 : 57). This magnitude 8, Astronomical League’s Southern Sky Binocular Challenge is a nice compression of stars to large binoculars and well resolved to a small telescope. The brightest members of NGC 2659 are unevolved B and A0 stars, and the cluster may also contain an A0 giant star.
Now turn your attention to Delta Velorum – the “8” symbol on our chart. Delta is the second brightest star here and the brightest star in the night sky that doesn’t have a proper name. Located about 80 light years from our solar system, Delta is a system of its own. That’s right… a multiple star system! This class A1 dwarf is at least triple star, and may be quintuple. Both the A and B stars are easily separated in a telescope – and the A (primary) star is also a spectroscopic binary star. Look about an arc minute away for two more – a pair of faint, disparate red dwarf stars.
Get your binoculars back out and hop north for the huge, open galactic star cluster IC 2391 (RA 8 : 40.2 Dec -53 : 04). Also known as the “Omicron Velorum Cluster”, this magnitude 2.5 stellar jewel box was first described by Al Sufi about 964 AD while Louis de Lacaille found it independently on February 11, 1752. Containing about 30 or so stars which are easily resolved in a telescope, this treat is also on the Astronomical League’s Southern Sky Binocular Club list as well as being a Caldwell object, too.
Keeping to a low power, wide field view – such as small binoculars or a rich field telescope, will help you to spot nearby open star cluster NGC 2669 (RA 8 : 44.9 Dec -52 : 58), too. At magnitude 6, this area will stand out as a small compression of the starfield that isn’t quite as interesting as its splashy neighbor, but it is on the AL Southern Sky Telescopic Club challenge list. Be sure to take a look, because it has been highly studied for proper motions.
Keep binoculars handy to split optical double star Gamma 1 and Gamma 2. The dimmer of the pair – Gamma 1 – is named Suhail, and is jokingly referred to as Regor. Is it special? You bet. Because it has some very unusual pattern in its stellar spectral signature, Suhail is also known as the “Spectral Gem of Southern Skies” because it contains bright emission lines instead of dark absorption lines. But don’t stop with just binoculars – use a telescope, too! Brighter Gamma 2 is actually a spectroscopic binary star composed of a blue supergiant and the heaviest known, massive Wolf-Rayet star discovered to date. The binary companion is a blue-white B-type subgiant star which can be separated from the Wolf-Rayet binary easily with binoculars!
Let’s head south for star cluster NGC 2547 (RA 8 : 10.7 Dec -49 : 16). This magnitude 4.7 gathering of stars spans a handsome 20 arc minutes and was discovered by Abbe Lacaille in 1751. Also known as Dunlop 410, Melotte 84 and Collinder 177, the area has been the target of the Spitzer Space Telescope for some very interesting things – like M dwarf debris disk candidates! According to research done by Jan Forbrich (et al): “With only six known examples, M-dwarf debris disks are rare, even though M dwarfs constitute the majority of stars in the Galaxy. After finding a new M dwarf debris disk in a shallow mid-infrared observation of NGC 2547, we present a considerably deeper Spitzer-MIPS image of the region, with a maximum exposure time of 15 minutes per pixel. Among sources selected from a previously published membership list, we identify nine new M dwarfs with excess emission at 24 micron tracing warm material close to the snow line of these stars, at orbital radii of less than 1 AU. We argue that these are likely debris disks, suggesting that planet formation is under way in these systems. Interestingly, the estimated excess fraction of M stars appears to be higher than that of G and K stars in our sample.” Wow… An open cluster that might have planet candidates in it!
Now, star hop north for galactic cluster NGC 2670 (RA 8 : 45.5 Dec -48 : 47). Near magnitude 8, this UFO-shaped configuration of stars is part of the Astronomical League’s Southern Sky Binocular Club and Deep Sky binocular observing list. It has been well studied for mass loss of its stars in the red giant star stage and will appear as a thin streak in small aperture.
Head northeast for open star cluster NGC 2910 (RA 9 : 30.4 Dec -52 : 54). This magnitude 7 beauty is also a Astronomical League’s Southern Sky Binocular Club object and part of the Deep Sky binocular observing list. It was discovered by John Herschel on April 10, 1834 and has been the target for study for triggered star formation.
Let’s go to the telescope to study globular cluster NGC 3201 (RA 10 : 17.6 Dec -46 : 25). Discovered by James Dunlop on May 28, 1826, this magnitude 7 globular is easy for a telescope of any size, and larger aperture will fully resolve the loose structure on this one. Known as a low galactic latitude globular cluster, the population of stars isn’t very high – and it was fully resolved by the Hubble Space Telescope!
Keep the telescope out as we hop north for galaxy NGC 3256 (RA 10 : 27.8 Dec -43 : 54). At magnitude 11 and spanning 3 arc minutes – this is one impressive little peculiar galaxy. NGC 3256 belongs to the Hydra-Centaurus galaxy supercluster complex – but what you see here is the remains of a galaxy collision that occurred long ago. In our backyard telescopes, we can see two distinct nucleus regions, but the Hubble Space Telescope was able to resolve out intricate filaments of dark dust, unusual tidal tails of stars – the result of a huge, galaxy interaction that’s still occurring!
Last, but not least, let’s make run for the border… the Antila border! Our target is NGC 3132 (RA 10 : 07.0 Dec -40 : 26), better known as the “Eightburst Planetary” or “Southern Ring Nebula”. At magnitude 8 you can make out planetary nebula signature with binoculars, but you’ll need at least a mid-sized telescope to begin to see any details. Only slightly larger than Jupiter in apparent size in the eyepiece, the Eightburst resides about 2,000 light years from our Sun and contains two central stars – one of 10th magnitude, the other 16th. Yep. A planetary nebula formed from a binary star! So who is responsible for the nebula shell we’re seeing? The fainter, white dwarf star. It is now smaller than our own Sun, but extremely hot – its flood of ultraviolet radiation igniting the region in the ghostly glow we can see!
Sources:
Wikipedia
SEDS
Chandra Observatory
Chart courtesy of Your Sky.