Space travel presents numerous challenges, not the least of which have to do with astronaut health and safety. And the farther these missions venture from Earth, the more significant they become. Beyond Earth’s protective atmosphere and magnetosphere, there’s the threat of long-term exposure to solar and cosmic radiation. But whereas radiation exposure can be mitigated with proper shielding, there are few strategies available for dealing with the other major hazard: long-term exposure to microgravity.
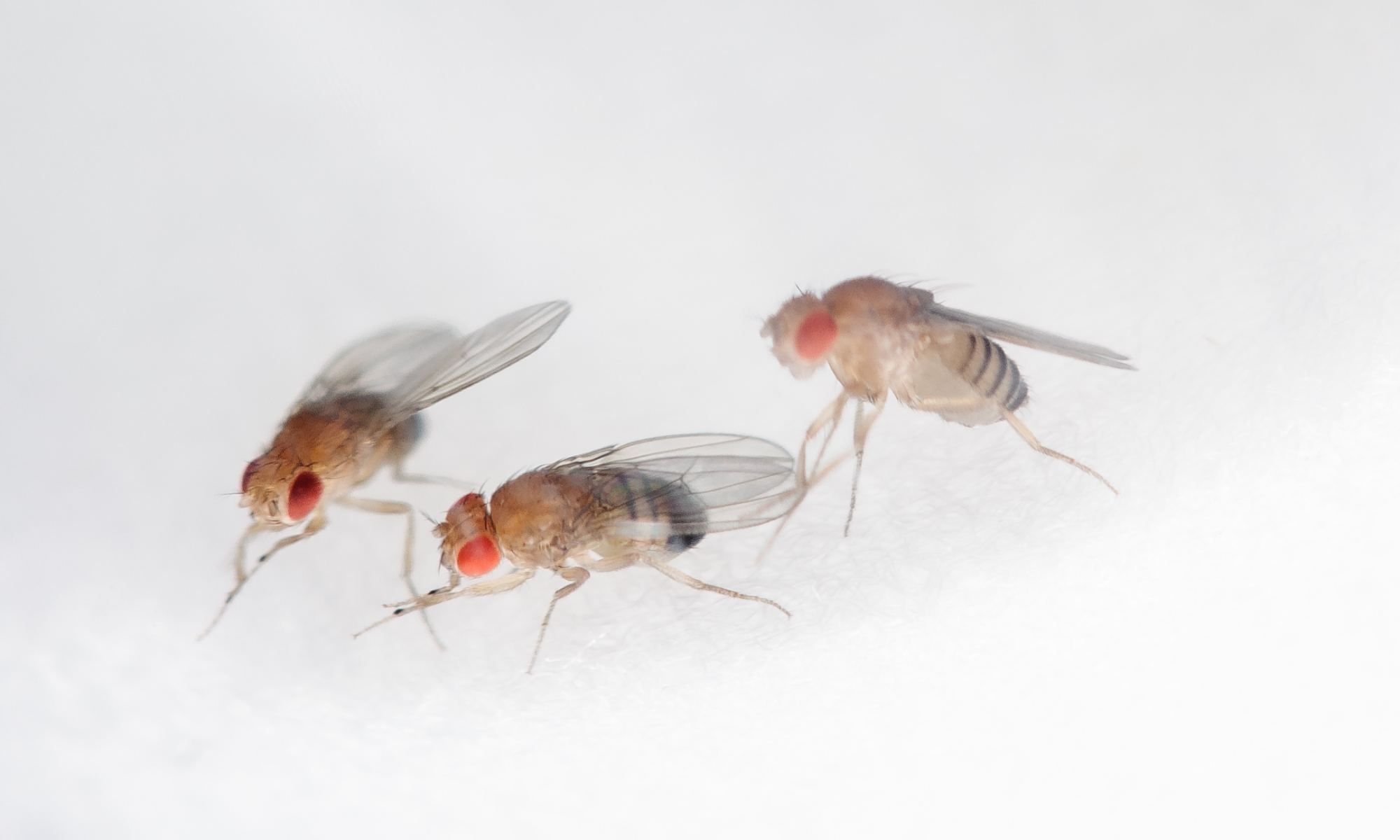
Aboard the International Space Station (ISS), astronauts rely on a strict regimen of exercise and resistance training to mitigate the physiological effects. These include muscle atrophy, bone density loss, organ function, eyesight, and effects on cardiovascular health, gene expression, and the central nervous system. But as a recent NASA study revealed, long-duration missions to Mars and other locations in deep space will need to be equipped with artificial gravity. This study examined the effects of microgravity on fruit flies aboard the ISS and demonstrated artificial gravity provides partial protection against those changes.
Continue reading “Want to Stay Healthy in Space? Then you Want Artificial Gravity”