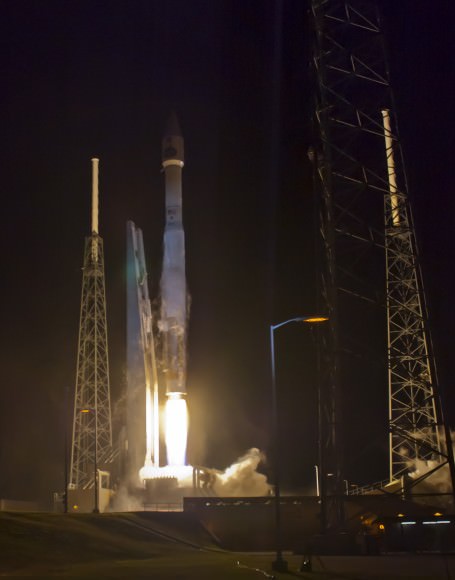
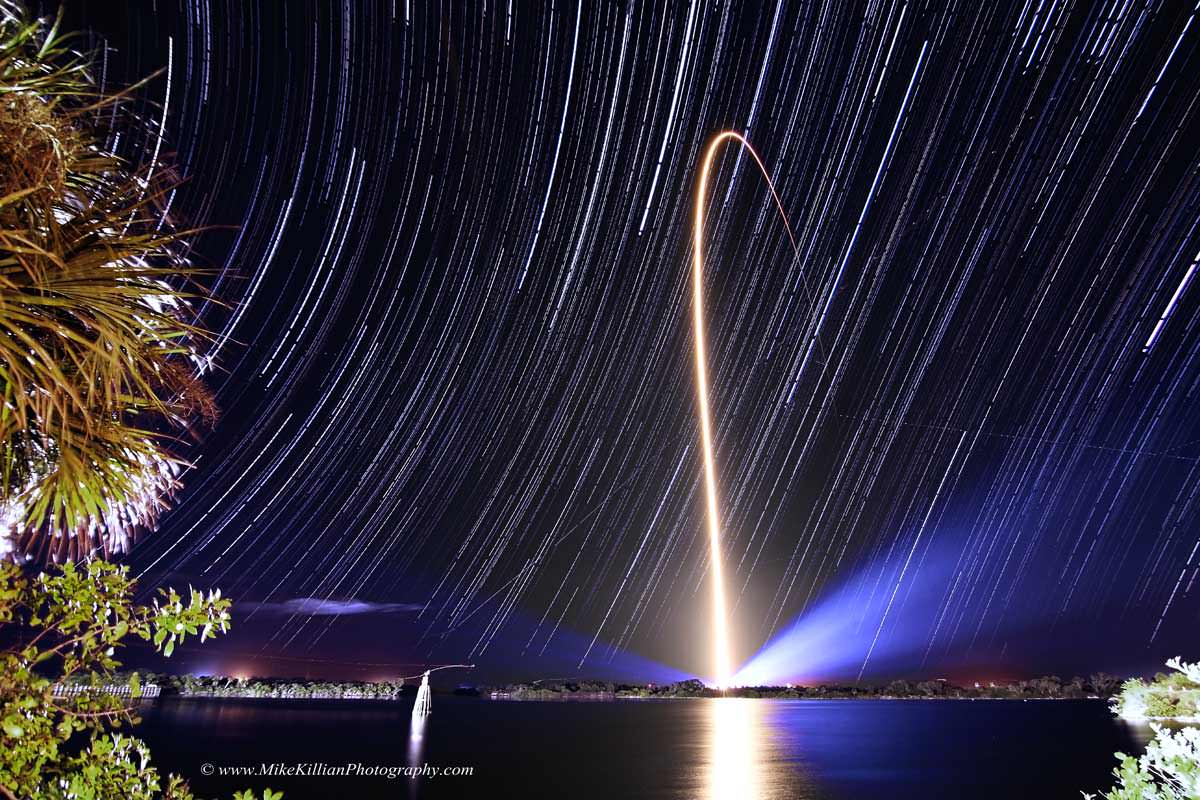
The rotation of the Earth captured in the trails of the stars over Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Jan 23, 2014. NASA’s latest Tracking & Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-L, is seen here hitching a fiery ride to orbit atop an Atlas-V rocket, as viewed from the Turn Basin on Kennedy Space Center just a few miles away. Credit: Mike Killian/www.MikeKillianPhotography.com/AmericaSpace
see Atlas V/TDRS-L Launch Galley below
Story updated[/caption]
Space photographer Mike Killian has captured an absolutely stunning astrophoto of this week’s Atlas V blastoff that innovatively combines astronomy and rocketry – its the streak shot featured above. See additional Atlas launch imagery below – and here.
Mike’s awe inspiring imagery melds Thursday night’s (Jan. 23) spectacular Atlas V liftoff of NASA’s latest Tracking & Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) from Cape Canaveral, Florida, with brilliant star trails, reflecting the Earth’s rotation, moving in the crystal clear dark sky overhead and brilliantly glowing xenons and flaming reflections in the waters beneath.
Update 30 Jan: This fabulous star trails/streak image has been featured as the APOD on Jan 30, 2014.

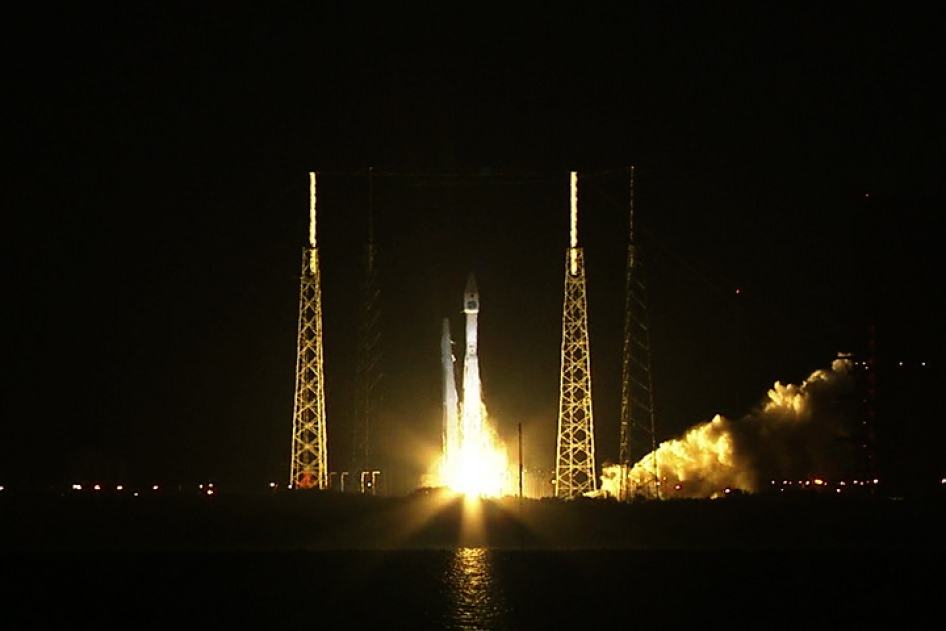
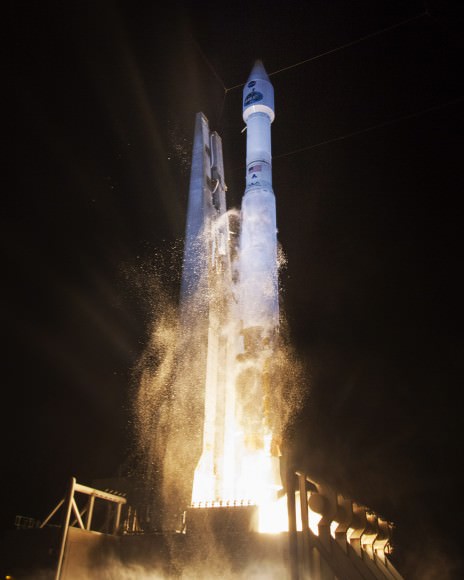
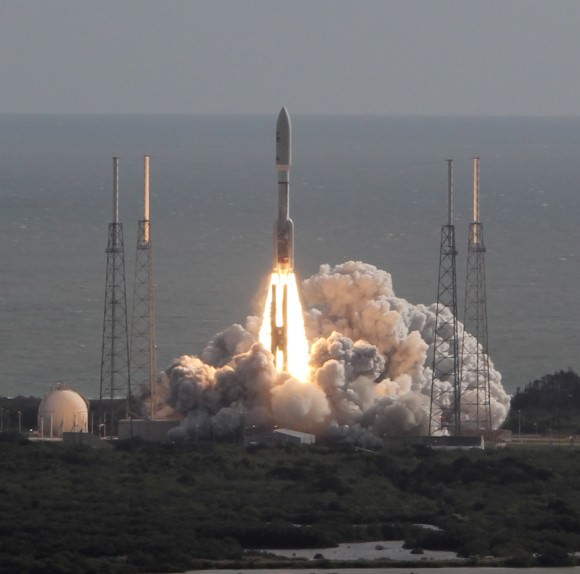
The 3.8 ton TDRS-L communications satellite was successfully delivered by the Atlas V to orbit where it will become an essential member of NASA’s vital network to relay all the crucial science and engineering data from a wide variety of science satellites – including the Hubble Space Telescope and the International Space Station.
The United Launch Alliance Atlas V launched at 9:33 p.m. from Pad 40.
Read my complete Atlas V/TDRS-L launch story – here.
Killian’s very creative image makes it looks as though the fiery rocket plume is slicing and dicing a path though the wandering stars as its thundering off the pad, arcing out over the Atlantic Ocean and soaring on to orbit.
And it’s all perfectly framed – as detailed below in my interview with Mike Killian.

Mike is a space friend of mine and we recently spent launch week together photographing the Jan. 9 Antares rocket launch from NASA’s Wallops Island Flight Facility in Virginia, amidst the bone chilling cold of the Polar Vortex – which by the way has returned! See a photo of us freezing together at NASA Wallops – below!!
See our Antares launch imagery – here and here.
Be sure to enjoy the Atlas V gallery herein including more space photog friends including Jeff Seibert, Alan Walters, Walter Scriptunas II and nasatech.net

Mike’s magnificent new astrophoto was snapped from the Press Site at the Kennedy Space Center – located right next to the world famous countdown clock and the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB).
The two launch sites – NASA Wallops and Cape Canaveral/NASA Kennedy Space Center – sit about 800 miles apart on the US East Coast.
His stunning new astrophoto was several years in the making and the result of rather careful planning and of course some good luck too.
Mike is a very experienced and exceptionally talented and accomplished photographer in general.
So for the benefit of Universe Today readers, I asked Mike to describe how he planned, executed and processed the fabulous Jan. 23 star trail/Atlas launch photo.
“I’ve wanted to attempt this shot for 2 years now & finally the conditions for it came together Thursday night – no moonlight, no clouds, barely a breeze, mostly dry air & enough TIME between sunset and liftoff to capture some descent star trails,” Mike Killian told me.
What was the shooting time and equipment involved?
“Approximate total shooting time was about 3 hours, 380 20-second exposures @ ISO 400, shot with a Canon T4i w/ a 11-16mm Tokina 2.8 lens,” said Killian.
“For the launch I adjusted those setting for the rocket’s bright flame, did that exposure, then took the images and stacked using Photoshop. All images are the exact same framing.”
Killian took the photos from right along the edge of the water basin at the Press Site at the Kennedy Space Center, located right next to the VAB where NASA’s Saturn V Moon rockets and Space Shuttles were processed for launch.
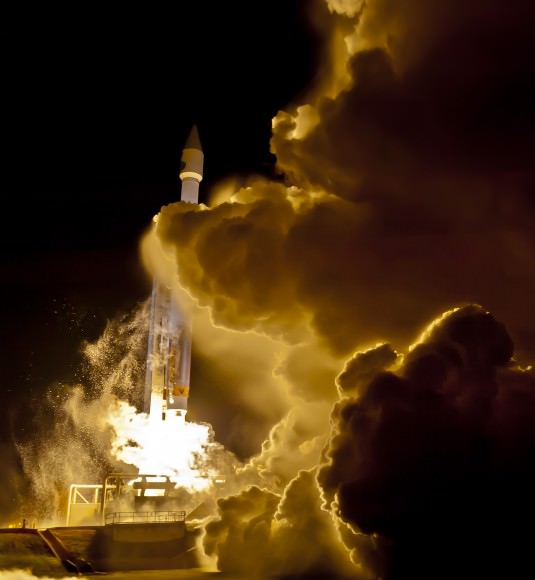

Why shoot from Kennedy Space Center instead of Cape Canaveral?
“I chose to shoot from the water’s edge at Turn Basin mainly because of the water, I always like a nice reflection from the xenon lights and the launch itself.
“Plus I knew nobody would shoot from there, as both the VAB roof & Cape Canaveral were available for media to view from (both have fantastic views).”
“I wanted to do something different.”
“Generally we get an hour or so at whatever area we are shooting any given launch from, before heading back to the press site.”
“But since the Turn Basin is AT the press site, the location was open for several hours due to TDRS-L being a night launch.”
“So I had enough time to attempt this shot from about as close as you can get (4 miles or so)!
Is Mike pleased with the result?
“I’m happy with how this one came out!” Mike ecstatically told me.
For some background on the VAB and the imminent end of public tours inside – read my new VAB story, here.
And here’s my daytime shot showing the Turn Basin and Mike’s approximate shooting location at the KSC Press Site. Mike is shooting in the opposite direction – from waters edge looking to the right.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Orion, Chang’e-3, Orbital Sciences, SpaceX, commercial space, LADEE, Mars and more news.



Spectacular Go Pro TDRS Launch Video by Matthew Travis































![Dream_Chaser_Atlas_V_Integrated_Launch_Configuration[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/Dream_Chaser_Atlas_V_Integrated_Launch_Configuration1-315x580.jpg)