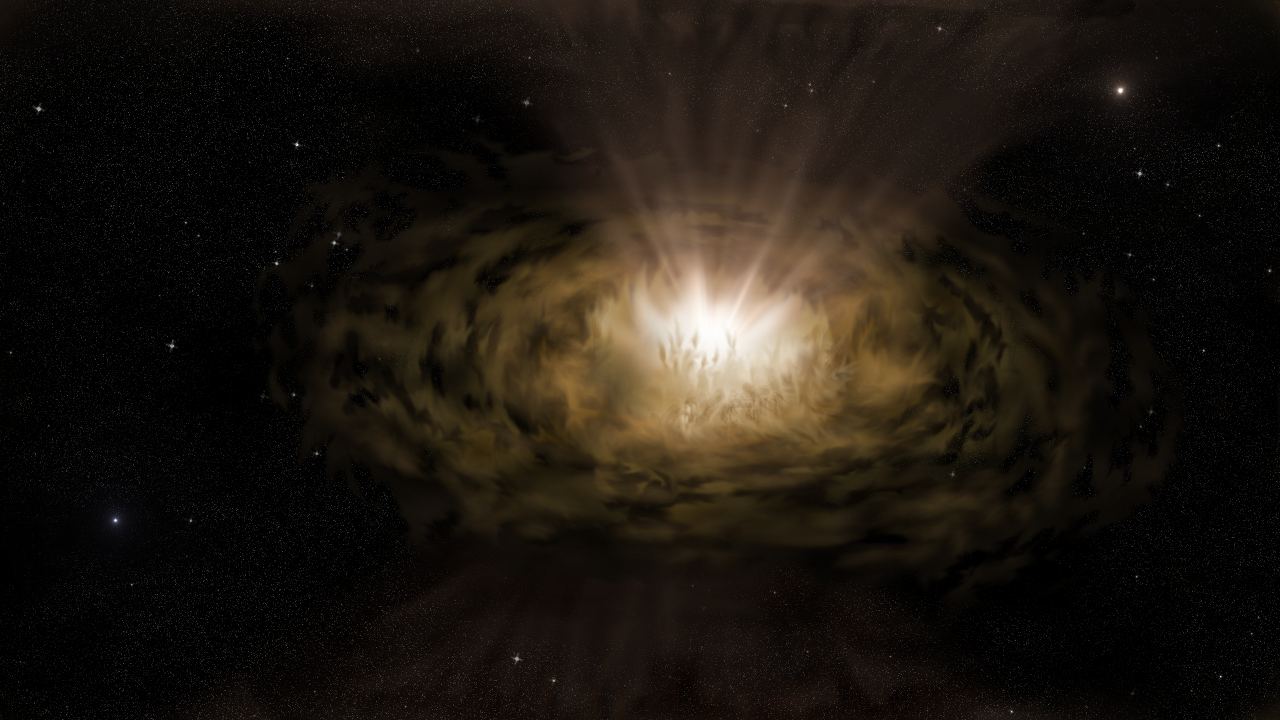
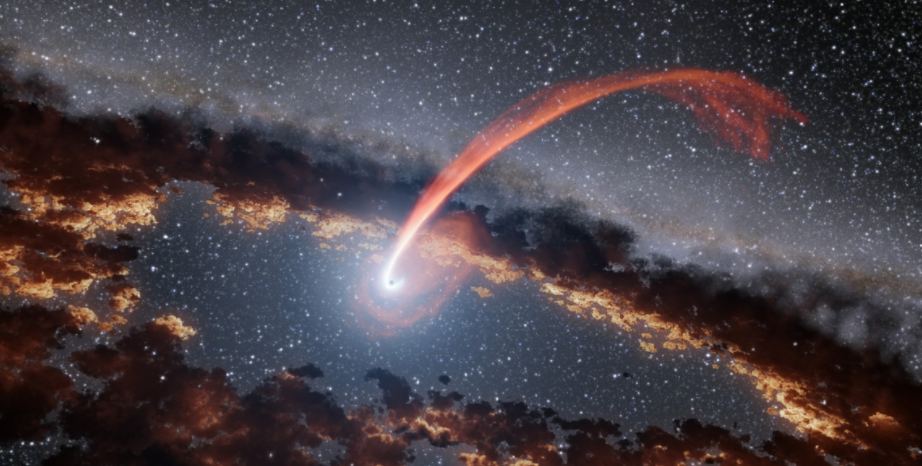
In the 1970s, astronomers discovered that the persistent radio source at the center of our galaxy was a supermassive black hole (SMBH). Today, this gravitational behemoth is known as Sagittarius A* and has a mass roughly 4 million times that of the Sun. Since then, surveys have shown that SMBHs reside at the center of most massive galaxies and play a vital role in star formation and galactic evolution. In addition, the way these black holes consume gas and dust causes their respective galaxies to emit a tremendous amount of radiation from their Galactic Centers.
These are what astronomers refer to as Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN), or quasars, which can become so bright that they temporarily outshine all the stars in their disks. In fact, AGNs are the most powerful compact steady sources of energy in the Universe, which is why astronomers are always trying to get a closer look at them. For instance, a new study led by the University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC) indicates that scientists have substantially underestimated the amount of energy emitted by AGN by not recognizing the extent to which their light is dimmed by dust.
Continue reading “Dust is Hiding how Powerful Quasars Really are”