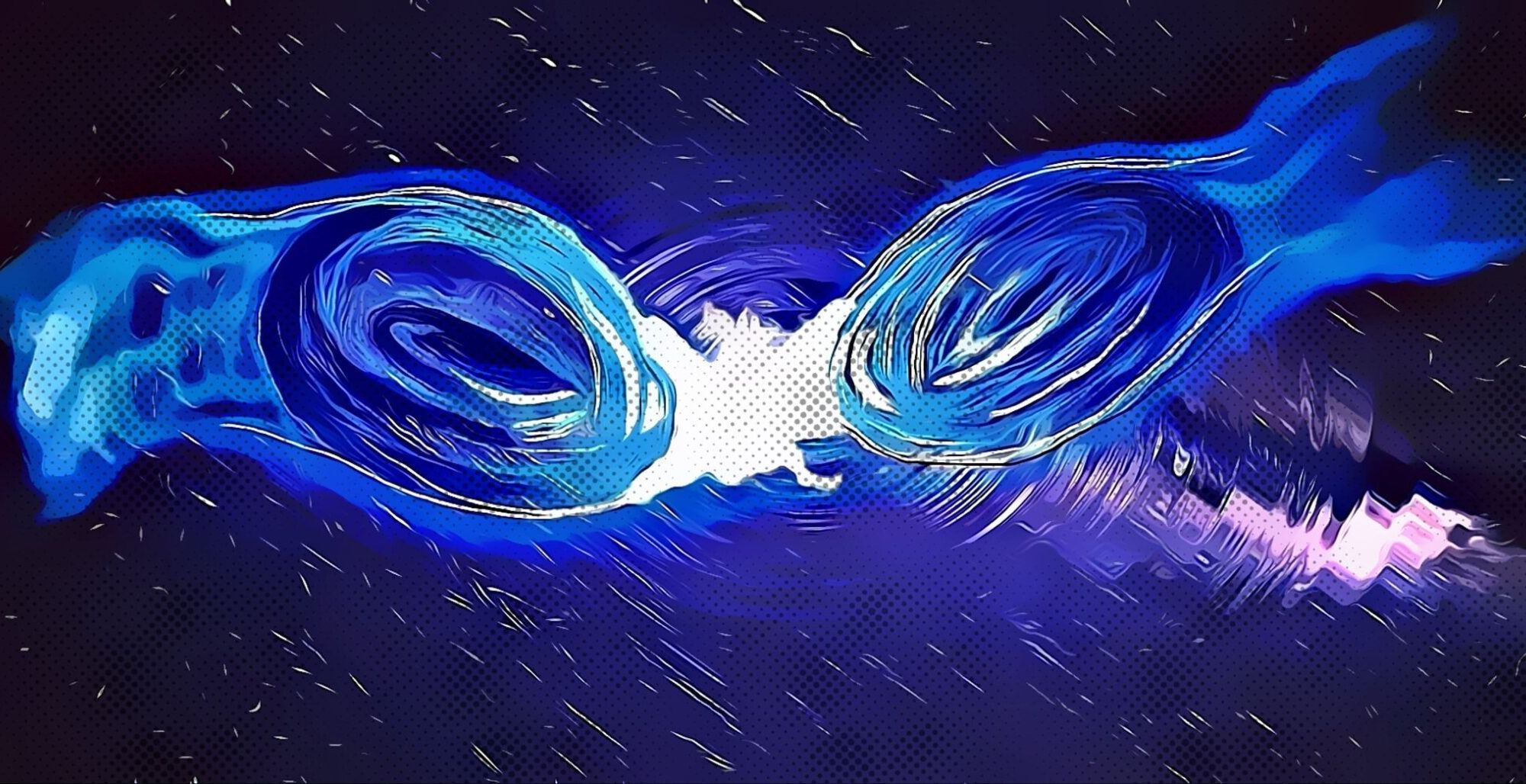
A team of theoretical physicists have discovered a strange structure in space-time that to an outside observer would look exactly like a black hole, but upon closer inspection would be anything but: they would be defects in the very fabric of the universe.
Continue reading “Black Holes Might be Defects in Spacetime”This Star Might be Orbiting a Strange “Boson Star”
A team of astronomers has claimed that observations of a sun-like star orbiting a small black hole might actually be the indication of something far more exotic – the existence of a boson star, a star composed entirely of dark matter.
Continue reading “This Star Might be Orbiting a Strange “Boson Star””Perseverance Finds an Ancient, Fast Flowing River
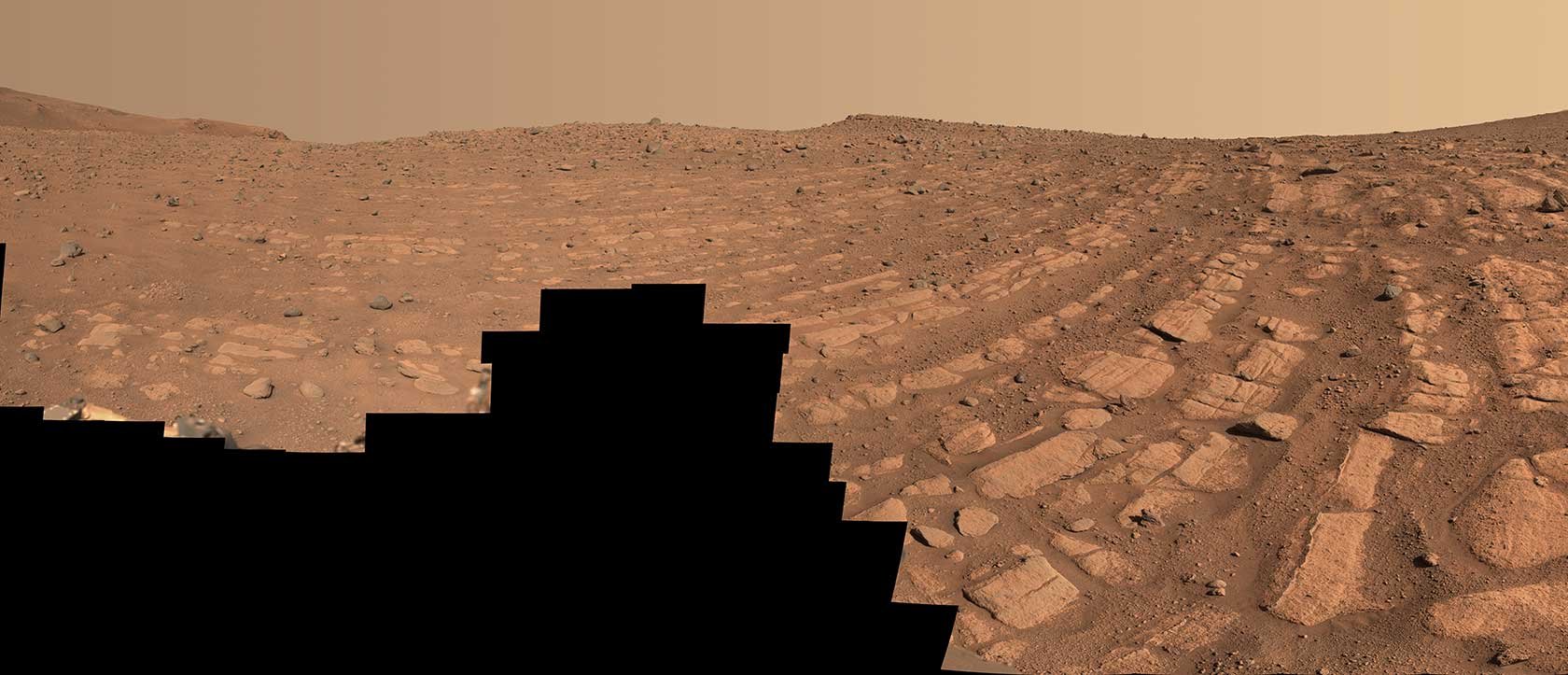
In a first for Martian water science, NASA’s Perseverance rover has discovered geological evidence of a large, fast-moving river in Mars’ ancient past. The high-energy river once emptied into Jezero crater, which the rover has been exploring since early 2021, and is a totally different water system than anything seen previously on the red planet.
Continue reading “Perseverance Finds an Ancient, Fast Flowing River”JWST Looks at the Atmosphere of a Stormy, Steamy Mini-Neptune
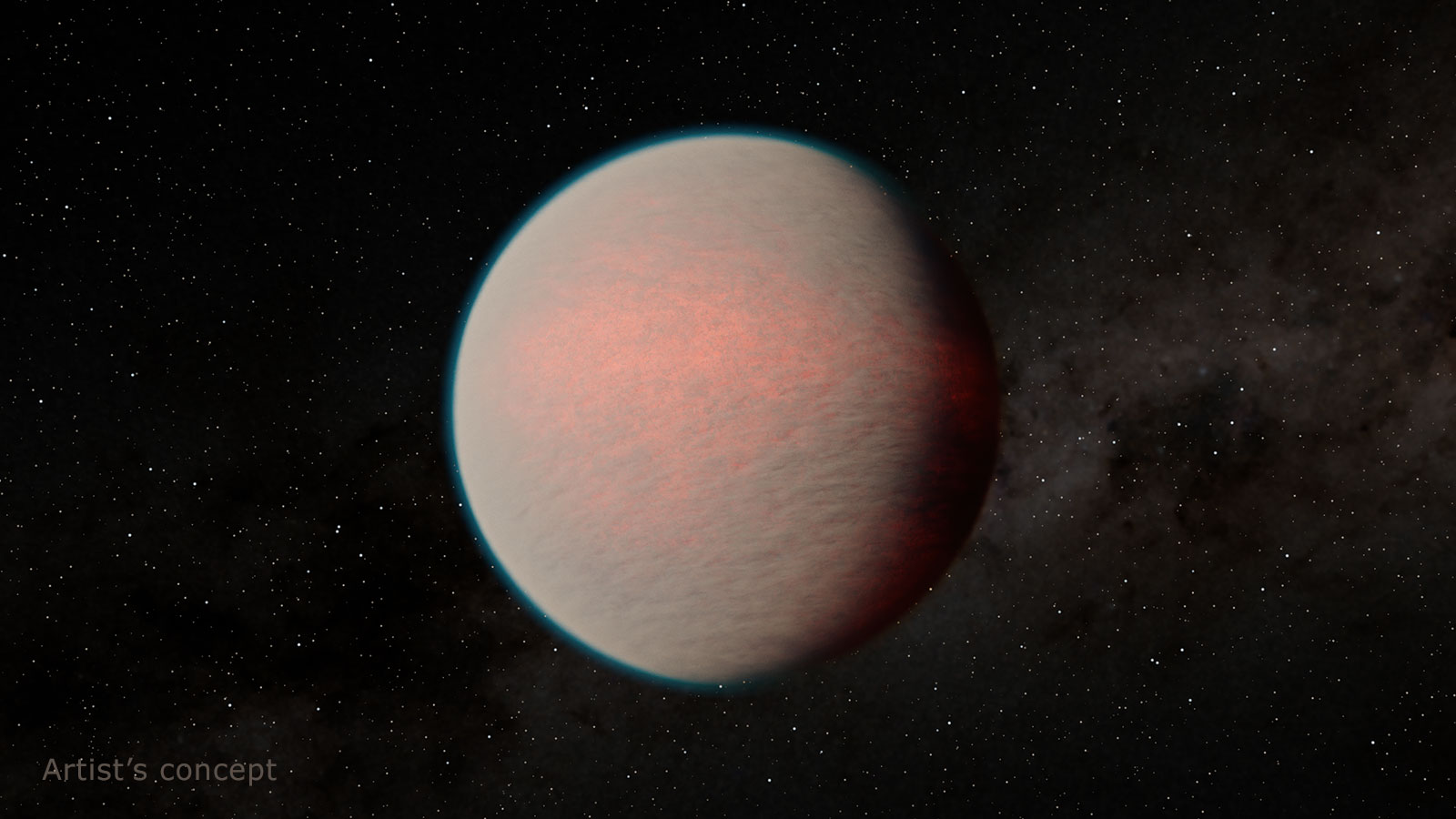
Just because there’s no Mini-Neptune in our Solar System doesn’t mean they’re not common. They appear to be widespread throughout the Milky Way, and according to NASA, are the most common exoplanet type. GJ 1214 b is one of them.
Continue reading “JWST Looks at the Atmosphere of a Stormy, Steamy Mini-Neptune”New Images Reveal the Magnetic Fields in the Horsehead Nebula
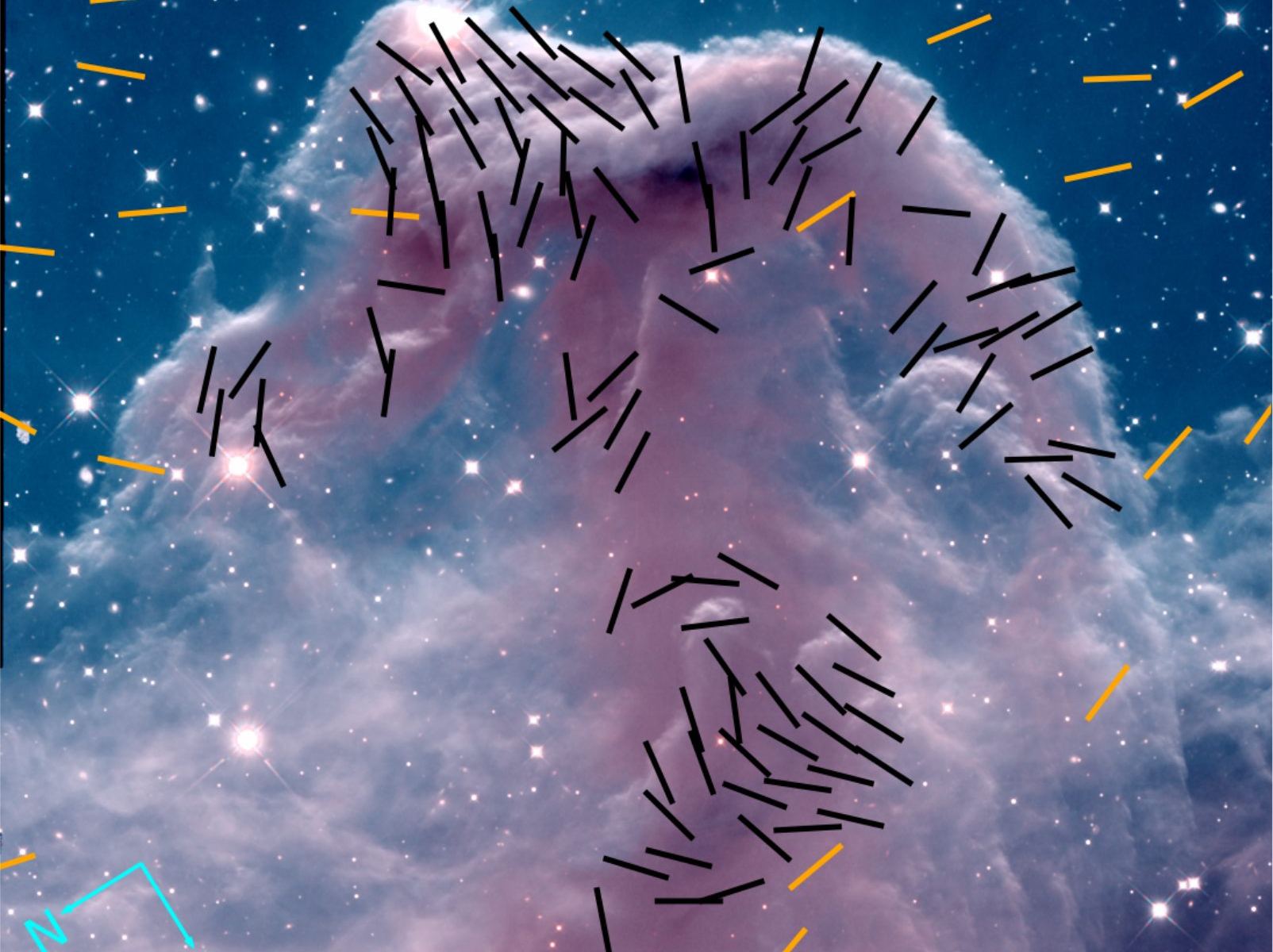

Located near the summit of Maunakea, Hawaii, the 15-meter (~49 ft) James Clerk Maxwell Telescope (JCMT) at the East Asia Observatory (EAO) is the largest telescope in the world designed to operate exclusively in the submillimetre-wavelength. In 2018, Molokai’i High School alumna Mallory Go was awarded time with the JCMT under the Maunakea Scholars program. With the assistance of EAO astronomer Dr. Harriet Parsons, Go obtained unique images of the Horsehead Nebula in polarized light, which revealed the nebula’s magnetic fields.
Continue reading “New Images Reveal the Magnetic Fields in the Horsehead Nebula”It Took Five Years and A Million Images to Make this Atlas of Stellar Nurseries

Star formation is an intricate process governed by a swarm of variables, and it all happens behind a thick veil of dust. Astrophysicists understand it to a certain degree. But this is nature, and nature doesn’t give up its intimate secrets without a concentrated effort.
To learn more about the star formation process, astronomers imaged five star-forming regions in the southern hemisphere with the ESO’s VISTA telescope. It took five years and over one million images, and the result is the VISIONS survey.
Continue reading “It Took Five Years and A Million Images to Make this Atlas of Stellar Nurseries”Dark Matter Can Make Dark Atoms
A team of theoretical astrophysicists have studied in detail a hypothetical form of dark matter that combines to form dark atoms. They found that the existence of dark atoms can drastically affect the evolution of galaxies.
Continue reading “Dark Matter Can Make Dark Atoms”One in Ten Stars Ate a Jupiter (Or Bigger)

In space, cataclysmic events happen to stars all the time. Some explode as supernovae, some get torn apart by black holes, and some suffer other fates. But when it comes to planets, stars turn the tables. Then it’s the stars who get to inflict destruction.
Expanding red giant stars consume and destroy planets that get too close, and a new study takes a deeper look at the process of stellar engulfment.
Continue reading “One in Ten Stars Ate a Jupiter (Or Bigger)”What Does the Milky Way Look Like?
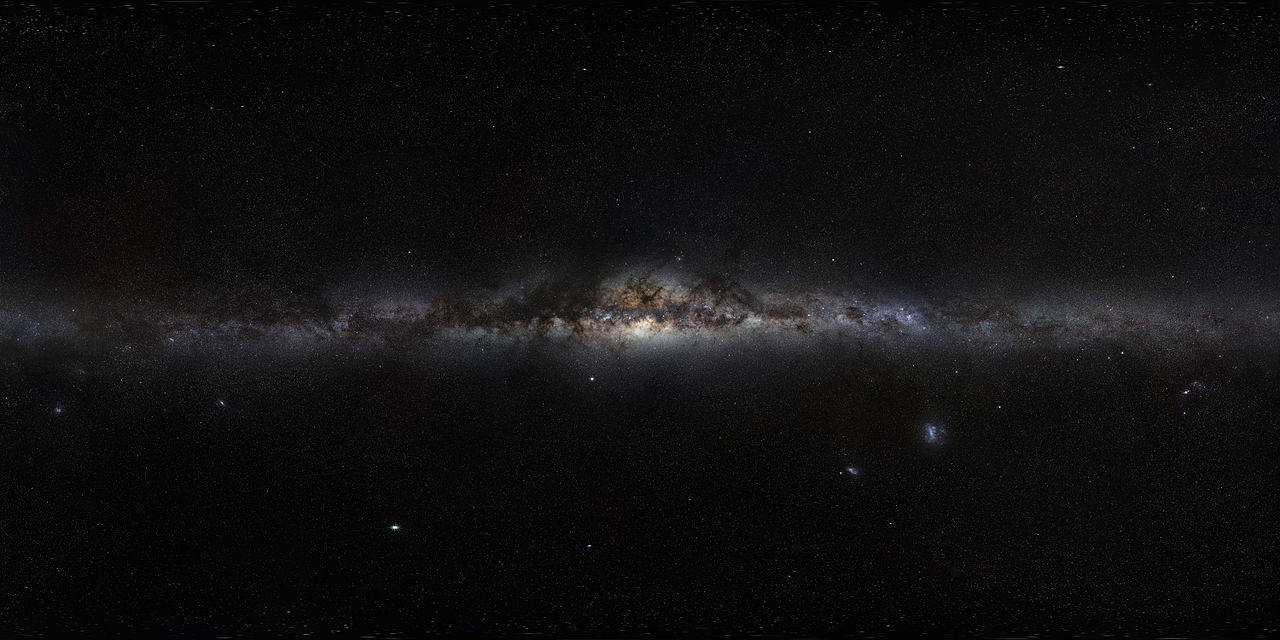
Beginning in 1610, when famed Renaissance polymath Galileo Galilei observed the night sky using a telescope of his own manufacture, astronomers gradually realized that our Solar System is part of a vast collection of stars known today as the Milky Way Galaxy. By the 20th century, astronomers had a good idea of its size and structure, which consisted of a central “bulge” surrounded by an extended disk with spiral arms. Despite all we’ve learned, determining the true morphology of the Milky Way has remained a challenge for astronomers.
Since we, the observers, are embedded in the Milky Way’s disk, we cannot see through the center and observe what’s on the other side. Using various methods, though, astronomers are getting closer to recreating what a “birds-eye” view of the galaxy would look like. For instance, a team of researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) used the precise locations of very young objects in our galaxy (for the first time) to measure the morphology of the Milky Way. This revealed a multiple-arm morphology consisting of two symmetrical arms in the inner region and many irregular ones in the outer region.
Continue reading “What Does the Milky Way Look Like?”Astronomers Watch a Star Gulp Down One of its Planets

A star like our Sun only shines the way it does because of its intrinsic balance. Stars are massive, and the inward gravitational pressure from all that mass acts to contain the outward thermal pressure from all the fusion inside the star. They are in equilibrium, or on the main sequence if you like, and the result is a spherical mass of plasma that holds its shape and emits radiation with relative stability for billions of years. Like our Sun.
But eventually, stars teeter over the edge and lose their balance. Stars like our Sun will expand, take on a malevolent red hue, and begin to destroy anything that comes within their grasp.
Like a planet.
Continue reading “Astronomers Watch a Star Gulp Down One of its Planets”